[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
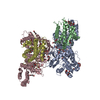
Yorodumi- EMDB-22203: Cryo-EM structure of the sodium leak channel NALCN-FAM155A complex -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-22203 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the sodium leak channel NALCN-FAM155A complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Sharpened map used for model refinement | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ion channel / membrane protein / complex / cysteine rich domain | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of synaptic transmission, cholinergic / leak channel activity / regulation of resting membrane potential / voltage-gated sodium channel activity / sodium channel activity / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / monoatomic ion channel complex / monoatomic cation channel activity / potassium ion transmembrane transport / sodium ion transmembrane transport ...positive regulation of synaptic transmission, cholinergic / leak channel activity / regulation of resting membrane potential / voltage-gated sodium channel activity / sodium channel activity / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / monoatomic ion channel complex / monoatomic cation channel activity / potassium ion transmembrane transport / sodium ion transmembrane transport / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic / calcium ion transmembrane transport / Stimuli-sensing channels / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kschonsak M / Chua HC / Noland CL / Weidling C / Clairfeuille T / Bahlke OO / Ameen AO / Li ZR / Arthur CP / Ciferri C ...Kschonsak M / Chua HC / Noland CL / Weidling C / Clairfeuille T / Bahlke OO / Ameen AO / Li ZR / Arthur CP / Ciferri C / Pless SA / Payandeh J | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Structure of the human sodium leak channel NALCN. Authors: Marc Kschonsak / Han Chow Chua / Cameron L Noland / Claudia Weidling / Thomas Clairfeuille / Oskar Ørts Bahlke / Aishat Oluwanifemi Ameen / Zhong Rong Li / Christopher P Arthur / Claudio ...Authors: Marc Kschonsak / Han Chow Chua / Cameron L Noland / Claudia Weidling / Thomas Clairfeuille / Oskar Ørts Bahlke / Aishat Oluwanifemi Ameen / Zhong Rong Li / Christopher P Arthur / Claudio Ciferri / Stephan Alexander Pless / Jian Payandeh /   Abstract: Persistently depolarizing sodium (Na) leak currents enhance electrical excitability. The ion channel responsible for the major background Na conductance in neurons is the Na leak channel, non- ...Persistently depolarizing sodium (Na) leak currents enhance electrical excitability. The ion channel responsible for the major background Na conductance in neurons is the Na leak channel, non-selective (NALCN). NALCN-mediated currents regulate neuronal excitability linked to respiration, locomotion and circadian rhythm. NALCN activity is under tight regulation and mutations in NALCN cause severe neurological disorders and early death. NALCN is an orphan channel in humans, and fundamental aspects of channel assembly, gating, ion selectivity and pharmacology remain obscure. Here we investigate this essential leak channel and determined the structure of NALCN in complex with a distinct auxiliary subunit, family with sequence similarity 155 member A (FAM155A). FAM155A forms an extracellular dome that shields the ion-selectivity filter from neurotoxin attack. The pharmacology of NALCN is further delineated by a walled-off central cavity with occluded lateral pore fenestrations. Unusual voltage-sensor domains with asymmetric linkages to the pore suggest mechanisms by which NALCN activity is modulated. We found a tightly closed pore gate in NALCN where the majority of missense patient mutations cause gain-of-function phenotypes that cluster around the S6 gate and distinctive π-bulges. Our findings provide a framework to further study the physiology of NALCN and a foundation for discovery of treatments for NALCN channelopathies and other electrical disorders. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
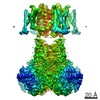
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_22203.map.gz emd_22203.map.gz | 165.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-22203-v30.xml emd-22203-v30.xml emd-22203.xml emd-22203.xml | 21.1 KB 21.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_22203.png emd_22203.png | 40.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-22203.cif.gz emd-22203.cif.gz | 8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_22203_additional.map.gz emd_22203_additional.map.gz | 165 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22203 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22203 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22203 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22203 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6xiwMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_22203.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_22203.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Sharpened map used for model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.824 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: non-sharpened map
| File | emd_22203_additional.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | non-sharpened map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : NALCN in complex with FAM155A
| Entire | Name: NALCN in complex with FAM155A |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: NALCN in complex with FAM155A
| Supramolecule | Name: NALCN in complex with FAM155A / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 Details: NALCN, FAM155A, UNC80 and UNC79 co-expressed and NALCN-FAM155A co-purified |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Sodium leak channel non-selective protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Sodium leak channel non-selective protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: TYR287 modeled with sulfonation (TYS) as the EM density indicates a post-translational modification of this residue. Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 206.341641 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MLKRKQSSRV EAQPVTDFGP DESLSDNADI LWINKPWVHS LLRICAIISV ISVCMNTPMT FEHYPPLQYV TFTLDTLLMF LYTAEMIAK MHIRGIVKGD SSYVKDRWCV FDGFMVFCLW VSLVLQVFEI ADIVDQMSPW GMLRIPRPLI MIRAFRIYFR F ELPRTRIT ...String: MLKRKQSSRV EAQPVTDFGP DESLSDNADI LWINKPWVHS LLRICAIISV ISVCMNTPMT FEHYPPLQYV TFTLDTLLMF LYTAEMIAK MHIRGIVKGD SSYVKDRWCV FDGFMVFCLW VSLVLQVFEI ADIVDQMSPW GMLRIPRPLI MIRAFRIYFR F ELPRTRIT NILKRSGEQI WSVSIFLLFF LLLYGILGVQ MFGTFTYHCV VNDTKPGNVT WNSLAIPDTH CSPELEEGYQ CP PGFKCMD LEDLGLSRQE LGYSGFNEIG TSIFTVYEAA SQEGWVFLM(TYS) RAIDSFPRWR SYFYFITLIF FLAWLVKNV FIAVIIETFA EIRVQFQQMW GSRSSTTSTA TTQMFHEDAA GGWQLVAVDV NKPQGRAPAC LQKMMRSSVF HMFILSMVTV DVIVAASNY YKGENFRRQY DEFYLAEVAF TVLFDLEALL KIWCLGFTGY ISSSLHKFEL LLVIGTTLHV YPDLYHSQFT Y FQVLRVVR LIKISPALED FVYKIFGPGK KLGSLVVFTA SLLIVMSAIS LQMFCFVEEL DRFTTFPRAF MSMFQILTQE GW VDVMDQT LNAVGHMWAP VVAIYFILYH LFATLILLSL FVAVILDNLE LDEDLKKLKQ LKQSEANADT KEKLPLRLRI FEK FPNRPQ MVKISKLPSD FTVPKIRESF MKQFIDRQQQ DTCCLLRSLP TTSSSSCDHS KRSAIEDNKY IDQKLRKSVF SIRA RNLLE KETAVTKILR ACTRQRMLSG SFEGQPAKER SILSVQHHIR QERRSLRHGS NSQRISRGKS LETLTQDHSN TVRYR NAQR EDSEIKMIQE KKEQAEMKRK VQEEELRENH PYFDKPLFIV GREHRFRNFC RVVVRARFNA SKTDPVTGAV KNTKYH QLY DLLGLVTYLD WVMIIVTICS CISMMFESPF RRVMHAPTLQ IAEYVFVIFM SIELNLKIMA DGLFFTPTAV IRDFGGV MD IFIYLVSLIF LCWMPQNVPA ESGAQLLMVL RCLRPLRIFK LVPQMRKVVR ELFSGFKEIF LVSILLLTLM LVFASFGV Q LFAGKLAKCN DPNIIRREDC NGIFRINVSV SKNLNLKLRP GEKKPGFWVP RVWANPRNFN FDNVGNAMLA LFEVLSLKG WVEVRDVIIH RVGPIHGIYI HVFVFLGCMI GLTLFVGVVI ANFNENKGTA LLTVDQRRWE DLKSRLKIAQ PLHLPPRPDN DGFRAKMYD ITQHPFFKRT IALLVLAQSV LLSVKWDVED PVTVPLATMS VVFTFIFVLE VTMKIIAMSP AGFWQSRRNR Y DLLVTSLG VVWVVLHFAL LNAYTYMMGA CVIVFRFFSI CGKHVTLKML LLTVVVSMYK SFFIIVGMFL LLLCYAFAGV VL FGTVKYG ENINRHANFS SAGKAITVLF RIVTGEDWNK IMHDCMVQPP FCTPDEFTYW ATDCGNYAGA LMYFCSFYVI IAY IMLNLL VAIIVENFSL FYSTEEDQLL SYNDLRHFQI IWNMVDDKRE GVIPTFRVKF LLRLLRGRLE VDLDKDKLLF KHMC YEMER LHNGGDVTFH DVLSMLSYRS VDIRKSLQLE ELLAREQLEY TIEEEVAKQT IRMWLKKCLK RIRAKQQQSC SIIHS LRES QQQELSRFLN PPSIETTQPS EDTNANSQDN SMQPETSSQQ QLLSPTLSDR GGSRQDAADA GKPQRKFGQW RLPSAP KPI SHSVSSVNLR FGGRTTMKSV VCKMNPMTDA ASCGSEVKKW WTRQLTVESD ESGDDLLDIG GGSGGWSHPQ FEKGGGS GG GSGGSAWSHP QFEKGSGDYK DDDDKGNSDY KDDDDK UniProtKB: Sodium leak channel NALCN |
-Macromolecule #2: Transmembrane protein FAM155A
| Macromolecule | Name: Transmembrane protein FAM155A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 54.205004 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MTRGAWMCRQ YDDGLKIWLA APRENEKPFI DSERAQKWRL SLASLLFFTV LLSDHLWFCA EAKLTRARDK EHQQQQRQQQ QQQQQQRQR QQQQQQRRQQ EPSWPALLAS MGESSPAAQA HRLLSASSSP TLPPSPGDGG GGGGKGNRGK DDRGKALFLG N SAKPVWRL ...String: MTRGAWMCRQ YDDGLKIWLA APRENEKPFI DSERAQKWRL SLASLLFFTV LLSDHLWFCA EAKLTRARDK EHQQQQRQQQ QQQQQQRQR QQQQQQRRQQ EPSWPALLAS MGESSPAAQA HRLLSASSSP TLPPSPGDGG GGGGKGNRGK DDRGKALFLG N SAKPVWRL ETCYPQGASS GQCFTVENAD AVCARNWSRG AAGGDGQEVR SKHPTPLWNL SDFYLSFCNS YTLWELFSGL SS PNTLNCS LDVVLKEGGE MTTCRQCVEA YQDYDHHAQE KYEEFESVLH KYLQSEEYSV KSCPEDCKIV YKAWLCSQYF EVT QFNCRK TIPCKQYCLE VQTRCPFILP DNDEVIYGGL SSFICTGLYE TFLTNDEPEC CDVRREEKSN NPSKGTVEKS GSCH RTSLT VSSATRLCNS RLKLCVLVLI LLHTVLTASA AQNTAGLSFG GINTLEENST NEEGGSGGSD YKDDDDKGNS DYKDD DDK UniProtKB: NALCN channel auxiliary factor 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #4: (1S)-2-{[(2-AMINOETHOXY)(HYDROXY)PHOSPHORYL]OXY}-1-[(PALMITOYLOXY...
| Macromolecule | Name: (1S)-2-{[(2-AMINOETHOXY)(HYDROXY)PHOSPHORYL]OXY}-1-[(PALMITOYLOXY)METHYL]ETHYL STEARATE type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: PEV |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 720.012 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PEV: |
-Macromolecule #5: (1R)-2-{[{[(2S)-2,3-DIHYDROXYPROPYL]OXY}(HYDROXY)PHOSPHORYL]OXY}-...
| Macromolecule | Name: (1R)-2-{[{[(2S)-2,3-DIHYDROXYPROPYL]OXY}(HYDROXY)PHOSPHORYL]OXY}-1-[(PALMITOYLOXY)METHYL]ETHYL (11E)-OCTADEC-11-ENOATE type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: PGV |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 749.007 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-PGV: |
-Macromolecule #6: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE
| Macromolecule | Name: CHOLESTEROL HEMISUCCINATE / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: Y01 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 486.726 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-Y01: |
-Macromolecule #7: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 5 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2.4 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R2/2 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 200 / Pretreatment - Type: PLASMA CLEANING / Pretreatment - Time: 10 sec. | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV | ||||||||||||
| Details | sample was gently cross-linked with 0.05% EM-grade glutaraldehyde for 10 min at room temperature and quenched with 0.09 M TRIS pH 7.5 |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Quantum LS / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 15080 / Average exposure time: 10.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 49.967 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal magnification: 165000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6xiw: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)