[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6hba: Crystal Structure of the small subunit-like domain 1 of CcmM from... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6hba | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
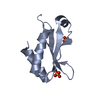
| Title | Crystal Structure of the small subunit-like domain 1 of CcmM from Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942), thiol-oxidized form | ||||||
 Components Components | Carbon dioxide concentrating mechanism protein CcmM | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN BINDING / alpha-beta structure / Rubisco / Carboxysome | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationstructural constituent of carboxysome shell / carboxysome / carbon fixation / photosynthesis Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) Synechococcus elongatus (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT /  molecular replacement / Resolution: 1.65 Å molecular replacement / Resolution: 1.65 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang, H. / Yan, X. / Aigner, H. / Bracher, A. / Nguyen, N.D. / Hee, W.Y. / Long, B.M. / Price, G.D. / Hartl, F.U. / Hayer-Hartl, M. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2019 Journal: Nature / Year: 2019Title: Rubisco condensate formation by CcmM in β-carboxysome biogenesis. Authors: H Wang / X Yan / H Aigner / A Bracher / N D Nguyen / W Y Hee / B M Long / G D Price / F U Hartl / M Hayer-Hartl /   Abstract: Cells use compartmentalization of enzymes as a strategy to regulate metabolic pathways and increase their efficiency. The α- and β-carboxysomes of cyanobacteria contain ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate ...Cells use compartmentalization of enzymes as a strategy to regulate metabolic pathways and increase their efficiency. The α- and β-carboxysomes of cyanobacteria contain ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco)-a complex of eight large (RbcL) and eight small (RbcS) subunits-and carbonic anhydrase. As HCO can diffuse through the proteinaceous carboxysome shell but CO cannot, carbonic anhydrase generates high concentrations of CO for carbon fixation by Rubisco. The shell also prevents access to reducing agents, generating an oxidizing environment. The formation of β-carboxysomes involves the aggregation of Rubisco by the protein CcmM, which exists in two forms: full-length CcmM (M58 in Synechococcus elongatus PCC7942), which contains a carbonic anhydrase-like domain followed by three Rubisco small subunit-like (SSUL) modules connected by flexible linkers; and M35, which lacks the carbonic anhydrase-like domain. It has long been speculated that the SSUL modules interact with Rubisco by replacing RbcS. Here we have reconstituted the Rubisco-CcmM complex and solved its structure. Contrary to expectation, the SSUL modules do not replace RbcS, but bind close to the equatorial region of Rubisco between RbcL dimers, linking Rubisco molecules and inducing phase separation into a liquid-like matrix. Disulfide bond formation in SSUL increases the network flexibility and is required for carboxysome function in vivo. Notably, the formation of the liquid-like condensate of Rubisco is mediated by dynamic interactions with the SSUL domains, rather than by low-complexity sequences, which typically mediate liquid-liquid phase separation in eukaryotes. Indeed, within the pyrenoids of eukaryotic algae, the functional homologues of carboxysomes, Rubisco adopts a liquid-like state by interacting with the intrinsically disordered protein EPYC1. Understanding carboxysome biogenesis will be important for efforts to engineer CO-concentrating mechanisms in plants. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6hba.cif.gz 6hba.cif.gz | 51.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6hba.ent.gz pdb6hba.ent.gz | 35.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6hba.json.gz 6hba.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hb/6hba https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hb/6hba ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hb/6hba ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hb/6hba | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  0180C  6hbbC  6hbcC  6hasS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
NCS domain segments: Component-ID: _ / Ens-ID: 1 / Beg auth comp-ID: PHE / Beg label comp-ID: PHE / End auth comp-ID: PRO / End label comp-ID: PRO / Refine code: _ / Auth seq-ID: 224 - 309 / Label seq-ID: 3 - 88
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 10550.686 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: SSUL domain 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942) (bacteria) Synechococcus elongatus (strain PCC 7942) (bacteria)Strain: PCC 7942 / Gene: ccmM, Synpcc7942_1423 / Plasmid: pHue / Production host:  #2: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 1.97 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 37.4 % / Mosaicity: 0.36 ° |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 277 K / Method: vapor diffusion / pH: 4.5 / Details: 25.5% PEG-3350 and 0.1 M Na-acetate pH 4.5 |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  ESRF ESRF  / Beamline: ID23-2 / Wavelength: 0.8726 Å / Beamline: ID23-2 / Wavelength: 0.8726 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS 2M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Jan 29, 2015 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.8726 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.65→44.59 Å / Num. obs: 19621 / % possible obs: 99.2 % / Redundancy: 4.2 % / CC1/2: 0.995 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.086 / Rpim(I) all: 0.047 / Rrim(I) all: 0.099 / Net I/σ(I): 9.4 / Num. measured all: 83107 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 1.65→1.67 Å / Redundancy: 3.8 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.833 / Num. unique obs: 866 / CC1/2: 0.548 / Rpim(I) all: 0.473 / Rrim(I) all: 0.963 / % possible all: 88.5 |
-Phasing
| Phasing | Method:  molecular replacement molecular replacement | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phasing MR |
|
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 6HAS Resolution: 1.65→30 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.958 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.933 / SU B: 2.617 / SU ML: 0.089 / SU R Cruickshank DPI: 0.1152 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / ESU R: 0.115 / ESU R Free: 0.115 Details: HYDROGENS HAVE BEEN ADDED IN THE RIDING POSITIONS U VALUES : REFINED INDIVIDUALLY
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Ion probe radii: 0.8 Å / Shrinkage radii: 0.8 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 103.47 Å2 / Biso mean: 27.824 Å2 / Biso min: 10.73 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: final / Resolution: 1.65→30 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints NCS | Ens-ID: 1 / Number: 4706 / Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Type: interatomic distance / Rms dev position: 0.14 Å / Weight position: 0.05
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 1.65→1.693 Å / Rfactor Rfree error: 0 / Total num. of bins used: 20
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj