[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-7062: Cryo-EM structure of human insulin degrading enzyme in complex wi... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-7062 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
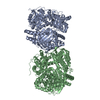
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of human insulin degrading enzyme in complex with insulin | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Insulin degrading enzyme in complex with insulin | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | IDE / insulin degrading enzyme / amyloid beta / BIOSYNTHETIC PROTEIN / HYDROLASE-IMMUNE SYSTEM-HORMONE complex | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationinsulysin / beta-endorphin binding / ubiquitin recycling / insulin catabolic process / insulin metabolic process / amyloid-beta clearance by cellular catabolic process / hormone catabolic process / bradykinin catabolic process / cytosolic proteasome complex / insulin binding ...insulysin / beta-endorphin binding / ubiquitin recycling / insulin catabolic process / insulin metabolic process / amyloid-beta clearance by cellular catabolic process / hormone catabolic process / bradykinin catabolic process / cytosolic proteasome complex / insulin binding / regulation of aerobic respiration / negative regulation of glycogen catabolic process / positive regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / negative regulation of fatty acid metabolic process / negative regulation of feeding behavior / Signaling by Insulin receptor / IRS activation / Insulin processing / regulation of protein secretion / peptide catabolic process / positive regulation of peptide hormone secretion / positive regulation of respiratory burst / Regulation of gene expression in beta cells / negative regulation of acute inflammatory response / peroxisomal matrix / amyloid-beta clearance / alpha-beta T cell activation / positive regulation of protein binding / Synthesis, secretion, and deacylation of Ghrelin / amyloid-beta metabolic process / positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / negative regulation of protein secretion / negative regulation of gluconeogenesis / positive regulation of glycogen biosynthetic process / fatty acid homeostasis / Signal attenuation / positive regulation of insulin receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / immunoglobulin complex / FOXO-mediated transcription of oxidative stress, metabolic and neuronal genes / negative regulation of lipid catabolic process / positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process / negative regulation of oxidative stress-induced intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway / regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane / transport vesicle / nitric oxide-cGMP-mediated signaling / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / Insulin receptor recycling / negative regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / positive regulation of brown fat cell differentiation / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / negative regulation of proteolysis / NPAS4 regulates expression of target genes / neuron projection maintenance / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of mitotic nuclear division / peptide binding / Insulin receptor signalling cascade / : / positive regulation of glycolytic process / positive regulation of cytokine production / endosome lumen / acute-phase response / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / positive regulation of D-glucose import across plasma membrane / positive regulation of protein secretion / insulin receptor binding / protein catabolic process / positive regulation of cell differentiation / Regulation of insulin secretion / Peroxisomal protein import / wound healing / positive regulation of neuron projection development / hormone activity / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I / metalloendopeptidase activity / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / regulation of synaptic plasticity / positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus / Golgi lumen / vasodilation / cognition / glucose metabolic process / positive regulation of protein catabolic process / insulin receptor signaling pathway / peroxisome / cell-cell signaling / glucose homeostasis / regulation of protein localization / amyloid-beta binding / PI5P, PP2A and IER3 Regulate PI3K/AKT Signaling / virus receptor activity / positive regulation of cell growth / protease binding / secretory granule lumen / endopeptidase activity / basolateral plasma membrane / adaptive immune response / positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
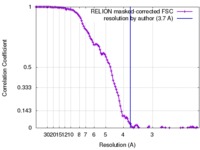
