[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
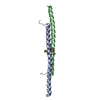
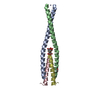
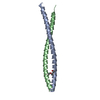
Yorodumi- PDB-6w0o: Amyloid-beta(1-40) fibril derived from Alzheimer's disease cortic... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6w0o | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Amyloid-beta(1-40) fibril derived from Alzheimer's disease cortical tissue | ||||||
 Components Components | Amyloid-beta precursor protein | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | PROTEIN FIBRIL / amyloid-beta / Alzheimer's disease | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationamyloid-beta complex / growth cone lamellipodium / cellular response to norepinephrine stimulus / growth cone filopodium / microglia development / collateral sprouting in absence of injury / Formyl peptide receptors bind formyl peptides and many other ligands / axo-dendritic transport / regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / regulation of synapse structure or activity ...amyloid-beta complex / growth cone lamellipodium / cellular response to norepinephrine stimulus / growth cone filopodium / microglia development / collateral sprouting in absence of injury / Formyl peptide receptors bind formyl peptides and many other ligands / axo-dendritic transport / regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / regulation of synapse structure or activity / axon midline choice point recognition / astrocyte activation involved in immune response / NMDA selective glutamate receptor signaling pathway / regulation of spontaneous synaptic transmission / mating behavior / growth factor receptor binding / peptidase activator activity / Golgi-associated vesicle / PTB domain binding / positive regulation of amyloid fibril formation / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / astrocyte projection / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / neuron remodeling / Deregulated CDK5 triggers multiple neurodegenerative pathways in Alzheimer's disease models / nuclear envelope lumen / dendrite development / positive regulation of protein metabolic process / TRAF6 mediated NF-kB activation / signaling receptor activator activity / negative regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / Advanced glycosylation endproduct receptor signaling / modulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / main axon / transition metal ion binding / The NLRP3 inflammasome / regulation of multicellular organism growth / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / ECM proteoglycans / regulation of presynapse assembly / positive regulation of T cell migration / neuronal dense core vesicle / Purinergic signaling in leishmaniasis infection / positive regulation of chemokine production / Notch signaling pathway / cellular response to manganese ion / clathrin-coated pit / extracellular matrix organization / neuron projection maintenance / astrocyte activation / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / Mitochondrial protein degradation / positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle / axonogenesis / protein serine/threonine kinase binding / response to interleukin-1 / platelet alpha granule lumen / cellular response to copper ion / cellular response to cAMP / positive regulation of glycolytic process / central nervous system development / dendritic shaft / trans-Golgi network membrane / endosome lumen / positive regulation of long-term synaptic potentiation / adult locomotory behavior / positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production / learning / Post-translational protein phosphorylation / positive regulation of JNK cascade / locomotory behavior / serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity / microglial cell activation / positive regulation of non-canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction / cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus / TAK1-dependent IKK and NF-kappa-B activation / regulation of long-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / recycling endosome / synapse organization / visual learning / response to lead ion / positive regulation of interleukin-6 production / Golgi lumen / cognition / Regulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF) transport and uptake by Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Proteins (IGFBPs) / endocytosis / cellular response to amyloid-beta / neuron projection development / positive regulation of inflammatory response / positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production / Platelet degranulation / heparin binding / regulation of translation / regulation of gene expression / early endosome membrane / G alpha (i) signalling events / perikaryon / G alpha (q) signalling events / dendritic spine Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / SOLID-STATE NMR / helical reconstruction / simulated annealing / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.77 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Ghosh, U. / Thurber, K.R. / Tycko, R. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021Title: Molecular structure of a prevalent amyloid-β fibril polymorph from Alzheimer's disease brain tissue. Authors: Ujjayini Ghosh / Kent R Thurber / Wai-Ming Yau / Robert Tycko /  Abstract: Amyloid-β (Aβ) fibrils exhibit self-propagating, molecular-level polymorphisms that may contribute to variations in clinical and pathological characteristics of Alzheimer's disease (AD). We report ...Amyloid-β (Aβ) fibrils exhibit self-propagating, molecular-level polymorphisms that may contribute to variations in clinical and pathological characteristics of Alzheimer's disease (AD). We report the molecular structure of a specific fibril polymorph, formed by 40-residue Aβ peptides (Aβ40), that is derived from cortical tissue of an AD patient by seeded fibril growth. The structure is determined from cryogenic electron microscopy (cryoEM) images, supplemented by mass-per-length (MPL) measurements and solid-state NMR (ssNMR) data. Previous ssNMR studies with multiple AD patients had identified this polymorph as the most prevalent brain-derived Aβ40 fibril polymorph from typical AD patients. The structure, which has 2.8-Å resolution according to standard criteria, differs qualitatively from all previously described Aβ fibril structures, both in its molecular conformations and its organization of cross-β subunits. Unique features include twofold screw symmetry about the fibril growth axis, despite an MPL value that indicates three Aβ40 molecules per 4.8-Å β-sheet spacing, a four-layered architecture, and fully extended conformations for molecules in the central two cross-β layers. The cryoEM density, ssNMR data, and MPL data are consistent with β-hairpin conformations for molecules in the outer cross-β layers. Knowledge of this brain-derived fibril structure may contribute to the development of structure-specific amyloid imaging agents and aggregation inhibitors with greater diagnostic and therapeutic utility. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6w0o.cif.gz 6w0o.cif.gz | 549.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6w0o.ent.gz pdb6w0o.ent.gz | 462.2 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6w0o.json.gz 6w0o.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w0/6w0o https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w0/6w0o ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w0/6w0o ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/w0/6w0o | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21501MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| Other databases |
|
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| |||||||||
| NMR ensembles |
| |||||||||
| Symmetry | Helical symmetry: (Circular symmetry: 1 / Dyad axis: no / N subunits divisor: 1 / Num. of operations: 6 / Rise per n subunits: 2.45 Å / Rotation per n subunits: 179.66 °) |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein/peptide | Mass: 4335.852 Da / Num. of mol.: 6 / Fragment: UNP residues 653-692 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P05067 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P05067 |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: FILAMENT / 3D reconstruction method: helical reconstruction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NMR experiment |
|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: amyloid-beta(1-40) fibrils derived from human AD brain Type: COMPLEX Details: Fibrils produced by seeded growth using amyloid-beta in brain extract as the source of seeds. CryoEM and solid state NMR measurements were performed on second-generation seeded fibrils. Entity ID: all / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 29 kDa/nm / Experimental value: YES |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 Details: 10 mM phosphate buffer with 0.01% NaN3 to avoid microbial contamination. Buffers were filtered to avoid contamination. |
| Buffer component | Conc.: 10 mM / Name: Phosphate buffer / Formula: Na2HPO4/NaH2PO4 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.45 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES Details: Protein exists in solution as amyloid fibrils of varying lengths. |
| Specimen support | Details: The grids were checked in microscope prior to use. / Grid material: GOLD / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 |
| Vitrification | Instrument: LEICA PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 293 K Details: The grids were preblotted for 10 seconds and blotted for 6 seconds before plunging. |
| Details | Type: fibrous protein Contents: 100 uM U-15N,13C amyloid-beta(1-40), phosphate buffer Details: lyophilized, rehydrated in MAS rotor, 100 uM concentration prior to pelleting Label: U-labeled fibrils / Solvent system: phosphate buffer |
| Sample | Conc.: 100 uM / Component: amyloid-beta(1-40) / Isotopic labeling: U-15N,13C |
| Sample conditions | Details: pelleted, lyophilized, rehydrated in MAS rotor / Ionic strength: 10 mM / Label: conditions_1 / pH: 7.4 / PH err: 0.05 / Pressure: 1 atm / Temperature: 297 K / Temperature err: 2 |
-Data collection
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS Details: Preliminary grid screening was done manually in FEI T12. |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: -3000 nm / Nominal defocus min: -500 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Residual tilt: 6 mradians |
| Image recording | Average exposure time: 10 sec. / Electron dose: 73.5 e/Å2 / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 / Num. of real images: 1337 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Quantum LS / Energyfilter slit width: 20 eV |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 50 / Used frames/image: 1-50 |
| NMR spectrometer | Type: Varian InfinityPlus / Manufacturer: Varian / Model: InfinityPlus / Field strength: 600 MHz |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Image processing | Details: The selected images were corrected for gain. The gain reference was not rotated or flipped. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Details: The correction was done in Gctf and is corrected for amplitude. Per -particle CTF refinement was done prior to final reconstruction. Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Helical symmerty | Angular rotation/subunit: 179.66 ° / Axial rise/subunit: 2.45 Å / Axial symmetry: C1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle selection | Num. of particles selected: 19790 Details: The particles were picked using Relion manual pick, with a 20A low pass filter and particle diameter of 30A. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.77 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 14775 / Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE Details: A modified version of RELION 3.0-beta was used for the reconstruction. The modified version allowed local averaging of the rotation angle. Final reconstruction used 2-fold screw symmetry. Num. of class averages: 1 / Symmetry type: HELICAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Space: REAL Details: Xplor-NIH was used to combine EM density with phi/psi restraints from NMR chemical shifts (from Talos-N Version 4.21 Rev 2016.343.11.31). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NMR software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Method: simulated annealing / Software ordinal: 3 Details: phi/psi from TalosN & EM density used as restraints | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NMR representative | Selection criteria: lowest energy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NMR ensemble | Conformer selection criteria: structures with the least restraint violations Conformers calculated total number: 60 / Conformers submitted total number: 10 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj