[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-0180: Structure of the repeat unit in the network formed by CcmM and Ru... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-0180 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
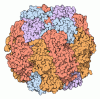
| Title | Structure of the repeat unit in the network formed by CcmM and Rubisco from Synechococcus elongatus | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Map after post-processing | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CcmM / M58 / M35 / SSUL domain / Rubisco / Carboxysome / PROTEIN BINDING | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationstructural constituent of carboxysome shell / photorespiration / carboxysome / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase / ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase activity / reductive pentose-phosphate cycle / carbon fixation / photosynthesis / monooxygenase activity / magnesium ion binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 (bacteria) / Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 (bacteria) /  Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942) (bacteria) Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942) (bacteria) | |||||||||
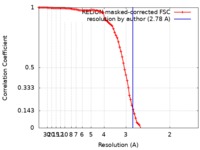
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.78 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang H / Yan X | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2019 Journal: Nature / Year: 2019Title: Rubisco condensate formation by CcmM in β-carboxysome biogenesis. Authors: H Wang / X Yan / H Aigner / A Bracher / N D Nguyen / W Y Hee / B M Long / G D Price / F U Hartl / M Hayer-Hartl /   Abstract: Cells use compartmentalization of enzymes as a strategy to regulate metabolic pathways and increase their efficiency. The α- and β-carboxysomes of cyanobacteria contain ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate ...Cells use compartmentalization of enzymes as a strategy to regulate metabolic pathways and increase their efficiency. The α- and β-carboxysomes of cyanobacteria contain ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco)-a complex of eight large (RbcL) and eight small (RbcS) subunits-and carbonic anhydrase. As HCO can diffuse through the proteinaceous carboxysome shell but CO cannot, carbonic anhydrase generates high concentrations of CO for carbon fixation by Rubisco. The shell also prevents access to reducing agents, generating an oxidizing environment. The formation of β-carboxysomes involves the aggregation of Rubisco by the protein CcmM, which exists in two forms: full-length CcmM (M58 in Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942), which contains a carbonic anhydrase-like domain followed by three Rubisco small subunit-like (SSUL) modules connected by flexible linkers; and M35, which lacks the carbonic anhydrase-like domain. It has long been speculated that the SSUL modules interact with Rubisco by replacing RbcS. Here we have reconstituted the Rubisco-CcmM complex and solved its structure. Contrary to expectation, the SSUL modules do not replace RbcS, but bind close to the equatorial region of Rubisco between RbcL dimers, linking Rubisco molecules and inducing phase separation into a liquid-like matrix. Disulfide bond formation in SSUL increases the network flexibility and is required for carboxysome function in vivo. Notably, the formation of the liquid-like condensate of Rubisco is mediated by dynamic interactions with the SSUL domains, rather than by low-complexity sequences, which typically mediate liquid-liquid phase separation in eukaryotes. Indeed, within the pyrenoids of eukaryotic algae, the functional homologues of carboxysomes, Rubisco adopts a liquid-like state by interacting with the intrinsically disordered protein EPYC1. Understanding carboxysome biogenesis will be important for efforts to engineer CO-concentrating mechanisms in plants. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_0180.map.gz emd_0180.map.gz | 5.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-0180-v30.xml emd-0180-v30.xml emd-0180.xml emd-0180.xml | 15.7 KB 15.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_0180_fsc.xml emd_0180_fsc.xml | 9.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_0180.png emd_0180.png | 82.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-0180.cif.gz emd-0180.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0180 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0180 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0180 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0180 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6hbcMC  6hbaC  6hbbC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_0180.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_0180.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Map after post-processing | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.822 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Repeat unit in the CcmM-Rubisco network consisting of a SSUL doma...
| Entire | Name: Repeat unit in the CcmM-Rubisco network consisting of a SSUL domain from CcmM and each two RbcL and two RbcS chains from Rubisco |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Repeat unit in the CcmM-Rubisco network consisting of a SSUL doma...
| Supramolecule | Name: Repeat unit in the CcmM-Rubisco network consisting of a SSUL domain from CcmM and each two RbcL and two RbcS chains from Rubisco type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: CcmM contains a succession of three highly similar SSUL domains (residues 225-313, 340-428 and 455-539, respectively), which bind to cleft on the surface of Rubisco. Rubisco is a hexadecamer ...Details: CcmM contains a succession of three highly similar SSUL domains (residues 225-313, 340-428 and 455-539, respectively), which bind to cleft on the surface of Rubisco. Rubisco is a hexadecamer of eight RbcL and eight RbcS subunits. The complex has D4 symmetry. The SSUL-RbcL2-RbcS2 repeat units can have one of two orientations (up or down). Thus Rubisco complexes saturated with SSUL domains can have four different configurations (uuuu, uuud, uudd, udud). In reality, some SSUL binding sites are probably left unoccupied. The network is formed by flexible linkers connecting the SSUL domains in CcmM, which then interlink Rubisco hexadecamers. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 (bacteria) / Organelle: Carboxysome Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 (bacteria) / Organelle: Carboxysome |
-Macromolecule #1: Carbon dioxide concentrating mechanism protein CcmM
| Macromolecule | Name: Carbon dioxide concentrating mechanism protein CcmM / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942) (bacteria) Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942) (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 10.550686 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SEFLSSEVIT QVRSLLNQGY RIGTEHADKR RFRTSSWQPC APIQSTNERQ VLSELENCLS EHEGEYVRLL GIDTNTRSRV FEALIQRPD GSV UniProtKB: Carboxysome assembly protein CcmM |
-Macromolecule #2: Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase large chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase large chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942) (bacteria) Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942) (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 52.516605 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MPKTQSAAGY KAGVKDYKLT YYTPDYTPKD TDLLAAFRFS PQPGVPADEA GAAIAAESST GTWTTVWTDL LTDMDRYKGK CYHIEPVQG EENSYFAFIA YPLDLFEEGS VTNILTSIVG NVFGFKAIRS LRLEDIRFPV ALVKTFQGPP HGIQVERDLL N KYGRPMLG ...String: MPKTQSAAGY KAGVKDYKLT YYTPDYTPKD TDLLAAFRFS PQPGVPADEA GAAIAAESST GTWTTVWTDL LTDMDRYKGK CYHIEPVQG EENSYFAFIA YPLDLFEEGS VTNILTSIVG NVFGFKAIRS LRLEDIRFPV ALVKTFQGPP HGIQVERDLL N KYGRPMLG CTIKPKLGLS AKNYGRAVYE CLRGGLDFTK DDENINSQPF QRWRDRFLFV ADAIHKSQAE TGEIKGHYLN VT APTCEEM MKRAEFAKEL GMPIIMHDFL TAGFTANTTL AKWCRDNGVL LHIHRAMHAV IDRQRNHGIH FRVLAKCLRL SGG DHLHSG TVVGKLEGDK ASTLGFVDLM REDHIEADRS RGVFFTQDWA SMPGVLPVAS GGIHVWHMPA LVEIFGDDSV LQFG GGTLG HPWGNAPGAT ANRVALEACV QARNEGRDLY REGGDILREA GKWSPELAAA LDLWKEIKFE FETMDKL UniProtKB: Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase large chain |
-Macromolecule #3: Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942) (bacteria) Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942) (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.349196 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSMKTLPKER RFETFSYLPP LSDRQIAAQI EYMIEQGFHP LIEFNEHSNP EEFYWTMWKL PLFDCKSPQQ VLDEVRECRS EYGDCYIRV AGFDNIKQCQ TVSFIVHRPG RY UniProtKB: Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 5 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
Details: Solutions were made fresh | |||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: PLASMA CLEANING / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 101.325 kPa | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: blot for 3 seconds before plunging. | |||||||||||||||
| Details | This sample contained 10 nm gold beads and was not monodisperse |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Average exposure time: 0.15 sec. / Average electron dose: 1.05 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Details | The cryoEM density for the repeat unit was masked by Refmac to the coordinates and converted into structure factors by Refmac. The model was adjusted with coot. This model was submitted to restrained refinement with Refmac against the structure factors. |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: RECIPROCAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Target criteria: Average Fourier shell correlation |
| Output model |  PDB-6hbc: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


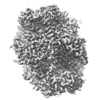
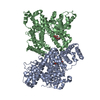


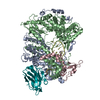







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)