+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8vuy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Rat GluN1-2B with Fab 003-102 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Channel / heterotetramer / receptor / antibody | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcellular response to curcumin / cellular response to corticosterone stimulus / cellular response to magnesium starvation / sensory organ development / positive regulation of Schwann cell migration / pons maturation / regulation of cell communication / regulation of cAMP/PKA signal transduction / sensitization / EPHB-mediated forward signaling ...cellular response to curcumin / cellular response to corticosterone stimulus / cellular response to magnesium starvation / sensory organ development / positive regulation of Schwann cell migration / pons maturation / regulation of cell communication / regulation of cAMP/PKA signal transduction / sensitization / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors / response to hydrogen sulfide / auditory behavior / olfactory learning / conditioned taste aversion / dendritic branch / regulation of respiratory gaseous exchange / regulation of ARF protein signal transduction / fear response / response to other organism / apical dendrite / protein localization to postsynaptic membrane / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / positive regulation of inhibitory postsynaptic potential / response to methylmercury / suckling behavior / response to manganese ion / response to glycine / response to carbohydrate / interleukin-1 receptor binding / propylene metabolic process / cellular response to dsRNA / cellular response to lipid / negative regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / response to growth hormone / heterocyclic compound binding / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / positive regulation of glutamate secretion / regulation of monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / NMDA glutamate receptor activity / response to amine / Synaptic adhesion-like molecules / response to glycoside / voltage-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / NMDA selective glutamate receptor complex / glutamate binding / neurotransmitter receptor complex / ligand-gated sodium channel activity / regulation of axonogenesis / calcium ion transmembrane import into cytosol / neuromuscular process / response to morphine / regulation of dendrite morphogenesis / protein heterotetramerization / male mating behavior / regulation of synapse assembly / glycine binding / small molecule binding / receptor clustering / startle response / positive regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse / behavioral response to pain / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / monoatomic ion channel complex / regulation of MAPK cascade / positive regulation of calcium ion transport into cytosol / regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / cellular response to glycine / response to magnesium ion / action potential / extracellularly glutamate-gated ion channel activity / response to electrical stimulus / associative learning / positive regulation of dendritic spine maintenance / regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity / monoatomic cation transport / social behavior / glutamate receptor binding / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / prepulse inhibition / long-term memory / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain / response to mechanical stimulus / neuron development / phosphatase binding / multicellular organismal response to stress / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / postsynaptic density, intracellular component / behavioral fear response / synaptic cleft / monoatomic cation channel activity / calcium ion homeostasis / response to fungicide / glutamate-gated receptor activity / regulation of long-term synaptic depression / cellular response to manganese ion / D2 dopamine receptor binding / glutamate-gated calcium ion channel activity / presynaptic active zone membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.81 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Michalski, K. / Furukawa, H. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024Title: Structural and functional mechanisms of anti-NMDAR autoimmune encephalitis. Authors: Kevin Michalski / Taha Abdulla / Sam Kleeman / Lars Schmidl / Ricardo Gómez / Noriko Simorowski / Francesca Vallese / Harald Prüss / Manfred Heckmann / Christian Geis / Hiro Furukawa /   Abstract: Autoantibodies against neuronal membrane proteins can manifest in autoimmune encephalitis, inducing seizures, cognitive dysfunction and psychosis. Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) ...Autoantibodies against neuronal membrane proteins can manifest in autoimmune encephalitis, inducing seizures, cognitive dysfunction and psychosis. Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) encephalitis is the most dominant autoimmune encephalitis; however, insights into how autoantibodies recognize and alter receptor functions remain limited. Here we determined structures of human and rat NMDARs bound to three distinct patient-derived antibodies using single-particle electron cryo-microscopy. These antibodies bind different regions within the amino-terminal domain of the GluN1 subunit. Through electrophysiology, we show that all three autoantibodies acutely and directly reduced NMDAR channel functions in primary neurons. Antibodies show different stoichiometry of binding and antibody-receptor complex formation, which in one antibody, 003-102, also results in reduced synaptic localization of NMDARs. These studies demonstrate mechanisms of diverse epitope recognition and direct channel regulation of anti-NMDAR autoantibodies underlying autoimmune encephalitis. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8vuy.cif.gz 8vuy.cif.gz | 625.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8vuy.ent.gz pdb8vuy.ent.gz | 490.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8vuy.json.gz 8vuy.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vu/8vuy https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vu/8vuy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vu/8vuy ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vu/8vuy | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  43544MC  8vuhC  8vujC  8vulC  8vunC  8vuqC  8vurC  8vusC  8vutC  8vuuC  8vuvC 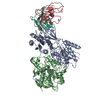 8vvhC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 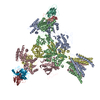
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 91944.094 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Protein | Mass: 91269.125 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #3: Antibody | Mass: 12477.862 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)#4: Antibody | Mass: 11582.475 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Rat GluN1-2B with Fab 003-102 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: OTHER |
| Electron lens | Mode: OTHER / Nominal defocus max: 2200 nm / Nominal defocus min: 800 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.81 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 516895 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj





