[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6jzk: Structure of FimA type-1 (FimA1) prepilin of the type V major fimbrium -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6jzk | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
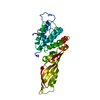
| Title | Structure of FimA type-1 (FimA1) prepilin of the type V major fimbrium | ||||||
 Components Components | Major fimbrium subunit FimA type-1 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CELL ADHESION / Type V pili / Major fimbrial subunit protein | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpilus / cell outer membrane / cell adhesion / structural molecule activity Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Porphyromonas gingivalis ATCC 33277 (bacteria) Porphyromonas gingivalis ATCC 33277 (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.1 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.1 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Okada, K. / Shoji, M. / Nakayam, K. / Imada, K. | ||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 1items Japan, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2020Title: Structure of polymerized type V pilin reveals assembly mechanism involving protease-mediated strand exchange. Authors: Satoshi Shibata / Mikio Shoji / Kodai Okada / Hideyuki Matsunami / Melissa M Matthews / Katsumi Imada / Koji Nakayama / Matthias Wolf /  Abstract: Bacterial adhesion is a general strategy for host-microbe and microbe-microbe interactions. Adhesive pili are essential for colonization, biofilm formation, virulence and pathogenesis of many ...Bacterial adhesion is a general strategy for host-microbe and microbe-microbe interactions. Adhesive pili are essential for colonization, biofilm formation, virulence and pathogenesis of many environmental and pathogenic bacteria. Members of the class Bacteroidia have unique type V pili, assembled by protease-mediated polymerization. Porphyromonas gingivalis is the main contributor to periodontal disease and its type V pili are a key factor for its virulence. However, the structure of the polymerized pilus and its assembly mechanism are unknown. Here we show structures of polymerized and monomeric states of FimA stalk pilin from P. gingivalis, determined by cryo-electron microscopy and crystallography. The atomic model of assembled FimA shows that the C-terminal strand of a donor subunit is inserted into a groove in the β-sheet of an acceptor subunit after N-terminal cleavage by the protease RgpB. The C terminus of the donor strand is essential for polymerization. We propose that type V pili assemble via a sequential polar assembly mechanism at the cell surface, involving protease-mediated strand exchange, employed by various Gram-negative species belonging to the class Bacteroidia. Our results reveal functional surfaces related to pathogenic properties of polymerized FimA. These insights may facilitate development of antibacterial drugs. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6jzk.cif.gz 6jzk.cif.gz | 154.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6jzk.ent.gz pdb6jzk.ent.gz | 118.6 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6jzk.json.gz 6jzk.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jz/6jzk https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jz/6jzk ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jz/6jzk ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/jz/6jzk | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  0724C  6jzjSC  6kmfC S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 39637.188 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Porphyromonas gingivalis ATCC 33277 (bacteria) Porphyromonas gingivalis ATCC 33277 (bacteria)Gene: fimA, PGN_0180 / Plasmid: pET15b / Production host:  #2: Chemical | ChemComp-GOL / | #3: Chemical | ChemComp-SO4 / | #4: Chemical | ChemComp-SRT / | #5: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.34 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 47.5 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 293 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop / pH: 5.6 Details: 0.1M Sodium citrate pH5.6, 1.8M ammonium sulfate, 0.2M sodium potassium tartrate |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K / Serial crystal experiment: N |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SPring-8 SPring-8  / Beamline: BL32XU / Wavelength: 1 Å / Beamline: BL32XU / Wavelength: 1 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS EIGER X 9M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: May 16, 2018 |
| Radiation | Monochromator: Double-crystal / Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.1→48.5 Å / Num. obs: 44884 / % possible obs: 100 % / Redundancy: 6.6 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 30.4 Å2 / CC1/2: 0.999 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.05 / Rpim(I) all: 0.031 / Rrim(I) all: 0.059 / Net I/σ(I): 21.3 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.1→2.16 Å / Redundancy: 6.9 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.397 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 4.4 / Num. unique obs: 3585 / CC1/2: 0.949 / Rpim(I) all: 0.244 / Rrim(I) all: 0.468 / % possible all: 100 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 6JZJ Resolution: 2.1→42.726 Å / SU ML: 0.24 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 1.35 / Phase error: 26.02
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.1→42.726 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









 PDBj
PDBj