+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: PDB / ID: 6b3q | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
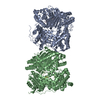
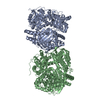
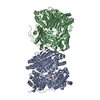
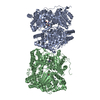
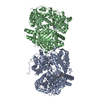
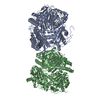
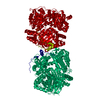
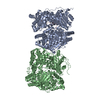
| タイトル | Cryo-EM structure of human insulin degrading enzyme in complex with insulin | |||||||||||||||
 要素 要素 |
| |||||||||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | HYDROLASE/HORMONE / IDE /  insulin degrading enzyme (インスリン分解酵素) / insulin degrading enzyme (インスリン分解酵素) /  amyloid beta (アミロイドβ) / HYDROLASE-HORMONE complex amyloid beta (アミロイドβ) / HYDROLASE-HORMONE complex | |||||||||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報 インスリシン / ubiquitin recycling / insulin catabolic process / insulin metabolic process / amyloid-beta clearance by cellular catabolic process / hormone catabolic process / bradykinin catabolic process / ubiquitin-modified protein reader activity / インスリシン / ubiquitin recycling / insulin catabolic process / insulin metabolic process / amyloid-beta clearance by cellular catabolic process / hormone catabolic process / bradykinin catabolic process / ubiquitin-modified protein reader activity /  insulin binding / negative regulation of NAD(P)H oxidase activity ... insulin binding / negative regulation of NAD(P)H oxidase activity ... インスリシン / ubiquitin recycling / insulin catabolic process / insulin metabolic process / amyloid-beta clearance by cellular catabolic process / hormone catabolic process / bradykinin catabolic process / ubiquitin-modified protein reader activity / インスリシン / ubiquitin recycling / insulin catabolic process / insulin metabolic process / amyloid-beta clearance by cellular catabolic process / hormone catabolic process / bradykinin catabolic process / ubiquitin-modified protein reader activity /  insulin binding / negative regulation of NAD(P)H oxidase activity / insulin binding / negative regulation of NAD(P)H oxidase activity /  regulation of aerobic respiration / negative regulation of glycogen catabolic process / regulation of cellular amino acid metabolic process / peptide catabolic process / Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / nitric oxide-cGMP-mediated signaling / negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / Insulin processing / negative regulation of feeding behavior / regulation of aerobic respiration / negative regulation of glycogen catabolic process / regulation of cellular amino acid metabolic process / peptide catabolic process / Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / nitric oxide-cGMP-mediated signaling / negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / Insulin processing / negative regulation of feeding behavior /  regulation of protein secretion / amyloid-beta clearance / positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion / regulation of protein secretion / amyloid-beta clearance / positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion /  Regulation of gene expression in beta cells / positive regulation of respiratory burst / peroxisomal matrix / positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / alpha-beta T cell activation / negative regulation of acute inflammatory response / negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / negative regulation of protein secretion / fatty acid homeostasis / Synthesis, secretion, and deacylation of Ghrelin / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / Signal attenuation / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / amyloid-beta metabolic process / negative regulation of lipid catabolic process / negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / Regulation of gene expression in beta cells / positive regulation of respiratory burst / peroxisomal matrix / positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / alpha-beta T cell activation / negative regulation of acute inflammatory response / negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / negative regulation of protein secretion / fatty acid homeostasis / Synthesis, secretion, and deacylation of Ghrelin / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / Signal attenuation / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / amyloid-beta metabolic process / negative regulation of lipid catabolic process / negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process /  小胞 / positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation / Insulin receptor recycling / 小胞 / positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation / Insulin receptor recycling /  insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / positive regulation of protein metabolic process / neuron projection maintenance / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation / activation of protein kinase B activity / positive regulation of glycolytic process / proteolysis involved in protein catabolic process / Insulin receptor signalling cascade / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / Regulation of insulin secretion / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / endosome lumen / positive regulation of cytokine production / acute-phase response / positive regulation of protein secretion / regulation of transmembrane transporter activity / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / positive regulation of protein metabolic process / neuron projection maintenance / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation / activation of protein kinase B activity / positive regulation of glycolytic process / proteolysis involved in protein catabolic process / Insulin receptor signalling cascade / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / Regulation of insulin secretion / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / endosome lumen / positive regulation of cytokine production / acute-phase response / positive regulation of protein secretion / regulation of transmembrane transporter activity /  Peroxisomal protein import / positive regulation of cell differentiation / positive regulation of glucose import / Peroxisomal protein import / positive regulation of cell differentiation / positive regulation of glucose import /  peptide binding / negative regulation of proteolysis / peptide binding / negative regulation of proteolysis /  regulation of synaptic plasticity / protein catabolic process / regulation of synaptic plasticity / protein catabolic process /  wound healing / wound healing /  insulin receptor binding / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / positive regulation of neuron projection development / insulin receptor binding / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / positive regulation of neuron projection development /  hormone activity / hormone activity /  metalloendopeptidase activity / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I / metalloendopeptidase activity / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I /  認識 / Golgi lumen / 認識 / Golgi lumen /  ペルオキシソーム / ペルオキシソーム /  vasodilation / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / glucose metabolic process / vasodilation / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / glucose metabolic process /  regulation of protein localization / regulation of protein localization /  glucose homeostasis / virus receptor activity / cell-cell signaling / insulin receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity / positive regulation of protein binding / PI5P, PP2A and IER3 Regulate PI3K/AKT Signaling / positive regulation of cell growth / basolateral plasma membrane / secretory granule lumen glucose homeostasis / virus receptor activity / cell-cell signaling / insulin receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity / positive regulation of protein binding / PI5P, PP2A and IER3 Regulate PI3K/AKT Signaling / positive regulation of cell growth / basolateral plasma membrane / secretory granule lumen類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||||||||
| 生物種 |   Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | |||||||||||||||
| 手法 |  電子顕微鏡法 / 電子顕微鏡法 /  単粒子再構成法 / 単粒子再構成法 /  クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 3.7 Å クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 3.7 Å | |||||||||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Liang, W.G. / Zhang, Z. / Bailey, L.J. / Kossiakoff, A.A. / Tan, Y.Z. / Wei, H. / Carragher, B. / Potter, S.C. / Tang, W.J. | |||||||||||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 4件 米国, 4件
| |||||||||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Elife / 年: 2018 ジャーナル: Elife / 年: 2018タイトル: Ensemble cryoEM elucidates the mechanism of insulin capture and degradation by human insulin degrading enzyme. 著者: Zhening Zhang / Wenguang G Liang / Lucas J Bailey / Yong Zi Tan / Hui Wei / Andrew Wang / Mara Farcasanu / Virgil A Woods / Lauren A McCord / David Lee / Weifeng Shang / Rebecca Deprez- ...著者: Zhening Zhang / Wenguang G Liang / Lucas J Bailey / Yong Zi Tan / Hui Wei / Andrew Wang / Mara Farcasanu / Virgil A Woods / Lauren A McCord / David Lee / Weifeng Shang / Rebecca Deprez-Poulain / Benoit Deprez / David R Liu / Akiko Koide / Shohei Koide / Anthony A Kossiakoff / Sheng Li / Bridget Carragher / Clinton S Potter / Wei-Jen Tang /   要旨: Insulin degrading enzyme (IDE) plays key roles in degrading peptides vital in type two diabetes, Alzheimer's, inflammation, and other human diseases. However, the process through which IDE recognizes ...Insulin degrading enzyme (IDE) plays key roles in degrading peptides vital in type two diabetes, Alzheimer's, inflammation, and other human diseases. However, the process through which IDE recognizes peptides that tend to form amyloid fibrils remained unsolved. We used cryoEM to understand both the apo- and insulin-bound dimeric IDE states, revealing that IDE displays a large opening between the homologous ~55 kDa N- and C-terminal halves to allow selective substrate capture based on size and charge complementarity. We also used cryoEM, X-ray crystallography, SAXS, and HDX-MS to elucidate the molecular basis of how amyloidogenic peptides stabilize the disordered IDE catalytic cleft, thereby inducing selective degradation by substrate-assisted catalysis. Furthermore, our insulin-bound IDE structures explain how IDE processively degrades insulin by stochastically cutting either chain without breaking disulfide bonds. Together, our studies provide a mechanism for how IDE selectively degrades amyloidogenic peptides and offers structural insights for developing IDE-based therapies. | |||||||||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| ムービー |
