[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-7480: Cryo-EM structure of mouse RAG1/2 HFC complex containing partial ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-7480 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of mouse RAG1/2 HFC complex containing partial HMGB1 linker(3.9 A) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryo-EM structure of mouse RAG1/2 HFC complex | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | V(D)J recombination / RAG1/2 / RSS / Immunity / RECOMBINATION / RECOMBINATION-DNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / positive regulation of myeloid progenitor cell differentiation / regulation of tolerance induction / calcium-dependent protein kinase regulator activity / regulation of T cell mediated immune response to tumor cell / positive regulation of mismatch repair / negative regulation of apoptotic cell clearance / plasmacytoid dendritic cell activation / negative regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / T-helper 1 cell activation ...: / positive regulation of myeloid progenitor cell differentiation / regulation of tolerance induction / calcium-dependent protein kinase regulator activity / regulation of T cell mediated immune response to tumor cell / positive regulation of mismatch repair / negative regulation of apoptotic cell clearance / plasmacytoid dendritic cell activation / negative regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / T-helper 1 cell activation / T-helper 1 cell differentiation / mature B cell differentiation involved in immune response / positive regulation of myeloid cell differentiation / myeloid dendritic cell activation / positive regulation of toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway / positive regulation of dendritic cell differentiation / DNA recombinase complex / C-X-C chemokine binding / negative regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation / positive regulation of toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway / B cell homeostatic proliferation / neutrophil clearance / endodeoxyribonuclease complex / negative regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus / positive regulation of glycogen catabolic process / DN2 thymocyte differentiation / pre-B cell allelic exclusion / DNA geometric change / positive regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway / endothelial cell chemotaxis / positive regulation of organ growth / RAGE receptor binding / eye development / Regulation of TLR by endogenous ligand / positive regulation of interleukin-1 production / bubble DNA binding / regulation of behavioral fear response / V(D)J recombination / negative regulation of T cell apoptotic process / alphav-beta3 integrin-HMGB1 complex / myeloid cell differentiation / myeloid progenitor cell differentiation / Apoptosis induced DNA fragmentation / phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding / inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus / negative regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process / MyD88 deficiency (TLR2/4) / macrophage activation involved in immune response / positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis / positive regulation of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 production / histone H3K4me3 reader activity / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / endothelial cell proliferation / positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation / phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding / positive regulation of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 production / cellular response to interleukin-7 / glycogen catabolic process / apoptotic cell clearance / IRAK4 deficiency (TLR2/4) / regulation of T cell differentiation / MyD88:MAL(TIRAP) cascade initiated on plasma membrane / dendritic cell chemotaxis / positive regulation of DNA binding / supercoiled DNA binding / DNA binding, bending / organ growth / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / T cell lineage commitment / phosphatidylserine binding / positive regulation of wound healing / B cell lineage commitment / positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis / chemoattractant activity / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment / phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding / T cell homeostasis / negative regulation of type II interferon production / TRAF6 mediated NF-kB activation / DNA topological change / negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration / Advanced glycosylation endproduct receptor signaling / positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation / positive regulation of interferon-alpha production / positive regulation of interleukin-10 production / T cell differentiation / positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration / Pyroptosis / protein kinase activator activity / protein autoubiquitination / four-way junction DNA binding / condensed chromosome / DNA polymerase binding / phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding / transcription repressor complex / positive regulation of interleukin-12 production / phosphatidylinositol binding / positive regulation of autophagy / activation of innate immune response / lung development Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chen X / Kim M | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2018 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2018Title: Cracking the DNA Code for V(D)J Recombination. Authors: Min-Sung Kim / Watchalee Chuenchor / Xuemin Chen / Yanxiang Cui / Xing Zhang / Z Hong Zhou / Martin Gellert / Wei Yang /    Abstract: To initiate V(D)J recombination for generating the adaptive immune response of vertebrates, RAG1/2 recombinase cleaves DNA at a pair of recombination signal sequences, the 12- and 23-RSS. We have ...To initiate V(D)J recombination for generating the adaptive immune response of vertebrates, RAG1/2 recombinase cleaves DNA at a pair of recombination signal sequences, the 12- and 23-RSS. We have determined crystal and cryo-EM structures of RAG1/2 with DNA in the pre-reaction and hairpin-forming complexes up to 2.75 Å resolution. Both protein and DNA exhibit structural plasticity and undergo dramatic conformational changes. Coding-flank DNAs extensively rotate, shift, and deform for nicking and hairpin formation. Two intertwined RAG1 subunits crisscross four times between the asymmetric pair of severely bent 12/23-RSS DNAs. Location-sensitive bending of 60° and 150° in 12- and 23-RSS spacers, respectively, must occur for RAG1/2 to capture the nonamers and pair the heptamers for symmetric double-strand breakage. DNA pairing is thus sequence-context dependent and structure specific, which partly explains the "beyond 12/23" restriction. Finally, catalysis in crystallo reveals the process of DNA hairpin formation and its stabilization by interleaved base stacking. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_7480.map.gz emd_7480.map.gz | 8.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-7480-v30.xml emd-7480-v30.xml emd-7480.xml emd-7480.xml | 25 KB 25 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_7480.png emd_7480.png | 169.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-7480.cif.gz emd-7480.cif.gz | 7.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7480 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7480 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7480 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7480 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6cijMC  7470C  5zdzC  5ze0C  5ze1C  5ze2C  6cg0C  6cikC  6cilC  6cimC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_7480.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_7480.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM structure of mouse RAG1/2 HFC complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.07 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
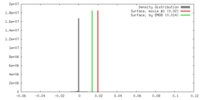
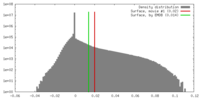
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : RAG1/2 in complex with nicked DNAs
+Supramolecule #1: RAG1/2 in complex with nicked DNAs
+Macromolecule #1: V(D)J recombination-activating protein 1
+Macromolecule #6: High mobility group protein B1
+Macromolecule #8: V(D)J recombination-activating protein 2
+Macromolecule #2: DNA (46-MER)
+Macromolecule #3: DNA (5'-D(*GP*AP*TP*CP*TP*GP*GP*CP*CP*TP*GP*TP*CP*TP*TP*A)-3')
+Macromolecule #4: DNA (5'-D(P*CP*TP*GP*GP*AP*TP*CP*TP*GP*GP*CP*CP*TP*GP*TP*CP*TP*TP...
+Macromolecule #5: DNA (60-MER)
+Macromolecule #7: DNA (30-MER)
+Macromolecule #9: DNA (41-MER)
+Macromolecule #10: ZINC ION
+Macromolecule #11: CALCIUM ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.3 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 57.6 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Target criteria: Correlation Coefficient |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6cij: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)