[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-5i0i: Crystal structure of myosin X motor domain with 2IQ motifs in pre... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 5i0i | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
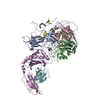
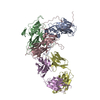
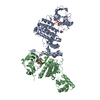
| Title | Crystal structure of myosin X motor domain with 2IQ motifs in pre-powerstroke state | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MOTOR PROTEIN / myosin / motor domain / molecular motor / pre-powerstrocke state / motility | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationplus-end directed microfilament motor activity / Netrin-1 signaling / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport / positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion / filopodium tip / : / : / : / : / : ...plus-end directed microfilament motor activity / Netrin-1 signaling / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport / positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion / filopodium tip / : / : / : / : / : / positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation / regulation of filopodium assembly / negative regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / : / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / filopodium membrane / myosin complex / positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / positive regulation of DNA binding / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / PKA activation / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / microfilament motor activity / spectrin binding / response to corticosterone / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / nitric-oxide synthase binding / presynaptic endocytosis / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / adenylate cyclase binding / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / Smooth Muscle Contraction / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / catalytic complex / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / enzyme regulator activity / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / calcium channel inhibitor activity / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / presynaptic cytosol / cellular response to interferon-beta / Protein methylation / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / ruffle / titin binding / Ion homeostasis / eNOS activation / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / calcium channel complex / substantia nigra development / regulation of heart rate / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / calyx of Held / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / adenylate cyclase activator activity / sarcomere / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.15 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.15 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Isabet, T. / Sweeney, H.L. / Houdusse, A. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  France, France,  United States, 6items United States, 6items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2016 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2016Title: The myosin X motor is optimized for movement on actin bundles. Authors: Virginie Ropars / Zhaohui Yang / Tatiana Isabet / Florian Blanc / Kaifeng Zhou / Tianming Lin / Xiaoyan Liu / Pascale Hissier / Frédéric Samazan / Béatrice Amigues / Eric D Yang / Hyokeun ...Authors: Virginie Ropars / Zhaohui Yang / Tatiana Isabet / Florian Blanc / Kaifeng Zhou / Tianming Lin / Xiaoyan Liu / Pascale Hissier / Frédéric Samazan / Béatrice Amigues / Eric D Yang / Hyokeun Park / Olena Pylypenko / Marco Cecchini / Charles V Sindelar / H Lee Sweeney / Anne Houdusse /    Abstract: Myosin X has features not found in other myosins. Its structure must underlie its unique ability to generate filopodia, which are essential for neuritogenesis, wound healing, cancer metastasis and ...Myosin X has features not found in other myosins. Its structure must underlie its unique ability to generate filopodia, which are essential for neuritogenesis, wound healing, cancer metastasis and some pathogenic infections. By determining high-resolution structures of key components of this motor, and characterizing the in vitro behaviour of the native dimer, we identify the features that explain the myosin X dimer behaviour. Single-molecule studies demonstrate that a native myosin X dimer moves on actin bundles with higher velocities and takes larger steps than on single actin filaments. The largest steps on actin bundles are larger than previously reported for artificially dimerized myosin X constructs or any other myosin. Our model and kinetic data explain why these large steps and high velocities can only occur on bundled filaments. Thus, myosin X functions as an antiparallel dimer in cells with a unique geometry optimized for movement on actin bundles. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  5i0i.cif.gz 5i0i.cif.gz | 794.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb5i0i.ent.gz pdb5i0i.ent.gz | 653.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  5i0i.json.gz 5i0i.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i0/5i0i https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i0/5i0i ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i0/5i0i ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/i0/5i0i | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 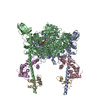
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||
| 2 | 
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 4 types, 5 molecules ABCEI
| #1: Protein | Mass: 91550.148 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MYO10, KIAA0799 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: MYO10, KIAA0799 / Production host:  unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: Q9HD67 unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: Q9HD67#2: Protein | | Mass: 16450.014 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: CALM1, CALM, CAM, CAM1, CALM2, CAM2, CAMB, CALM3, CALML2, CAM3, CAMC, CAMIII Production host:  unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: P62158, UniProt: P0DP23*PLUS unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: P62158, UniProt: P0DP23*PLUS#3: Protein | | Mass: 16373.917 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: CALM1, CALM, CAM, CAM1, CALM2, CAM2, CAMB, CALM3, CALML2, CAM3, CAMC, CAMIII Production host:  unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: P62158, UniProt: P0DP23*PLUS unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: P62158, UniProt: P0DP23*PLUS#5: Protein | | Mass: 7408.098 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: CALM1, CALM, CAM, CAM1, CALM2, CAM2, CAMB, CALM3, CALML2, CAM3, CAMC, CAMIII Production host:  unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: P62158, UniProt: P0DP23*PLUS unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: P62158, UniProt: P0DP23*PLUS |
|---|
-Protein/peptide , 1 types, 1 molecules G
| #4: Protein/peptide | Mass: 4977.496 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: CALM1, CALM, CAM, CAM1, CALM2, CAM2, CAMB, CALM3, CALML2, CAM3, CAMC, CAMIII Production host:  unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: P62158, UniProt: P0DP23*PLUS unidentified baculovirus / References: UniProt: P62158, UniProt: P0DP23*PLUS |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 6 types, 32 molecules 









| #6: Chemical | | #7: Chemical | #8: Chemical | #9: Chemical | #10: Chemical | ChemComp-SO4 / #11: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 3.84 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 68 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 277 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 7 Details: 7.5% PEG 10000, 100mM MOPS pH 7.0, 1mM TCEP and 50mM Magnesium acetate |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SOLEIL SOLEIL  / Beamline: PROXIMA 1 / Wavelength: 0.9801 Å / Beamline: PROXIMA 1 / Wavelength: 0.9801 Å |
| Detector | Type: DECTRIS PILATUS 6M / Detector: PIXEL / Date: Apr 9, 2013 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.9801 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 3.15→50 Å / Num. obs: 61853 / % possible obs: 99.9 % / Redundancy: 16.9 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 118.26 Å2 / Net I/σ(I): 14.48 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 3.15→3.23 Å / Redundancy: 16.8 % / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 1.15 / % possible all: 99.7 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.15→49.53 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.9356 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.9334 / SU R Cruickshank DPI: 3.519 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / SU R Blow DPI: 1.802 / SU Rfree Blow DPI: 0.333 / SU Rfree Cruickshank DPI: 0.342 MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 3.15→49.53 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.9356 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.9334 / SU R Cruickshank DPI: 3.519 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 / SU R Blow DPI: 1.802 / SU Rfree Blow DPI: 0.333 / SU Rfree Cruickshank DPI: 0.342
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 126.34 Å2
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine analyze | Luzzati coordinate error obs: 0.383 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 3.15→49.53 Å
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 3.15→3.23 Å / Total num. of bins used: 20
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS group |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 PDBj
PDBj