 ムービービューア ムービービューア |
|---|---|
| 構造ビューア | 分子:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
- ダウンロード
ダウンロード
| PDBx/mmCIF形式 |  6b3q.cif.gz 6b3q.cif.gz | 353.3 KB | 表示 |  PDBx/mmCIF形式 PDBx/mmCIF形式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB形式 |  pdb6b3q.ent.gz pdb6b3q.ent.gz | 287.3 KB | 表示 |  PDB形式 PDB形式 |
| PDBx/mmJSON形式 |  6b3q.json.gz 6b3q.json.gz | ツリー表示 |  PDBx/mmJSON形式 PDBx/mmJSON形式 | |
| その他 |  その他のダウンロード その他のダウンロード |
-検証レポート
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b3/6b3q https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b3/6b3q ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b3/6b3q ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b3/6b3q | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-関連構造データ
| 関連構造データ |  7041MC  7062C  7065C  7066C  7090C  7091C  7092C  7093C  5wobC  6b70C  6b7yC  6b7zC  6bf6C  6bf7C  6bf8C  6bf9C  6bfcC M: このデータのモデリングに利用したマップデータ C: 同じ文献を引用 ( |
|---|---|
| 類似構造データ |
- リンク
リンク
- 集合体
集合体
| 登録構造単位 | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 | 
|
- 要素
要素
| #1: タンパク質 |  インスリン分解酵素 / Abeta-degrading protease / Insulin protease / Insulinase / Insulysin インスリン分解酵素 / Abeta-degrading protease / Insulin protease / Insulinase / Insulysin分子量: 114561.562 Da / 分子数: 2 / 断片: residues 42-1019 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)   Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: IDE / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: IDE / 発現宿主:   Escherichia coli (大腸菌) / 参照: UniProt: P14735, Escherichia coli (大腸菌) / 参照: UniProt: P14735,  インスリシン インスリシン#2: タンパク質 |  インスリン インスリン分子量: 11989.862 Da / 分子数: 2 / 由来タイプ: 組換発現 / 由来: (組換発現)   Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: INS / 発現宿主: Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: INS / 発現宿主:   Escherichia coli (大腸菌) / 参照: UniProt: P01308 Escherichia coli (大腸菌) / 参照: UniProt: P01308 |
|---|
-実験情報
-実験
| 実験 | 手法:  電子顕微鏡法 電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
| EM実験 | 試料の集合状態: PARTICLE / 3次元再構成法:  単粒子再構成法 単粒子再構成法 |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 構成要素 | 名称: Insulin degrading enzyme/Insulin / タイプ: COMPLEX 詳細: Cryo-EM structure of human insulin degrading enzyme in complex with insulin Entity ID: all / 由来: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分子量 | 値: 0.1 MDa / 実験値: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:   Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 由来(組換発現) | 生物種:   Escherichia coli (大腸菌) / 株: BL Escherichia coli (大腸菌) / 株: BL | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 緩衝液 | pH: 7.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 緩衝液成分 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| 試料 | 濃度: 0.3 mg/ml / 包埋: NO / シャドウイング: NO / 染色 : NO / 凍結 : NO / 凍結 : YES / 詳細: The sample was monodisperse : YES / 詳細: The sample was monodisperse | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 試料支持 | グリッドの材料: COPPER / グリッドのサイズ: 300 divisions/in. / グリッドのタイプ: homemade nanowire grid | ||||||||||||||||||||
急速凍結 | 装置: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / 凍結剤: ETHANE / 湿度: 85 % / 凍結前の試料温度: 298 K 詳細: The cryo grids were made using Spotiton and homemade plunger |
- 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| 顕微鏡 | モデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| 電子銃 | 電子線源 : :  FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM |
| 電子レンズ | モード: BRIGHT FIELD Bright-field microscopy / 倍率(公称値): 22500 X / 倍率(補正後): 46598 X / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2200 nm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 940 nm / Cs Bright-field microscopy / 倍率(公称値): 22500 X / 倍率(補正後): 46598 X / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 2200 nm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 940 nm / Cs : 2.7 mm / C2レンズ絞り径: 70 µm / アライメント法: COMA FREE : 2.7 mm / C2レンズ絞り径: 70 µm / アライメント法: COMA FREE |
| 試料ホルダ | 凍結剤: NITROGEN 試料ホルダーモデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER 最高温度: 70 K / 最低温度: 70 K / Residual tilt: 10 mradians |
| 撮影 | 平均露光時間: 10 sec. / 電子線照射量: 71.4 e/Å2 / 検出モード: COUNTING フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) 撮影したグリッド数: 3 / 実像数: 3085 |
| 画像スキャン | サンプリングサイズ: 5 µm / 横: 3710 / 縦: 3838 / 動画フレーム数/画像: 50 / 利用したフレーム数/画像: 1-50 |
- 解析
解析
| ソフトウェア | 名称: PHENIX / バージョン: 1.12_2829: / 分類: 精密化 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EMソフトウェア |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CTF補正 | タイプ: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 粒子像の選択 | 選択した粒子像数: 762283 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 点対称性 : C1 (非対称) : C1 (非対称) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
3次元再構成 | 解像度: 3.7 Å / 解像度の算出法: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / 粒子像の数: 116122 / アルゴリズム: FOURIER SPACE / クラス平均像の数: 1 / 対称性のタイプ: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 原子モデル構築 | B value: 92 / プロトコル: FLEXIBLE FIT / 空間: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 拘束条件 |
|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー



 PDBj
PDBj