+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Structural basis of stepwise proton sensing-mediated GPCR activation. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Cell Res, Vol. 35, Issue 6, Page 423-436, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Apr 11, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Xiaolei Yue / Li Peng / Shenhui Liu / Bingjie Zhang / Xiaodan Zhang / Hao Chang / Yuan Pei / Xiaoting Li / Junlin Liu / Wenqing Shui / Lijie Wu / Huji Xu / Zhi-Jie Liu / Tian Hua /  |
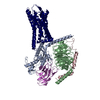
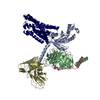
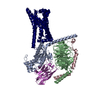
| PubMed Abstract | The regulation of pH homeostasis is crucial in many biological processes vital for survival, growth, and function of life. The pH-sensing G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), including GPR4, GPR65 ...The regulation of pH homeostasis is crucial in many biological processes vital for survival, growth, and function of life. The pH-sensing G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), including GPR4, GPR65 and GPR68, play a pivotal role in detecting changes in extracellular proton concentrations, impacting both physiological and pathological states. However, comprehensive understanding of the proton sensing mechanism is still elusive. Here, we determined the cryo-electron microscopy structures of GPR4 and GPR65 in various activation states across different pH levels, coupled with G, G or G proteins, as well as a small molecule NE52-QQ57-bound inactive GPR4 structure. These structures reveal the dynamic nature of the extracellular loop 2 and its signature conformations in different receptor states, and disclose the proton sensing mechanism mediated by networks of extracellular histidine and carboxylic acid residues. Notably, we unexpectedly captured partially active intermediate states of both GPR4-G and GPR4-G complexes, and identified a unique allosteric binding site for NE52-QQ57 in GPR4. By integrating prior investigations with our structural analysis and mutagenesis data, we propose a detailed atomic model for stepwise proton sensation and GPCR activation. These insights may pave the way for the development of selective ligands and targeted therapeutic interventions for pH sensing-relevant diseases. |
 External links External links |  Cell Res / Cell Res /  PubMed:40211064 / PubMed:40211064 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.67 - 3.35 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-39927, PDB-8zce: EMDB-39928, PDB-8zcf: EMDB-61439, PDB-9jft: EMDB-61440, PDB-9jfu: EMDB-61441, PDB-9jfv: EMDB-61442, PDB-9jfw: EMDB-61443, PDB-9jfx: EMDB-61445, PDB-9jfz: EMDB-61489, PDB-9jhp: EMDB-63068, PDB-9lgm: |
| Chemicals |  PDB-1l1e: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN/IMMUNE SYSTEM / GPCR / GPR4 / DNGs / Proton sensing / SIGNALING PROTEIN / SIGNALING PROTEIN-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex / GPR65 / miniGs / Gs / Gsq / G Protein / miniG13 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers




















 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)

