[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
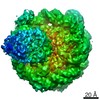
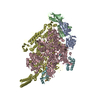
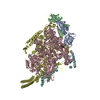
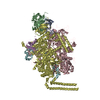
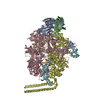
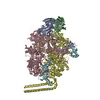
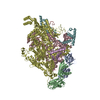
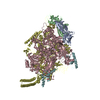
Yorodumi- PDB-6xjd: Two mouse cGAS catalytic domain binding to human assembled nucleosome -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6xjd | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Two mouse cGAS catalytic domain binding to human assembled nucleosome | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM/DNA / Immunity / IMMUNE SYSTEM / IMMUNE SYSTEM-DNA complex | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information2',3'-cyclic GMP-AMP synthase activity / cyclic GMP-AMP synthase / regulation of type I interferon production / paracrine signaling / poly-ADP-D-ribose modification-dependent protein binding / regulation of immunoglobulin production / cGAS/STING signaling pathway / regulation of T cell activation / : / : ...2',3'-cyclic GMP-AMP synthase activity / cyclic GMP-AMP synthase / regulation of type I interferon production / paracrine signaling / poly-ADP-D-ribose modification-dependent protein binding / regulation of immunoglobulin production / cGAS/STING signaling pathway / regulation of T cell activation / : / : / negative regulation of DNA repair / negative regulation of cGAS/STING signaling pathway / cellular response to exogenous dsRNA / regulation of immune response / negative regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / nucleosome binding / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / positive regulation of type I interferon production / positive regulation of defense response to virus by host / CENP-A containing nucleosome / phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / activation of innate immune response / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Interleukin-7 signaling / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / determination of adult lifespan / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / innate immune response in mucosa / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / Defective pyroptosis / Negative Regulation of CDH1 Gene Transcription / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / molecular condensate scaffold activity / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / HDMs demethylate histones / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / RMTs methylate histone arginines / HCMV Early Events / structural constituent of chromatin / positive regulation of cellular senescence / UCH proteinases / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / antibacterial humoral response / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / site of double-strand break / HATs acetylate histones / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / double-stranded DNA binding / gene expression / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / defense response to virus / chromosome, telomeric region / Ub-specific processing proteases / nuclear body / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.8 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Xu, P. / Li, P. / Zhao, B. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2items United States, 2items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: The molecular basis of tight nuclear tethering and inactivation of cGAS. Authors: Baoyu Zhao / Pengbiao Xu / Chesley M Rowlett / Tao Jing / Omkar Shinde / Yuanjiu Lei / A Phillip West / Wenshe Ray Liu / Pingwei Li /  Abstract: Nucleic acids derived from pathogens induce potent innate immune responses. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) is a double-stranded DNA sensor that catalyses the synthesis of the cyclic dinucleotide ...Nucleic acids derived from pathogens induce potent innate immune responses. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) is a double-stranded DNA sensor that catalyses the synthesis of the cyclic dinucleotide cyclic GMP-AMP, which mediates the induction of type I interferons through the STING-TBK1-IRF3 signalling axis. cGAS was previously thought to not react with self DNA owing to its cytosolic localization; however, recent studies have shown that cGAS is localized mostly in the nucleus and has low activity as a result of tight nuclear tethering. Here we show that cGAS binds to nucleosomes with nanomolar affinity and that nucleosome binding potently inhibits its catalytic activity. To elucidate the molecular basis of cGAS inactivation by nuclear tethering, we determined the structure of mouse cGAS bound to human nucleosome by cryo-electron microscopy. The structure shows that cGAS binds to a negatively charged acidic patch formed by histones H2A and H2B via its second DNA-binding site. High-affinity nucleosome binding blocks double-stranded DNA binding and maintains cGAS in an inactive conformation. Mutations of cGAS that disrupt nucleosome binding alter cGAS-mediated signalling in cells. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6xjd.cif.gz 6xjd.cif.gz | 414.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6xjd.ent.gz pdb6xjd.ent.gz | 318.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6xjd.json.gz 6xjd.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xj/6xjd https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xj/6xjd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xj/6xjd ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xj/6xjd | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 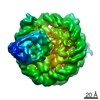 22206MC  6x59C  6x5aC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 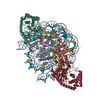
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 5 types, 10 molecules AEBFCGDHKL
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15257.838 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: H3C15, HIST2H3A, H3C14, H3F2, H3FM, HIST2H3C, H3C13, HIST2H3D Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 11263.231 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, ...Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, H4FE, HIST1H4K, H4/D, H4FD, HIST1H4L, H4/K, H4FK, HIST2H4A, H4/N, H4F2, H4FN, HIST2H4, HIST2H4B, H4/O, H4FO, HIST4H4 Production host:  #3: Protein | Mass: 13990.342 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: H2AC11, H2AFP, HIST1H2AG, H2AC13, H2AFC, HIST1H2AI, H2AC15, H2AFD, HIST1H2AK, H2AC16, H2AFI, HIST1H2AL, H2AC17, H2AFN, HIST1H2AM Production host:  #4: Protein | Mass: 13795.980 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: H2BC4, H2BFL, HIST1H2BC, H2BC6, H2BFH, HIST1H2BE, H2BC7, H2BFG, HIST1H2BF, H2BC8, H2BFA, HIST1H2BG, H2BC10, H2BFK, HIST1H2BI Production host:  #7: Protein | Mass: 43647.352 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 45145.754 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
|---|---|
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 45604.047 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 2 molecules 
| #8: Chemical |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | N |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.4 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 700 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 48 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.16_3549: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 6.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 9454 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj











































