[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
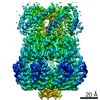
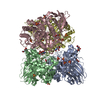
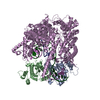
Yorodumi- PDB-6vym: Cryo-EM structure of mechanosensitive channel MscS in PC-18:1 nan... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6vym | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of mechanosensitive channel MscS in PC-18:1 nanodiscs treated with beta-cyclodextran | ||||||
 Components Components | Mechanosensitive channel MscS | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / Mechanosensitive channel / MscS / Nanodiscs / Lipid | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationintracellular water homeostasis / mechanosensitive monoatomic ion channel activity / protein homooligomerization / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / membrane / identical protein binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.7 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang, Y. / Daday, C. / Gu, R. / Cox, C.D. / Martinac, B. / Groot, B. / Walz, T. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: Visualization of the mechanosensitive ion channel MscS under membrane tension. Authors: Yixiao Zhang / Csaba Daday / Ruo-Xu Gu / Charles D Cox / Boris Martinac / Bert L de Groot / Thomas Walz /    Abstract: Mechanosensitive channels sense mechanical forces in cell membranes and underlie many biological sensing processes. However, how exactly they sense mechanical force remains under investigation. The ...Mechanosensitive channels sense mechanical forces in cell membranes and underlie many biological sensing processes. However, how exactly they sense mechanical force remains under investigation. The bacterial mechanosensitive channel of small conductance, MscS, is one of the most extensively studied mechanosensitive channels, but how it is regulated by membrane tension remains unclear, even though the structures are known for its open and closed states. Here we used cryo-electron microscopy to determine the structure of MscS in different membrane environments, including one that mimics a membrane under tension. We present the structures of MscS in the subconducting and desensitized states, and demonstrate that the conformation of MscS in a lipid bilayer in the open state is dynamic. Several associated lipids have distinct roles in MscS mechanosensation. Pore lipids are necessary to prevent ion conduction in the closed state. Gatekeeper lipids stabilize the closed conformation and dissociate with membrane tension, allowing the channel to open. Pocket lipids in a solvent-exposed pocket between subunits are pulled out under sustained tension, allowing the channel to transition to the subconducting state and then to the desensitized state. Our results provide a mechanistic underpinning and expand on the 'force-from-lipids' model for MscS mechanosensation. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6vym.cif.gz 6vym.cif.gz | 295.1 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6vym.ent.gz pdb6vym.ent.gz | 243.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6vym.json.gz 6vym.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vy/6vym https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vy/6vym ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vy/6vym ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/vy/6vym | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21464MC  6vykC  6vylC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 30922.898 Da / Num. of mol.: 7 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Mechanosensitive channel MscS / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: all / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.21 MDa / Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NITROGEN |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 55 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: NONE |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.7 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 51333 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj