[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
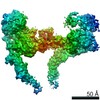
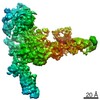
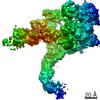
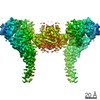
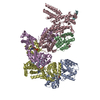
Yorodumi- PDB-7mo9: Cryo-EM map of the c-MET II/HGF I/HGF II (K4 and SPH) sub-complex -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7mo9 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM map of the c-MET II/HGF I/HGF II (K4 and SPH) sub-complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / c-MET / HGF / receptor tyrosine kinase | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of p38MAPK cascade / skeletal muscle cell proliferation / negative regulation of guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / hepatocyte growth factor receptor activity / regulation of branching involved in salivary gland morphogenesis by mesenchymal-epithelial signaling / Drug-mediated inhibition of MET activation / MET activates STAT3 / negative regulation of hydrogen peroxide-mediated programmed cell death / MET Receptor Activation / MET interacts with TNS proteins ...regulation of p38MAPK cascade / skeletal muscle cell proliferation / negative regulation of guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity / hepatocyte growth factor receptor activity / regulation of branching involved in salivary gland morphogenesis by mesenchymal-epithelial signaling / Drug-mediated inhibition of MET activation / MET activates STAT3 / negative regulation of hydrogen peroxide-mediated programmed cell death / MET Receptor Activation / MET interacts with TNS proteins / endothelial cell morphogenesis / hepatocyte growth factor receptor signaling pathway / semaphorin receptor activity / MET receptor recycling / pancreas development / MET activates PTPN11 / MET activates RAP1 and RAC1 / Sema4D mediated inhibition of cell attachment and migration / MET activates PI3K/AKT signaling / positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis / negative regulation of stress fiber assembly / MET activates PTK2 signaling / positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process / cellular response to hepatocyte growth factor stimulus / positive chemotaxis / branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube / negative regulation of Rho protein signal transduction / negative regulation of release of cytochrome c from mitochondria / chemoattractant activity / negative regulation of thrombin-activated receptor signaling pathway / semaphorin-plexin signaling pathway / negative regulation of interleukin-6 production / myoblast proliferation / positive regulation of interleukin-10 production / epithelial to mesenchymal transition / establishment of skin barrier / positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in cell cycle and proliferation / MET activates RAS signaling / negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors / MECP2 regulates neuronal receptors and channels / positive regulation of microtubule polymerization / Interleukin-7 signaling / negative regulation of autophagy / cell surface receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway / basal plasma membrane / platelet alpha granule lumen / molecular function activator activity / epithelial cell proliferation / InlB-mediated entry of Listeria monocytogenes into host cell / cell chemotaxis / excitatory postsynaptic potential / growth factor activity / liver development / receptor protein-tyrosine kinase / Negative regulation of MET activity / negative regulation of inflammatory response / cell morphogenesis / neuron differentiation / Constitutive Signaling by Aberrant PI3K in Cancer / Platelet degranulation / PIP3 activates AKT signaling / mitotic cell cycle / PI5P, PP2A and IER3 Regulate PI3K/AKT Signaling / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / protein tyrosine kinase activity / Interleukin-4 and Interleukin-13 signaling / protein phosphatase binding / cell surface receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction / receptor complex / positive regulation of MAPK cascade / postsynapse / positive regulation of cell migration / signaling receptor binding / negative regulation of apoptotic process / cell surface / signal transduction / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / extracellular space / extracellular region / ATP binding / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Uchikawa, E. / Chen, Z.M. / Xiao, G.Y. / Zhang, X.W. / Bai, X.C. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Structural basis of the activation of c-MET receptor. Authors: Emiko Uchikawa / Zhiming Chen / Guan-Yu Xiao / Xuewu Zhang / Xiao-Chen Bai /   Abstract: The c-MET receptor is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) that plays essential roles in normal cell development and motility. Aberrant activation of c-MET can lead to both tumors growth and metastatic ...The c-MET receptor is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) that plays essential roles in normal cell development and motility. Aberrant activation of c-MET can lead to both tumors growth and metastatic progression of cancer cells. C-MET can be activated by either hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), or its natural isoform NK1. Here, we report the cryo-EM structures of c-MET/HGF and c-MET/NK1 complexes in the active state. The c-MET/HGF complex structure reveals that, by utilizing two distinct interfaces, one HGF molecule is sufficient to induce a specific dimerization mode of c-MET for receptor activation. The binding of heparin as well as a second HGF to the 2:1 c-MET:HGF complex further stabilize this active conformation. Distinct to HGF, NK1 forms a stable dimer, and bridges two c-METs in a symmetrical manner for activation. Collectively, our studies provide structural insights into the activation mechanisms of c-MET, and reveal how two isoforms of the same ligand use dramatically different mechanisms to activate the receptor. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7mo9.cif.gz 7mo9.cif.gz | 272.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7mo9.ent.gz pdb7mo9.ent.gz | 188.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7mo9.json.gz 7mo9.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mo/7mo9 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mo/7mo9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mo/7mo9 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mo/7mo9 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  23921MC  7mo7C  7mo8C  7moaC  7mobC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 83249.828 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HGF, HPTA / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HGF, HPTA / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P14210 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P14210#2: Protein | | Mass: 155720.625 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MET / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MET / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P08581, receptor protein-tyrosine kinase #3: Polysaccharide | 2-O-sulfo-alpha-L-idopyranuronic acid-(1-4)-2-deoxy-6-O-sulfo-2-(sulfoamino)-alpha-D-glucopyranose- ...2-O-sulfo-alpha-L-idopyranuronic acid-(1-4)-2-deoxy-6-O-sulfo-2-(sulfoamino)-alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-O-sulfo-alpha-L-idopyranuronic acid-(1-4)-2-deoxy-6-O-sulfo-2-(sulfoamino)-alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-O-sulfo-alpha-L-idopyranuronic acid-(1-4)-2-deoxy-6-O-sulfo-2-(sulfoamino)-alpha-D-glucopyranose | Has ligand of interest | Y | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: c-MET II/HGF I/HGF II (K4 and SPH) sub-complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 45471 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj