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang Z / Liang WG / Bailey LJ / Tan YZ / Wei H / Kossiakoff AA / Carragher B / Potter SC / Tang WJ | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4 items United States, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Elife / Year: 2018 Journal: Elife / Year: 2018Title: Ensemble cryoEM elucidates the mechanism of insulin capture and degradation by human insulin degrading enzyme. Authors: Zhening Zhang / Wenguang G Liang / Lucas J Bailey / Yong Zi Tan / Hui Wei / Andrew Wang / Mara Farcasanu / Virgil A Woods / Lauren A McCord / David Lee / Weifeng Shang / Rebecca Deprez- ...Authors: Zhening Zhang / Wenguang G Liang / Lucas J Bailey / Yong Zi Tan / Hui Wei / Andrew Wang / Mara Farcasanu / Virgil A Woods / Lauren A McCord / David Lee / Weifeng Shang / Rebecca Deprez-Poulain / Benoit Deprez / David R Liu / Akiko Koide / Shohei Koide / Anthony A Kossiakoff / Sheng Li / Bridget Carragher / Clinton S Potter / Wei-Jen Tang /   Abstract: Insulin degrading enzyme (IDE) plays key roles in degrading peptides vital in type two diabetes, Alzheimer's, inflammation, and other human diseases. However, the process through which IDE recognizes ...Insulin degrading enzyme (IDE) plays key roles in degrading peptides vital in type two diabetes, Alzheimer's, inflammation, and other human diseases. However, the process through which IDE recognizes peptides that tend to form amyloid fibrils remained unsolved. We used cryoEM to understand both the apo- and insulin-bound dimeric IDE states, revealing that IDE displays a large opening between the homologous ~55 kDa N- and C-terminal halves to allow selective substrate capture based on size and charge complementarity. We also used cryoEM, X-ray crystallography, SAXS, and HDX-MS to elucidate the molecular basis of how amyloidogenic peptides stabilize the disordered IDE catalytic cleft, thereby inducing selective degradation by substrate-assisted catalysis. Furthermore, our insulin-bound IDE structures explain how IDE processively degrades insulin by stochastically cutting either chain without breaking disulfide bonds. Together, our studies provide a mechanism for how IDE selectively degrades amyloidogenic peptides and offers structural insights for developing IDE-based therapies. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_7062.map.gz emd_7062.map.gz | 8.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-7062-v30.xml emd-7062-v30.xml emd-7062.xml emd-7062.xml | 26.3 KB 26.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
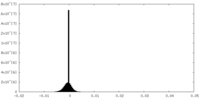
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_7062_fsc.xml emd_7062_fsc.xml | 11.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_7062.png emd_7062.png | 77.9 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_7062_msk_1.map emd_7062_msk_1.map | 125 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-7062.cif.gz emd-7062.cif.gz | 7.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_7062_half_map_1.map.gz emd_7062_half_map_1.map.gz emd_7062_half_map_2.map.gz emd_7062_half_map_2.map.gz | 98.5 MB 98.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7062 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7062 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7062 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7062 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 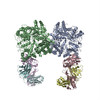 6b70MC  7041C  7065C  7066C  7090C  7091C  7092C  7093C  5wobC  6b3qC  6b7yC  6b7zC  6bf6C  6bf7C  6bf8C  6bf9C  6bfcC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_7062.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_7062.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Insulin degrading enzyme in complex with insulin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.073 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
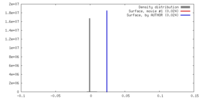
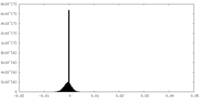
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_7062_msk_1.map emd_7062_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
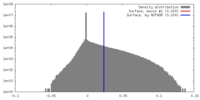
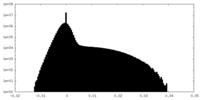
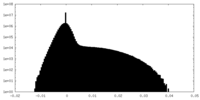
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Insulin degrading enzyme in complex with insulin
| File | emd_7062_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Insulin degrading enzyme in complex with insulin | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Insulin degrading enzyme in complex with insulin
| File | emd_7062_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Insulin degrading enzyme in complex with insulin | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Insulin degrading enzyme/Insulin
| Entire | Name: Insulin degrading enzyme/Insulin |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Insulin degrading enzyme/Insulin
| Supramolecule | Name: Insulin degrading enzyme/Insulin / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: Cryo-EM structure of human insulin degrading enzyme in complex with insulin |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 100 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Insulin-degrading enzyme
| Macromolecule | Name: Insulin-degrading enzyme / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: insulysin |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 111.866484 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: AIKRIGNHIT KSPEDKREYR GLELANGIKV LLISDPTTDK SSAALDVHIG SLSDPPNIAG LSHFLEHMLF LGTKKYPKEN EYSQFLSEH AGSSNAFTSG EHTNYYFDVS HEHLEGALDR FAQFFLSPLF DESAKDREVN AVDSEHEKNV MNDAWRLFQL E KATGNPKH ...String: AIKRIGNHIT KSPEDKREYR GLELANGIKV LLISDPTTDK SSAALDVHIG SLSDPPNIAG LSHFLEHMLF LGTKKYPKEN EYSQFLSEH AGSSNAFTSG EHTNYYFDVS HEHLEGALDR FAQFFLSPLF DESAKDREVN AVDSEHEKNV MNDAWRLFQL E KATGNPKH PFSKFGTGNK YTLETRPNQE GIDVRQELLK FHSAYYSSNL MAVVVLGRES LDDLTNLVVK LFSEVENKNV PL PEFPEHP FQEEHLKQLY KIVPIKDIRN LYVTFPIPDL QKYYKSNPGH YLGHLIGHEG PGSLLSELKS KGWVNTLVGG QKE GARGFM FFIINVDLTE EGLLHVEDII LHMFQYIQKL RAEGPQEWVF QELKDLNAVA FRFKDKERPR GYTSKIAGIL HYYP LEEVL TAEYLLEEFR PDLIEMVLDK LRPENVRVAI VSKSFEGKTD RTEEWYGTQY KQEAIPDEVI KKWQNADLNG KFKLP TKNE FIPTNFEILP LEKEATPYPA LIKDTAMSKL WFKQDDKFFL PKANLNFEFF SPFAYVDPLH SNMAYLYLEL LKDSLN EYA YAAELAGLSY DLQNTIYGMY LSVKGYNDKQ PILLKKIIEK MATFEIDEKR FEIIKEAYMR SLNNFRAEQP HQHAMYY LR LLMTEVAWTK DELKEALDDV TLPRLKAFIP QLLSRLHIEA LLHGNITKQA ALGIMQMVED TLIEHAHTKP LLPSQLVR Y REVQLPDRGW FVYQQRNEVH NNSGIEIYYQ TDMQSTSENM FLELFAQIIS EPAFNTLRTK EQLGYIVFSG PRRANGIQG LRFIIQSEKP PHYLESRVEA FLITMEKSIE DMTEEAFQKH IQALAIRRLD KPKKLSAESA KYWGEIISQQ YNFDRDNTEV AYLKTLTKE DIIKFYKEML AVDAPRRHKV SVHVLAREMD SCPVVGEFPC QNDINLSQAP ALPQPEVIQN MTEFKRGLPL F PLVKPH UniProtKB: Insulin-degrading enzyme |
-Macromolecule #2: FAB H11-E heavy chain
| Macromolecule | Name: FAB H11-E heavy chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.057748 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: EVQLVESGGG LVQPGGSLRL SCAASGFNIS SSSIHWVRQA PGKGLEWVAS IYSYSGSTYY ADSVKGRFTI SADTSKNTAY LQMNSLRAE DTAVYYCARH YSAVAGLDYW GQGTLVTVFN QIKPPSVFPL APSSKSTSGG TAALGCLVKD YFPEPVTVSW N SGALTSGV ...String: EVQLVESGGG LVQPGGSLRL SCAASGFNIS SSSIHWVRQA PGKGLEWVAS IYSYSGSTYY ADSVKGRFTI SADTSKNTAY LQMNSLRAE DTAVYYCARH YSAVAGLDYW GQGTLVTVFN QIKPPSVFPL APSSKSTSGG TAALGCLVKD YFPEPVTVSW N SGALTSGV HTFPAVLQSS GLYSLSSVVT VPSSSLGTQT YICNVNHKPS NTKVDKKVEP UniProtKB: Immunoglobulin gamma-1 heavy chain |
-Macromolecule #3: FAB H11-E light chain
| Macromolecule | Name: FAB H11-E light chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.087609 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: DIQMTQSPSS LSASVGDRVT ITCRASQSVS SAVAWYQQKP GKAPKLLIYS ASSLYSGVPS RFSGSRSGTD YTLTISSLQP EDFATYYCQ QSYFNPITFG QGTKVEIKRT VAAPSVFIFP PSDEQLKSGT ASVVCLLNNF YPREAKVQWK VDNALQSGNS Q ESVTEQDS ...String: DIQMTQSPSS LSASVGDRVT ITCRASQSVS SAVAWYQQKP GKAPKLLIYS ASSLYSGVPS RFSGSRSGTD YTLTISSLQP EDFATYYCQ QSYFNPITFG QGTKVEIKRT VAAPSVFIFP PSDEQLKSGT ASVVCLLNNF YPREAKVQWK VDNALQSGNS Q ESVTEQDS KDSTYSLSST LTLSKADYEK HKVYACEVTH QGLSSPVTKS FNR UniProtKB: Ig-like domain-containing protein |
-Macromolecule #4: Insulin
| Macromolecule | Name: Insulin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.989862 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MALWMRLLPL LALLALWGPD PAAAFVNQHL CGSHLVEALY LVCGERGFFY TPKTRREAED LQVGQVELGG GPGAGSLQPL ALEGSLQKR GIVEQCCTSI CSLYQLENYC N UniProtKB: Insulin |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.3 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.8 Component:
| ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Homemade / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Support film - Film thickness: 10 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 10 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: OTHER / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.001 kPa | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 85 % / Chamber temperature: 298 K / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER Details: The cryo grids were made using Spotiton and homemade plunger. | ||||||||||||
| Details | The sample was monodisperse |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Min: 70.0 K / Max: 70.0 K |
| Alignment procedure | Coma free - Residual tilt: 10.0 mrad |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 3710 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 3838 pixel / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-50 / Number grids imaged: 3 / Number real images: 3085 / Average exposure time: 10.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 71.4 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Calibrated magnification: 46598 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.9400000000000001 µm / Nominal magnification: 22500 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Overall B value: 92 |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6b70: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)