[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6bf9: Cryo-EM structure of human insulin degrading enzyme in complex wi... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6bf9 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of human insulin degrading enzyme in complex with FAB H11-E heavy chain, FAB H11-E light chain | |||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HYDROLASE/IMMUNE SYSTEM / IDE / amyloid beta / HYDROLASE-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationinsulysin / beta-endorphin binding / ubiquitin recycling / insulin catabolic process / insulin metabolic process / amyloid-beta clearance by cellular catabolic process / hormone catabolic process / bradykinin catabolic process / cytosolic proteasome complex / insulin binding ...insulysin / beta-endorphin binding / ubiquitin recycling / insulin catabolic process / insulin metabolic process / amyloid-beta clearance by cellular catabolic process / hormone catabolic process / bradykinin catabolic process / cytosolic proteasome complex / insulin binding / regulation of aerobic respiration / peptide catabolic process / peroxisomal matrix / amyloid-beta clearance / positive regulation of protein binding / amyloid-beta metabolic process / immunoglobulin complex / Insulin receptor recycling / negative regulation of proteolysis / peptide binding / : / protein catabolic process / Peroxisomal protein import / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I / metalloendopeptidase activity / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / insulin receptor signaling pathway / peroxisome / amyloid-beta binding / virus receptor activity / endopeptidase activity / basolateral plasma membrane / adaptive immune response / Ub-specific processing proteases / external side of plasma membrane / protein-containing complex binding / cell surface / protein homodimerization activity / ATP hydrolysis activity / mitochondrion / proteolysis / extracellular space / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 7.2 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Liang, W.G. / Zhang, Z. / Bailey, L.J. / Kossiakoff, A.A. / Tan, Y.Z. / Wei, H. / Carragher, B. / Potter, S.C. / Tang, W.J. | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4items United States, 4items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2018 Journal: Elife / Year: 2018Title: Ensemble cryoEM elucidates the mechanism of insulin capture and degradation by human insulin degrading enzyme. Authors: Zhening Zhang / Wenguang G Liang / Lucas J Bailey / Yong Zi Tan / Hui Wei / Andrew Wang / Mara Farcasanu / Virgil A Woods / Lauren A McCord / David Lee / Weifeng Shang / Rebecca Deprez- ...Authors: Zhening Zhang / Wenguang G Liang / Lucas J Bailey / Yong Zi Tan / Hui Wei / Andrew Wang / Mara Farcasanu / Virgil A Woods / Lauren A McCord / David Lee / Weifeng Shang / Rebecca Deprez-Poulain / Benoit Deprez / David R Liu / Akiko Koide / Shohei Koide / Anthony A Kossiakoff / Sheng Li / Bridget Carragher / Clinton S Potter / Wei-Jen Tang /   Abstract: Insulin degrading enzyme (IDE) plays key roles in degrading peptides vital in type two diabetes, Alzheimer's, inflammation, and other human diseases. However, the process through which IDE recognizes ...Insulin degrading enzyme (IDE) plays key roles in degrading peptides vital in type two diabetes, Alzheimer's, inflammation, and other human diseases. However, the process through which IDE recognizes peptides that tend to form amyloid fibrils remained unsolved. We used cryoEM to understand both the apo- and insulin-bound dimeric IDE states, revealing that IDE displays a large opening between the homologous ~55 kDa N- and C-terminal halves to allow selective substrate capture based on size and charge complementarity. We also used cryoEM, X-ray crystallography, SAXS, and HDX-MS to elucidate the molecular basis of how amyloidogenic peptides stabilize the disordered IDE catalytic cleft, thereby inducing selective degradation by substrate-assisted catalysis. Furthermore, our insulin-bound IDE structures explain how IDE processively degrades insulin by stochastically cutting either chain without breaking disulfide bonds. Together, our studies provide a mechanism for how IDE selectively degrades amyloidogenic peptides and offers structural insights for developing IDE-based therapies. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6bf9.cif.gz 6bf9.cif.gz | 489.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6bf9.ent.gz pdb6bf9.ent.gz | 393.5 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6bf9.json.gz 6bf9.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bf/6bf9 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bf/6bf9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bf/6bf9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/bf/6bf9 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7093MC  7041C  7062C  7065C  7066C  7090C  7091C  7092C  5wobC  6b3qC  6b70C  6b7yC  6b7zC  6bf6C  6bf7C  6bf8C  6bfcC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 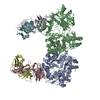
|
|---|---|
| 1 | 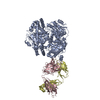
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 111866.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: residues 46-1011 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: IDE / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: IDE / Production host:  #2: Antibody | Mass: 23057.748 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Production host:  #3: Antibody | Mass: 23087.609 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Production host:  Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Insulin degrading enzyme / Type: COMPLEX Details: Cryo-EM structure of human Apo insulin degrading enzyme Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.1 MDa / Experimental value: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES / Details: The sample was monodisperse | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: The grids are homemade lacey gold nanowire grids / Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Homemade | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 85 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K / Details: The cryo grids were made using Spotiton |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS / Details: The image was collected at 20-50 degree tilt | |||||||||
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM | |||||||||
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 22500 X / Calibrated magnification: 46598 X / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 940 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE | |||||||||
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Temperature (max): 70 K / Temperature (min): 70 K / Residual tilt: 10 mradians | |||||||||
| Image recording | Imaging-ID: 1 / Average exposure time: 10 sec. / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1
| |||||||||
| Image scans | Sampling size: 5 µm / Width: 3710 / Height: 3820 / Movie frames/image: 50 / Used frames/image: 1-50 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.12_2829: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 762283 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 7.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 110499 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 92 / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 PDBj
PDBj