[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6wqz: Structure of human ATG9A, the only transmembrane protein of the c... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6wqz | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
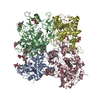
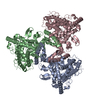
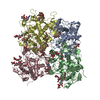
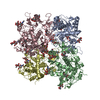
| Title | Structure of human ATG9A, the only transmembrane protein of the core autophagy machinery | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Autophagy-related protein 9A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / TG9A / autophagosome / autophagy / cryoEM / molecular dynamics / transmembrane protein / membranecurvature / cellular compartments / membrane morphology / lipids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of macrophage cytokine production / phospholipid scramblase activity / protein localization to Golgi apparatus / programmed necrotic cell death / protein localization to phagophore assembly site / phagophore assembly site membrane / piecemeal microautophagy of the nucleus / negative regulation of interferon-beta production / bone morphogenesis / phagophore assembly site ...negative regulation of macrophage cytokine production / phospholipid scramblase activity / protein localization to Golgi apparatus / programmed necrotic cell death / protein localization to phagophore assembly site / phagophore assembly site membrane / piecemeal microautophagy of the nucleus / negative regulation of interferon-beta production / bone morphogenesis / phagophore assembly site / reticulophagy / Macroautophagy / autophagosome assembly / mitophagy / autophagosome / synaptic membrane / PINK1-PRKN Mediated Mitophagy / trans-Golgi network / recycling endosome / mitochondrial membrane / recycling endosome membrane / late endosome membrane / late endosome / endosome / Golgi membrane / innate immune response / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / Golgi apparatus / mitochondrion / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Guardia, C.M. / Tan, X. / Lian, T. / Rana, M.S. / Zhou, W. / Christenson, E.T. / Lowry, A.J. / Faraldo-Gomez, J.D. / Bonifacino, J.S. / Jiang, J. / Banerjee, A. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2020 Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2020Title: Structure of Human ATG9A, the Only Transmembrane Protein of the Core Autophagy Machinery. Authors: Carlos M Guardia / Xiao-Feng Tan / Tengfei Lian / Mitra S Rana / Wenchang Zhou / Eric T Christenson / Augustus J Lowry / José D Faraldo-Gómez / Juan S Bonifacino / Jiansen Jiang / Anirban Banerjee /  Abstract: Autophagy is a catabolic process involving capture of cytoplasmic materials into double-membraned autophagosomes that subsequently fuse with lysosomes for degradation of the materials by lysosomal ...Autophagy is a catabolic process involving capture of cytoplasmic materials into double-membraned autophagosomes that subsequently fuse with lysosomes for degradation of the materials by lysosomal hydrolases. One of the least understood components of the autophagy machinery is the transmembrane protein ATG9. Here, we report a cryoelectron microscopy structure of the human ATG9A isoform at 2.9-Å resolution. The structure reveals a fold with a homotrimeric domain-swapped architecture, multiple membrane spans, and a network of branched cavities, consistent with ATG9A being a membrane transporter. Mutational analyses support a role for the cavities in the function of ATG9A. In addition, structure-guided molecular simulations predict that ATG9A causes membrane bending, explaining the localization of this protein to small vesicles and highly curved edges of growing autophagosomes. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6wqz.cif.gz 6wqz.cif.gz | 348.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6wqz.ent.gz pdb6wqz.ent.gz | 268 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6wqz.json.gz 6wqz.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wq/6wqz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wq/6wqz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wq/6wqz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wq/6wqz | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21874MC  6wr4C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 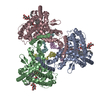
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 81095.531 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ATG9A, APG9L1 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: ATG9A, APG9L1 / Cell line (production host): HEK293T / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q7Z3C6 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q7Z3C6#2: Chemical | ChemComp-LMN / Has ligand of interest | N | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Autophagy Related 9A with LMNG / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / C2 aperture diameter: 70 µm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 57 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 593720 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso max: 93.38 Å2 / Biso mean: 33.5636 Å2 / Biso min: 7.76 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj