+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7kue | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
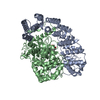
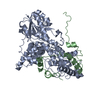
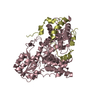
| Title | CryoEM structure of Yeast TFIIK (Kin28/Ccl1/Tfb3) Complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSCRIPTION/Transferase / Polymerase CTD / TFIIH / Phosphorylation / Kinase / CDK / Cyclin / TRANSCRIPTION-Transferase complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of Atg1/ULK1 kinase complex assembly / transcription factor TFIIK complex / transcription factor TFIIH holo complex / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / [RNA-polymerase]-subunit kinase / cellular response to nitrogen starvation / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / mRNA Capping ...positive regulation of Atg1/ULK1 kinase complex assembly / transcription factor TFIIK complex / transcription factor TFIIH holo complex / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / [RNA-polymerase]-subunit kinase / cellular response to nitrogen starvation / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / RNA Pol II CTD phosphorylation and interaction with CE / Formation of the Early Elongation Complex / mRNA Capping / RNA polymerase II transcribes snRNA genes / TP53 Regulates Transcription of DNA Repair Genes / RNA Polymerase II Promoter Escape / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Pre-Initiation And Promoter Opening / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation / RNA Polymerase II Transcription Initiation And Promoter Clearance / RNA Polymerase II Pre-transcription Events / Formation of TC-NER Pre-Incision Complex / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Gap-filling DNA repair synthesis and ligation in TC-NER / Dual incision in TC-NER / 7-methylguanosine mRNA capping / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / transcription by RNA polymerase I / RNA polymerase II CTD heptapeptide repeat kinase activity / positive regulation of autophagy / nucleotide-excision repair / transcription initiation at RNA polymerase II promoter / positive regulation of transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein kinase activity / regulation of cell cycle / cell division / DNA repair / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / mitochondrion / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | van Eeuwen, T. / Murakami, K. / Li, T. / Tsai, K.L. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2021 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2021Title: Structure of TFIIK for phosphorylation of CTD of RNA polymerase II. Authors: Trevor van Eeuwen / Tao Li / Hee Jong Kim / Jose J Gorbea Colón / Mitchell I Parker / Roland L Dunbrack / Benjamin A Garcia / Kuang-Lei Tsai / Kenji Murakami /  Abstract: During transcription initiation, the general transcription factor TFIIH marks RNA polymerase II by phosphorylating Ser5 of the carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) of Rpb1, which is followed by extensive ...During transcription initiation, the general transcription factor TFIIH marks RNA polymerase II by phosphorylating Ser5 of the carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) of Rpb1, which is followed by extensive modifications coupled to transcription elongation, mRNA processing, and histone dynamics. We have determined a 3.5-Å resolution cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the TFIIH kinase module (TFIIK in yeast), which is composed of Kin28, Ccl1, and Tfb3, yeast homologs of CDK7, cyclin H, and MAT1, respectively. The carboxyl-terminal region of Tfb3 was lying at the edge of catalytic cleft of Kin28, where a conserved Tfb3 helix served to stabilize the activation loop in its active conformation. By combining the structure of TFIIK with the previous cryo-EM structure of the preinitiation complex, we extend the previously proposed model of the CTD path to the active site of TFIIK. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7kue.cif.gz 7kue.cif.gz | 130.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7kue.ent.gz pdb7kue.ent.gz | 92.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7kue.json.gz 7kue.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ku/7kue https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ku/7kue ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ku/7kue ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ku/7kue | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  23036MC  6xi8C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 38128.355 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: Q03290 |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 35369.867 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c References: UniProt: P06242, [RNA-polymerase]-subunit kinase |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 45259.414 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source Source: (natural)  Strain: ATCC 204508 / S288c / References: UniProt: P37366 |
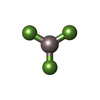
| #4: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / |
| #5: Chemical | ChemComp-AF3 / |
| Has ligand of interest | N |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Ternary complex of Kin28-Ccl1-Tfb3 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Type: COMPLEX Details: the yeast Cdk7 complex, that phosphorylates the RNA pol II C-terminal domain (CTD) in transcription initiation. Entity ID: #1-#3 / Source: NATURAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.073 MDa / Experimental value: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) | Organism:  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.08 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA EM CPC / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 0 % / Chamber temperature: 293 K Details: blotted for 2 seconds with Whatman 41 ashless filter paper |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 105000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2800 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 2.24 sec. / Electron dose: 45 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 4620 Details: Images collected in super-resolution mode. Movies were 35 frames. Imaging 1 image/hole, image shift between 4 holes. Focus once per image shift |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.18.1_3865: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Image processing | Details: Movies collected in super resolution mode and binned during motion correction by MotionCorr2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 3288475 Details: small particle set picked by blob used to generate 2D references used for large scale particle picking | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 81466 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj