+Search query
-Structure paper
| Title | Evolutionary study and structural basis of proton sensing by Mus GPR4 and Xenopus GPR4. |
|---|---|
| Journal, issue, pages | Cell, Vol. 188, Issue 3, Page 653-670.e24, Year 2025 |
| Publish date | Feb 6, 2025 |
 Authors Authors | Xin Wen / Pan Shang / Haidi Chen / Lulu Guo / Naikang Rong / Xiaoyu Jiang / Xuan Li / Junyan Liu / Gongming Yang / Jiacheng Zhang / Kongkai Zhu / Qingbiao Meng / Xuefei He / Zhihai Wang / Zili Liu / Haoran Cheng / Yilin Zheng / Bifei Zhang / Jiaojiao Pang / Zhaoqian Liu / Peng Xiao / Yuguo Chen / Lunxu Liu / Fengming Luo / Xiao Yu / Fan Yi / Pengju Zhang / Fan Yang / Cheng Deng / Jin-Peng Sun /  |
| PubMed Abstract | Animals have evolved pH-sensing membrane receptors, such as G-protein-coupled receptor 4 (GPR4), to monitor pH changes related to their physiology and generate adaptive reactions. However, the ...Animals have evolved pH-sensing membrane receptors, such as G-protein-coupled receptor 4 (GPR4), to monitor pH changes related to their physiology and generate adaptive reactions. However, the evolutionary trajectory and structural mechanism of proton sensing by GPR4 remain unresolved. Here, we observed a positive correlation between the optimal pH of GPR4 activity and the blood pH range across different species. By solving 7-cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of Xenopus tropicalis GPR4 (xtGPR4) and Mus musculus GPR4 (mmGPR4) under varying pH conditions, we identified that protonation of H and H enabled polar network establishment and tighter association between the extracellular loop 2 (ECL2) and 7 transmembrane (7TM) domain, as well as a conserved propagating path, which are common mechanisms underlying protonation-induced GPR4 activation across different species. Moreover, protonation of distinct extracellular H contributed to the more acidic optimal pH range of xtGPR4. Overall, our study revealed common and distinct mechanisms of proton sensing by GPR4, from a structural, functional, and evolutionary perspective. |
 External links External links |  Cell / Cell /  PubMed:39753131 PubMed:39753131 |
| Methods | EM (single particle) |
| Resolution | 2.36 - 3.78 Å |
| Structure data | EMDB-39946, PDB-8zd1: EMDB-60050, PDB-8zf4: EMDB-60051, PDB-8zf6: EMDB-60052, PDB-8zf7: EMDB-60053, PDB-8zf9: EMDB-60054, PDB-8zfa: EMDB-60055, PDB-8zfb: EMDB-60056, PDB-8zfc: EMDB-60057, PDB-8zfd: EMDB-60058, PDB-8zfe: EMDB-61838, PDB-9jvg: EMDB-61839, PDB-9jvh: EMDB-61840, PDB-9jvm: |
| Source |
|
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN/IMMUNE SYSTEM / pH6.2 / xGPR4 / Gs / MEMBRANE PROTEIN / MEMBRANE PROTEIN-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex / receptor / pH6.7 / pH7.2 / mmGPR4 / xtGPR4 / pH7.6 / pH8.0 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Structure viewers
Structure viewers About Yorodumi Papers
About Yorodumi Papers












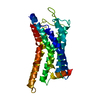

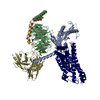
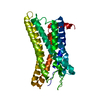






 homo sapiens (human)
homo sapiens (human)
