[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6wjf: PKA RIIbeta holoenzyme with DnaJB1-PKAc fusion in fibrolamellar h... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6wjf | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
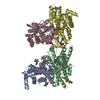
| Title | PKA RIIbeta holoenzyme with DnaJB1-PKAc fusion in fibrolamellar hepatoceullar carcinoma | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SIGNALING PROTEIN / fibrolamellar hepatoceullar carcinoma / PKA / cAMP / Kinase | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationPKA activation in glucagon signalling / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / DARPP-32 events / : / GPER1 signaling / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane ...PKA activation in glucagon signalling / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / DARPP-32 events / : / GPER1 signaling / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / Hedgehog 'off' state / PKA activation / PKA-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / PKA-mediated phosphorylation of key metabolic factors / cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulator activity / ROBO receptors bind AKAP5 / sperm head / HDL assembly / negative regulation of inclusion body assembly / channel activator activity / mitochondrial protein catabolic process / Regulation of glycolysis by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate metabolism / nucleotide-activated protein kinase complex / response to antipsychotic drug / cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / high-density lipoprotein particle assembly / Rap1 signalling / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / negative regulation of cAMP/PKA signal transduction / Vasopressin regulates renal water homeostasis via Aquaporins / cAMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor activity / cAMP-dependent protein kinase / regulation of protein processing / cAMP-dependent protein kinase activity / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / protein localization to lipid droplet / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / regulation of bicellular tight junction assembly / cAMP-dependent protein kinase complex / cellular response to parathyroid hormone stimulus / PKA activation / negative regulation of interleukin-2 production / regulation of osteoblast differentiation / cellular response to cold / sperm capacitation / negative regulation of glycolytic process through fructose-6-phosphate / ciliary base / Triglyceride catabolism / protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding / protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding / forebrain development / intracellular potassium ion homeostasis / ATPase activator activity / : / mesoderm formation / RET signaling / cAMP/PKA signal transduction / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / Interleukin-3, Interleukin-5 and GM-CSF signaling / plasma membrane raft / PKA activation in glucagon signalling / DARPP-32 events / regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / regulation of cardiac conduction / HSF1-dependent transactivation / Regulation of HSF1-mediated heat shock response / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / response to unfolded protein / regulation of macroautophagy / sperm flagellum / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / Attenuation phase / postsynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / vascular endothelial cell response to laminar fluid shear stress / renal water homeostasis / cAMP binding / transcription regulator inhibitor activity / Hedgehog 'off' state / regulation of cellular response to heat / Ion homeostasis / sperm midpiece / negative regulation of TORC1 signaling / Hsp70 protein binding / cellular response to epinephrine stimulus / calcium channel complex / positive regulation of gluconeogenesis / Mitochondrial protein degradation / protein folding chaperone / protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity / cellular response to glucagon stimulus / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / CD209 (DC-SIGN) signaling / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / acrosomal vesicle / positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / regulation of heart rate Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 7.5 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lu, T.-W. / Aoto, P.C. / Weng, J.-H. / Nielsen, C. / Cash, J.N. / Hall, J. / Zhang, P. / Simon, S.M. / Cianfrocco, M.A. / Taylor, S.S. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3items United States, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: PLoS Biol / Year: 2020 Journal: PLoS Biol / Year: 2020Title: Structural analyses of the PKA RIIβ holoenzyme containing the oncogenic DnaJB1-PKAc fusion protein reveal protomer asymmetry and fusion-induced allosteric perturbations in fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma. Authors: Tsan-Wen Lu / Phillip C Aoto / Jui-Hung Weng / Cole Nielsen / Jennifer N Cash / James Hall / Ping Zhang / Sanford M Simon / Michael A Cianfrocco / Susan S Taylor /  Abstract: When the J-domain of the heat shock protein DnaJB1 is fused to the catalytic (C) subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), replacing exon 1, this fusion protein, J-C subunit (J-C), becomes the ...When the J-domain of the heat shock protein DnaJB1 is fused to the catalytic (C) subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA), replacing exon 1, this fusion protein, J-C subunit (J-C), becomes the driver of fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma (FL-HCC). Here, we use cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to characterize J-C bound to RIIβ, the major PKA regulatory (R) subunit in liver, thus reporting the first cryo-EM structure of any PKA holoenzyme. We report several differences in both structure and dynamics that could not be captured by the conventional crystallography approaches used to obtain prior structures. Most striking is the asymmetry caused by the absence of the second cyclic nucleotide binding (CNB) domain and the J-domain in one of the RIIβ:J-C protomers. Using molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, we discovered that this asymmetry is already present in the wild-type (WT) RIIβ2C2 but had been masked in the previous crystal structure. This asymmetry may link to the intrinsic allosteric regulation of all PKA holoenzymes and could also explain why most disease mutations in PKA regulatory subunits are dominant negative. The cryo-EM structure, combined with small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), also allowed us to predict the general position of the Dimerization/Docking (D/D) domain, which is essential for localization and interacting with membrane-anchored A-Kinase-Anchoring Proteins (AKAPs). This position provides a multivalent mechanism for interaction of the RIIβ holoenzyme with membranes and would be perturbed in the oncogenic fusion protein. The J-domain also alters several biochemical properties of the RIIβ holoenzyme: It is easier to activate with cAMP, and the cooperativity is reduced. These results provide new insights into how the finely tuned allosteric PKA signaling network is disrupted by the oncogenic J-C subunit, ultimately leading to the development of FL-HCC. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6wjf.cif.gz 6wjf.cif.gz | 401.5 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6wjf.ent.gz pdb6wjf.ent.gz | 330.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6wjf.json.gz 6wjf.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6wjf_validation.pdf.gz 6wjf_validation.pdf.gz | 750.2 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6wjf_full_validation.pdf.gz 6wjf_full_validation.pdf.gz | 757 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6wjf_validation.xml.gz 6wjf_validation.xml.gz | 34 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6wjf_validation.cif.gz 6wjf_validation.cif.gz | 51.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wj/6wjf https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wj/6wjf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wj/6wjf ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wj/6wjf | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 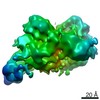 21692MC  6wjgC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 47337.984 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DNAJB1, DNAJ1, HDJ1, HSPF1, PRKACA, PKACA / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DNAJB1, DNAJ1, HDJ1, HSPF1, PRKACA, PKACA / Production host:  References: UniProt: P25685, UniProt: P17612, cAMP-dependent protein kinase #2: Protein | Mass: 46177.852 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source (natural) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 5.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 80 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) |
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 7.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 11182 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj