+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human GluN1-2A with Fab 003-102 Local refinement of ATD | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Channel / heterotetramer / receptor / antibody / MEMBRANE PROTEIN-IMMUNE SYSTEM complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationglycine-gated cation channel activity / excitatory chemical synaptic transmission / directional locomotion / Synaptic adhesion-like molecules / protein localization to postsynaptic membrane / serotonin metabolic process / sleep / propylene metabolic process / response to glycine / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors ...glycine-gated cation channel activity / excitatory chemical synaptic transmission / directional locomotion / Synaptic adhesion-like molecules / protein localization to postsynaptic membrane / serotonin metabolic process / sleep / propylene metabolic process / response to glycine / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors / regulation of monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / Neurexins and neuroligins / NMDA glutamate receptor activity / NMDA selective glutamate receptor complex / glutamate binding / neurotransmitter receptor complex / ligand-gated sodium channel activity / glutamate receptor signaling pathway / calcium ion transmembrane import into cytosol / protein heterotetramerization / glycine binding / startle response / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / positive regulation of reactive oxygen species biosynthetic process / dopamine metabolic process / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / monoatomic cation transmembrane transport / positive regulation of calcium ion transport into cytosol / Long-term potentiation / regulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity / monoatomic cation transport / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / synaptic cleft / calcium ion homeostasis / MECP2 regulates neuronal receptors and channels / glutamate-gated calcium ion channel activity / EPHB-mediated forward signaling / neurogenesis / excitatory synapse / sensory perception of pain / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / synaptic membrane / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / sodium ion transmembrane transport / response to amphetamine / protein catabolic process / excitatory postsynaptic potential / regulation of membrane potential / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / negative regulation of protein catabolic process / regulation of synaptic plasticity / brain development / visual learning / postsynaptic density membrane / response to wounding / calcium ion transmembrane transport / memory / terminal bouton / synaptic vesicle / long-term synaptic potentiation / signaling receptor activity / amyloid-beta binding / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / presynaptic membrane / dendritic spine / response to ethanol / chemical synaptic transmission / learning or memory / postsynaptic membrane / calmodulin binding / neuron projection / postsynaptic density / positive regulation of apoptotic process / response to xenobiotic stimulus / calcium ion binding / dendrite / synapse / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / protein-containing complex binding / glutamatergic synapse / cell surface / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / zinc ion binding / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.83 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Michalski K / Furukawa H | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2024Title: Structural and functional mechanisms of anti-NMDAR autoimmune encephalitis. Authors: Kevin Michalski / Taha Abdulla / Sam Kleeman / Lars Schmidl / Ricardo Gómez / Noriko Simorowski / Francesca Vallese / Harald Prüss / Manfred Heckmann / Christian Geis / Hiro Furukawa /   Abstract: Autoantibodies against neuronal membrane proteins can manifest in autoimmune encephalitis, inducing seizures, cognitive dysfunction and psychosis. Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) ...Autoantibodies against neuronal membrane proteins can manifest in autoimmune encephalitis, inducing seizures, cognitive dysfunction and psychosis. Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) encephalitis is the most dominant autoimmune encephalitis; however, insights into how autoantibodies recognize and alter receptor functions remain limited. Here we determined structures of human and rat NMDARs bound to three distinct patient-derived antibodies using single-particle electron cryo-microscopy. These antibodies bind different regions within the amino-terminal domain of the GluN1 subunit. Through electrophysiology, we show that all three autoantibodies acutely and directly reduced NMDAR channel functions in primary neurons. Antibodies show different stoichiometry of binding and antibody-receptor complex formation, which in one antibody, 003-102, also results in reduced synaptic localization of NMDARs. These studies demonstrate mechanisms of diverse epitope recognition and direct channel regulation of anti-NMDAR autoantibodies underlying autoimmune encephalitis. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_43532.map.gz emd_43532.map.gz | 230.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-43532-v30.xml emd-43532-v30.xml emd-43532.xml emd-43532.xml | 20.9 KB 20.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_43532.png emd_43532.png | 66.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-43532.cif.gz emd-43532.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_43532_half_map_1.map.gz emd_43532_half_map_1.map.gz emd_43532_half_map_2.map.gz emd_43532_half_map_2.map.gz | 226.5 MB 226.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43532 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43532 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43532 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43532 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8vulMC  8vuhC  8vujC  8vunC  8vuqC  8vurC  8vusC  8vutC  8vuuC  8vuvC  8vuyC  8vvhC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_43532.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_43532.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.1 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
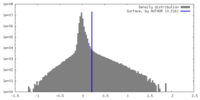
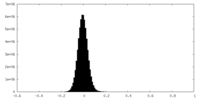
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_43532_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
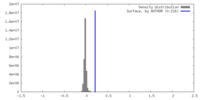
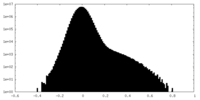
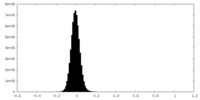
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_43532_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
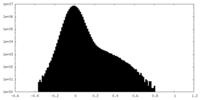
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human GluN1-2A with Fab 003-102 Local refinement of ATD
| Entire | Name: Human GluN1-2A with Fab 003-102 Local refinement of ATD |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human GluN1-2A with Fab 003-102 Local refinement of ATD
| Supramolecule | Name: Human GluN1-2A with Fab 003-102 Local refinement of ATD type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.267938 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: KIVNIGAVLS TRKHEQMFRE AVNQANKRHG SWKIQLNATS VTHKPNAIQM ALSVCEDLIS SQVYAILVSH PPTPNDHFTP TPVSYTAGF YRIPVLGLTT RMSIYSDKSI HLSFLRTVPP YSHQSSVWFE MMRVYSWNHI ILLVSDDHEG RAAQKRLETL L EERESKAE ...String: KIVNIGAVLS TRKHEQMFRE AVNQANKRHG SWKIQLNATS VTHKPNAIQM ALSVCEDLIS SQVYAILVSH PPTPNDHFTP TPVSYTAGF YRIPVLGLTT RMSIYSDKSI HLSFLRTVPP YSHQSSVWFE MMRVYSWNHI ILLVSDDHEG RAAQKRLETL L EERESKAE KVLQFDPGTK NVTALLMEAK ELEARVIILS ASEDDAATVY RAAAMLNMTG SGYVWLVGER EISGNALRYA PD GILGLQL INGKNESAHI SDAVGVVAQA VHELLEKENI TDPPRGCVGN TNIWKTGPLF KRVLMSSKYA DGVTGRVEFN EDG DRKFAN YSIMNLQNRK LVQVGIYNGT HVIPNDRKII WPGGETEKPR GYQ UniProtKB: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2A
| Macromolecule | Name: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 41.29502 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: LNIAVMLGHS HDVTERELRT LWGPEQAAGL PLDVNVVALL MNRTDPKSLI THVCDLMSGA RIHGLVFGDD TDQEAVAQML DFISSHTFV PILGIHGGAS MIMADKDPTS TFFQFGASIQ QQATVMLKIM QDYDWHVFSL VTTIFPGYRE FISFVKTTVD N SFVGWDMQ ...String: LNIAVMLGHS HDVTERELRT LWGPEQAAGL PLDVNVVALL MNRTDPKSLI THVCDLMSGA RIHGLVFGDD TDQEAVAQML DFISSHTFV PILGIHGGAS MIMADKDPTS TFFQFGASIQ QQATVMLKIM QDYDWHVFSL VTTIFPGYRE FISFVKTTVD N SFVGWDMQ NVITLDTSFE DAKTQVQLKK IHSSVILLYC SKDEAVLILS EARSLGLTGY DFFWIVPSLV SGNTELIPKE FP SGLISVS YDDWDYSLEA RVRDGIGILT TAASSMLEKF SYIPEAKASC YGQMERPEVP MHTLHPFMVN VTWDGKDLSF TEE GYQVHP RLVVIVLNKD REWEKVGKWE NHTLSLRHAV WPRYKSFSDC UniProtKB: Glutamate receptor ionotropic, NMDA 2A |
-Macromolecule #3: 003-102 Heavy
| Macromolecule | Name: 003-102 Heavy / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 12.852252 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: LQLQESGPGL VKPSQTLSLT CTVSGGSISS SNWWSWVRQP PGKGLEWIGE IYHSGNTNYN PSLKSRVTVS VDKSKNQFSL KLTSVTAAD TAVYYCARDV SGGVNWFDPW GQGTLVTVSS |
-Macromolecule #4: 003-102 Light
| Macromolecule | Name: 003-102 Light / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.681605 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: NFMLTQPHSV SESPGKTVTI SCTRSSGSIA SNYVQWYQQR PGSAPTTVIY EDNQRPSGVP DRFSGSIDSS SNSASLTISG LKTEDEADY YCQSYDSSTV VFGGGTKLTV |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: OTHER / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)