[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
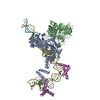
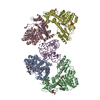
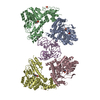
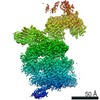
Yorodumi- PDB-5zdz: Hairpin Forming Complex, RAG1/2-Nicked 12RSS/23RSS complex in Ca2+ -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5zdz | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Hairpin Forming Complex, RAG1/2-Nicked 12RSS/23RSS complex in Ca2+ | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | DNA BINDING PROTEIN / V(D)J recombination / RAG1-2-12RSS-23RSS complex / Hairpin forming complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationApoptosis induced DNA fragmentation / open form four-way junction DNA binding / crossed form four-way junction DNA binding / Advanced glycosylation endproduct receptor signaling / Pyroptosis / regulation of tolerance induction / calcium-dependent protein kinase regulator activity / positive regulation of myeloid progenitor cell differentiation / Regulation of TLR by endogenous ligand / regulation of T cell mediated immune response to tumor cell ...Apoptosis induced DNA fragmentation / open form four-way junction DNA binding / crossed form four-way junction DNA binding / Advanced glycosylation endproduct receptor signaling / Pyroptosis / regulation of tolerance induction / calcium-dependent protein kinase regulator activity / positive regulation of myeloid progenitor cell differentiation / Regulation of TLR by endogenous ligand / regulation of T cell mediated immune response to tumor cell / positive regulation of mismatch repair / negative regulation of apoptotic cell clearance / plasmacytoid dendritic cell activation / negative regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / T-helper 1 cell activation / TRAF6 mediated NF-kB activation / T-helper 1 cell differentiation / mature B cell differentiation involved in immune response / positive regulation of myeloid cell differentiation / myeloid dendritic cell activation / positive regulation of toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway / positive regulation of dendritic cell differentiation / C-X-C chemokine binding / negative regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation / bent DNA binding / positive regulation of toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway / TAK1-dependent IKK and NF-kappa-B activation / B cell homeostatic proliferation / neutrophil clearance / negative regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus / positive regulation of glycogen catabolic process / DN2 thymocyte differentiation / pre-B cell allelic exclusion / DNA geometric change / positive regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway / endothelial cell chemotaxis / positive regulation of organ growth / eye development / induction of positive chemotaxis / bubble DNA binding / regulation of behavioral fear response / V(D)J recombination / negative regulation of T cell apoptotic process / myeloid cell differentiation / alphav-beta3 integrin-HMGB1 complex / myeloid progenitor cell differentiation / phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding / inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus / negative regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process / histone H3K4me3 reader activity / positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis / macrophage activation involved in immune response / positive regulation of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 production / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / positive regulation of innate immune response / endothelial cell proliferation / positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation / phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding / positive regulation of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 production / cellular response to interleukin-7 / glycogen catabolic process / apoptotic cell clearance / positive regulation of mesenchymal cell proliferation / regulation of T cell differentiation / supercoiled DNA binding / DNA binding, bending / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / organ growth / T cell lineage commitment / positive regulation of wound healing / phosphatidylserine binding / B cell lineage commitment / positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment / phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding / T cell homeostasis / negative regulation of type II interferon production / negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration / positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation / positive regulation of interferon-alpha production / positive regulation of interleukin-10 production / T cell differentiation / positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration / protein kinase activator activity / protein autoubiquitination / four-way junction DNA binding / condensed chromosome / DNA polymerase binding / phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding / transcription repressor complex / Neutrophil degranulation / positive regulation of interleukin-12 production / positive regulation of autophagy / phosphatidylinositol binding / positive regulation of mitotic cell cycle / activation of innate immune response / lung development / positive regulation of interferon-beta production / response to glucocorticoid / B cell differentiation Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  synthetic construct (others) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.8 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.8 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Kim, M.S. / Chuenchor, W. / Chen, X. / Gellert, M. / Yang, W. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1items United States, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2018 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2018Title: Cracking the DNA Code for V(D)J Recombination. Authors: Min-Sung Kim / Watchalee Chuenchor / Xuemin Chen / Yanxiang Cui / Xing Zhang / Z Hong Zhou / Martin Gellert / Wei Yang /    Abstract: To initiate V(D)J recombination for generating the adaptive immune response of vertebrates, RAG1/2 recombinase cleaves DNA at a pair of recombination signal sequences, the 12- and 23-RSS. We have ...To initiate V(D)J recombination for generating the adaptive immune response of vertebrates, RAG1/2 recombinase cleaves DNA at a pair of recombination signal sequences, the 12- and 23-RSS. We have determined crystal and cryo-EM structures of RAG1/2 with DNA in the pre-reaction and hairpin-forming complexes up to 2.75 Å resolution. Both protein and DNA exhibit structural plasticity and undergo dramatic conformational changes. Coding-flank DNAs extensively rotate, shift, and deform for nicking and hairpin formation. Two intertwined RAG1 subunits crisscross four times between the asymmetric pair of severely bent 12/23-RSS DNAs. Location-sensitive bending of 60° and 150° in 12- and 23-RSS spacers, respectively, must occur for RAG1/2 to capture the nonamers and pair the heptamers for symmetric double-strand breakage. DNA pairing is thus sequence-context dependent and structure specific, which partly explains the "beyond 12/23" restriction. Finally, catalysis in crystallo reveals the process of DNA hairpin formation and its stabilization by interleaved base stacking. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5zdz.cif.gz 5zdz.cif.gz | 535.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5zdz.ent.gz pdb5zdz.ent.gz | 414.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5zdz.json.gz 5zdz.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zd/5zdz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zd/5zdz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zd/5zdz ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/zd/5zdz | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7470C  7480C  5ze0C  5ze1C  5ze2C  6cg0C  6cijC  6cikC  6cilC  6cimC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 3 types, 5 molecules ACBDN
| #1: Protein | Mass: 71871.305 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: UNP residues 384-1008 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)References: UniProt: P15919, Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds, RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase #2: Protein | Mass: 43225.711 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: UNP residues 1-387 / Mutation: M1V Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P21784 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P21784#3: Protein | | Mass: 18897.885 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: UNP residues 1-163 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-DNA chain , 6 types, 6 molecules FIJGLM
| #4: DNA chain | Mass: 13978.961 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 4864.165 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 4855.150 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
| #7: DNA chain | Mass: 16640.654 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
| #8: DNA chain | Mass: 9138.938 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
| #9: DNA chain | Mass: 12036.805 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 137 molecules 








| #10: Chemical | | #11: Chemical | #12: Chemical | #13: Chemical | #14: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 3.49 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 64.79 % Description: THE ENTRY CONTAINS FRIEDEL PAIRS IN F_PLUS/MINUS COLUMNS. |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 277 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop Details: 100mM MES (pH 6.8), 15% PEG 3350, 200mM Potassium formate |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  APS APS  / Beamline: 22-ID / Wavelength: 1 Å / Beamline: 22-ID / Wavelength: 1 Å |
| Detector | Type: MARMOSAIC 300 mm CCD / Detector: CCD / Date: Aug 20, 2016 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.8→50 Å / Num. obs: 198942 / % possible obs: 99.6 % / Redundancy: 4.1 % / Net I/σ(I): 14.5 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.8→2.9 Å |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.8→43.719 Å / SU ML: 0.4 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.35 / Phase error: 27.76 MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.8→43.719 Å / SU ML: 0.4 / Cross valid method: FREE R-VALUE / σ(F): 1.35 / Phase error: 27.76 Details: SF FILE CONTAINS FRIEDEL PAIRS UNDER I/F_MINUS AND I/F_PLUS COLUMNS.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Shrinkage radii: 0.9 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.11 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.8→43.719 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj





















































