[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-7khr: Cryo-EM structure of bafilomycin A1-bound intact V-ATPase from bo... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7khr | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
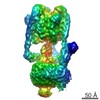
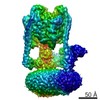
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of bafilomycin A1-bound intact V-ATPase from bovine brain | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTON TRANSPORT / bafilomycin A1 | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Insulin receptor recycling / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Ion channel transport / Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / plasma membrane proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / pH reduction / RHOA GTPase cycle / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification ...ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Insulin receptor recycling / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Ion channel transport / Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / plasma membrane proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / pH reduction / RHOA GTPase cycle / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / vacuolar transport / cellular response to increased oxygen levels / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V1 domain / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / clathrin-coated vesicle membrane / lysosomal lumen acidification / endosomal lumen acidification / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / cell projection organization / vacuolar acidification / regulation of cellular pH / dendritic spine membrane / Neutrophil degranulation / ATPase activator activity / autophagosome membrane / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / cilium assembly / regulation of macroautophagy / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / ATP metabolic process / H+-transporting two-sector ATPase / transport vesicle / receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell / endomembrane system / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / RNA endonuclease activity / proton transmembrane transport / receptor-mediated endocytosis / transmembrane transport / endocytosis / melanosome / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / synaptic vesicle membrane / signaling receptor activity / ATPase binding / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / early endosome / postsynaptic membrane / lysosome / apical plasma membrane / endosome / endosome membrane / cilium / nuclear speck / hydrolase activity / axon / external side of plasma membrane / lysosomal membrane / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / Golgi apparatus / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.62 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang, R. / Li, X. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Molecular basis of V-ATPase inhibition by bafilomycin A1. Authors: Rong Wang / Jin Wang / Abdirahman Hassan / Chia-Hsueh Lee / Xiao-Song Xie / Xiaochun Li /  Abstract: Pharmacological inhibition of vacuolar-type H-ATPase (V-ATPase) by its specific inhibitor can abrogate tumor metastasis, prevent autophagy, and reduce cellular signaling responses. Bafilomycin A1, a ...Pharmacological inhibition of vacuolar-type H-ATPase (V-ATPase) by its specific inhibitor can abrogate tumor metastasis, prevent autophagy, and reduce cellular signaling responses. Bafilomycin A1, a member of macrolide antibiotics and an autophagy inhibitor, serves as a specific and potent V-ATPases inhibitor. Although there are many V-ATPase structures reported, the molecular basis of specific inhibitors on V-ATPase remains unknown. Here, we report the cryo-EM structure of bafilomycin A1 bound intact bovine V-ATPase at an overall resolution of 3.6-Å. The structure reveals six bafilomycin A1 molecules bound to the c-ring. One bafilomycin A1 molecule engages with two c subunits and disrupts the interactions between the c-ring and subunit a, thereby preventing proton translocation. Structural and sequence analyses demonstrate that the bafilomycin A1-binding residues are conserved in yeast and mammalian species and the 7'-hydroxyl group of bafilomycin A1 acts as a unique feature recognized by subunit c. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7khr.cif.gz 7khr.cif.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7khr.ent.gz pdb7khr.ent.gz | 1.1 MB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7khr.json.gz 7khr.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kh/7khr https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kh/7khr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kh/7khr ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/kh/7khr | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  22880MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-V-type proton ATPase ... , 14 types, 30 molecules ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPabdescgklmnopq
| #1: Protein | Mass: 68420.914 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: P31404, H+-transporting two-sector ATPase #2: Protein | Mass: 56637.555 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #3: Protein | | Mass: 44042.566 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #4: Protein | | Mass: 28297.893 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #5: Protein | Mass: 26178.371 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #6: Protein | | Mass: 13417.275 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #7: Protein | Mass: 13588.344 Da / Num. of mol.: 3 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #8: Protein | | Mass: 54155.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #9: Protein | | Mass: 96431.398 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #10: Protein | | Mass: 21530.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #11: Protein | | Mass: 40369.949 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #12: Protein | | Mass: 9188.992 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #13: Protein | | Mass: 51818.754 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #15: Protein | Mass: 15727.726 Da / Num. of mol.: 9 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|
-Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules rf
| #14: Protein | Mass: 39529.266 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #16: Protein | Mass: 11030.029 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  References: UniProt: Q3ZC23, Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds |
-Sugars , 3 types, 9 molecules 
| #17: Polysaccharide | alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D- ...alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-glucopyranose-(1-3)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-2)-alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-3)-beta-D-mannopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose-(1-4)-2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose |
|---|---|
| #18: Polysaccharide | alpha-D-mannopyranose-(1-6)-alpha-D-mannopyranose |
| #23: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / |
-Non-polymers , 6 types, 18 molecules 







| #19: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #20: Chemical | ChemComp-ADP / | ||||
| #21: Chemical | ChemComp-WJP / | ||||
| #22: Chemical | ChemComp-POV / ( #24: Chemical | ChemComp-OLA / | #25: Chemical | ChemComp-WEV / ( |
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Cryo-EM structure of bafilomycin A1-bound intact V-ATPase from bovine brain Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#16 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 60 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING ONLY |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.62 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 26530 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj













