+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-10151 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
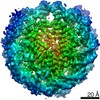
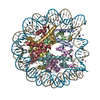
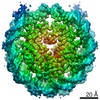
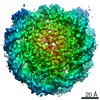
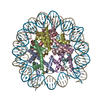
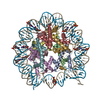
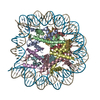
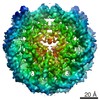
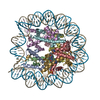
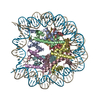
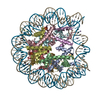
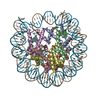
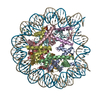
| Title | CENP-A nucleosome | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | CENP-A nucleosome | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CENP-A / nucleosome / centromere / centromeric chromatin / NUCLEAR PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationCENP-A containing chromatin assembly / kinetochore assembly / protein localization to chromosome, centromeric region / condensed chromosome, centromeric region / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / mitotic cytokinesis / chromosome, centromeric region / pericentric heterochromatin / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin ...CENP-A containing chromatin assembly / kinetochore assembly / protein localization to chromosome, centromeric region / condensed chromosome, centromeric region / establishment of mitotic spindle orientation / mitotic cytokinesis / chromosome, centromeric region / pericentric heterochromatin / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / innate immune response in mucosa / Defective pyroptosis / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / HDMs demethylate histones / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / HCMV Early Events / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / structural constituent of chromatin / Separation of Sister Chromatids / UCH proteinases / antibacterial humoral response / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / chromosome, telomeric region / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium / Ub-specific processing proteases / protein heterodimerization activity / Amyloid fiber formation / chromatin binding / protein-containing complex / extracellular space / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleus / membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ali-Ahmad A / Bilokapic S | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Norway, Norway,  Germany, 2 items Germany, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: EMBO Rep / Year: 2019 Journal: EMBO Rep / Year: 2019Title: CENP-C unwraps the human CENP-A nucleosome through the H2A C-terminal tail. Authors: Ahmad Ali-Ahmad / Silvija Bilokapić / Ingmar B Schäfer / Mario Halić / Nikolina Sekulić /    Abstract: Centromeres are defined epigenetically by nucleosomes containing the histone H3 variant CENP-A, upon which the constitutive centromere-associated network of proteins (CCAN) is built. CENP-C is ...Centromeres are defined epigenetically by nucleosomes containing the histone H3 variant CENP-A, upon which the constitutive centromere-associated network of proteins (CCAN) is built. CENP-C is considered to be a central organizer of the CCAN. We provide new molecular insights into the structure of human CENP-A nucleosomes, in isolation and in complex with the CENP-C central region (CENP-C ), the main CENP-A binding module of human CENP-C. We establish that the short αN helix of CENP-A promotes DNA flexibility at the nucleosome ends, independently of the sequence it wraps. Furthermore, we show that, in vitro, two regions of human CENP-C (CENP-C and CENP-C ) both bind exclusively to the CENP-A nucleosome. We find CENP-C to bind with high affinity due to an extended hydrophobic area made up of CENP-A and CENP-A . Importantly, we identify two key conformational changes within the CENP-A nucleosome upon CENP-C binding. First, the loose DNA wrapping of CENP-A nucleosomes is further exacerbated, through destabilization of the H2A C-terminal tail. Second, CENP-C rigidifies the N-terminal tail of H4 in the conformation favoring H4 monomethylation, essential for a functional centromere. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_10151.map.gz emd_10151.map.gz | 49.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-10151-v30.xml emd-10151-v30.xml emd-10151.xml emd-10151.xml | 18 KB 18 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_10151.png emd_10151.png | 71.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-10151.cif.gz emd-10151.cif.gz | 6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10151 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10151 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10151 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10151 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_10151_validation.pdf.gz emd_10151_validation.pdf.gz | 525.3 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_10151_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_10151_full_validation.pdf.gz | 524.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_10151_validation.xml.gz emd_10151_validation.xml.gz | 5.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_10151_validation.cif.gz emd_10151_validation.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-10151 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-10151 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-10151 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-10151 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6se0MC  6se6C  6seeC  6sefC  6segC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_10151.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_10151.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
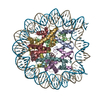
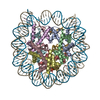
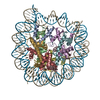
| Annotation | CENP-A nucleosome | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : CENP-A nucleosome
+Supramolecule #1: CENP-A nucleosome
+Supramolecule #2: CENP-A nucleosome
+Supramolecule #3: DNA
+Macromolecule #1: Histone H3-like centromeric protein A
+Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
+Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 2-A
+Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B type 1-C/E/F/G/I
+Macromolecule #5: Histone H2A type 2-A
+Macromolecule #6: DNA (145-MER)
+Macromolecule #7: DNA (145-MER)
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.2 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER / Support film - Material: CARBON |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 100.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 170000 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




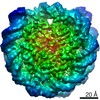
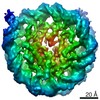
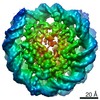
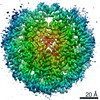
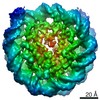
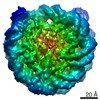
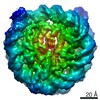
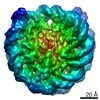















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






















