[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-1o9w: F17-aG lectin domain from Escherichia coli in complex with N-acet... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 1o9w | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | F17-aG lectin domain from Escherichia coli in complex with N-acetyl-glucosamine | ||||||
 Components Components | F17A-G FIMBRIAL ADHESIN | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | SUGAR BINDING PROTEIN / BACTERIAL ADHESIN / BACTERIAL ATTACHMENT / SUGAR BINDING PROTEIN PATHOGENESIS / IMMUNOGLOBULIN FOLD | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationadhesion of symbiont to host / cell adhesion involved in single-species biofilm formation / pilus / carbohydrate binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.65 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.65 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Buts, L. / De Genst, E. / Loris, R. / Oscarson, S. / Lahmann, M. / Messens, J. / Brosens, E. / Wyns, L. / Bouckaert, J. / De Greve, H. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol.Microbiol. / Year: 2003 Journal: Mol.Microbiol. / Year: 2003Title: The Fimbrial Adhesin F17-G of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli Has an Immunoglobulin-Like Lectin Domain that Binds N-Acetylglucosamine Authors: Buts, L. / Bouckaert, J. / De Genst, E. / Loris, R. / Oscarson, S. / Lahmann, M. / Messens, J. / Brosens, E. / Wyns, L. / De Greve, H. #1: Journal: Acta Crystallogr.,Sect.D / Year: 2003 Title: Solving the Phase Problem for Carbohydrate -Binding Proteins Using Selenium Derivatives of Their Ligands: A Case Study Involving the Bacterial F17-G Adhesin Authors: Buts, L. / Loris, R. / De Genst, E. / Oscarson, S. / Lahmann, M. / Messens, J. / Brosens, E. / Wyns, L. / De Greve, H. / Bouckaert, J. #2: Journal: J.Bacteriol. / Year: 1991 Title: Identification, Characterization and Nucleotide Sequence of the F17G Gene, which Determines Receptor Binding of Escherichia Coli F17 Fimbriae Authors: Lintermans, P.F. / Bertels, A. / Schlicker, C. / Deboeck, F. / Charlier, G. / Pohl, P. / Norgren, M. / Normark, S. / Van Montagu, M. / De Greve, H. | ||||||
| History |
| ||||||
| Remark 700 | SHEET THE SHEET STRUCTURE OF THIS MOLECULE IS BIFURCATED. IN ORDER TO REPRESENT THIS FEATURE IN ... SHEET THE SHEET STRUCTURE OF THIS MOLECULE IS BIFURCATED. IN ORDER TO REPRESENT THIS FEATURE IN THE SHEET RECORDS BELOW, TWO SHEETS ARE DEFINED. |
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  1o9w.cif.gz 1o9w.cif.gz | 48 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb1o9w.ent.gz pdb1o9w.ent.gz | 33.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  1o9w.json.gz 1o9w.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  1o9w_validation.pdf.gz 1o9w_validation.pdf.gz | 418.6 KB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  1o9w_full_validation.pdf.gz 1o9w_full_validation.pdf.gz | 418.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  1o9w_validation.xml.gz 1o9w_validation.xml.gz | 5.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  1o9w_validation.cif.gz 1o9w_validation.cif.gz | 8.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o9/1o9w https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o9/1o9w ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o9/1o9w ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/o9/1o9w | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  1o9vSC  1o9zC S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 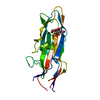
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 19048.227 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: CARBOHYDRATE-BINDING DOMAIN, RESIDUES 23-199 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #2: Sugar | ChemComp-NAG / |
| #3: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 1.89 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 33 % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal grow | pH: 4.6 Details: 30% PEG4000, 0.1M SODIUM ACETATE (PH 4.6), 0.2M AMMONIUM ACETATE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal grow | *PLUS pH: 8 / Method: vapor diffusion | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Components of the solutions | *PLUS
|
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  EMBL/DESY, HAMBURG EMBL/DESY, HAMBURG  / Beamline: X13 / Wavelength: 0.8019 / Beamline: X13 / Wavelength: 0.8019 |
| Detector | Type: MARRESEARCH / Detector: CCD / Date: Aug 15, 2002 / Details: MIRRORS |
| Radiation | Monochromator: GRAPHITE / Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.8019 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 1.65→25 Å / Num. obs: 20396 / % possible obs: 100 % / Redundancy: 48 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 27.8 Å2 / Rsym value: 0.073 / Net I/σ(I): 8.2 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 1.66→1.81 Å / Rsym value: 0.52 / % possible all: 99.9 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: PDB ENTRY 1O9V Resolution: 1.65→24.77 Å / Rfactor Rfree error: 0.007 / Data cutoff high absF: 1557043.04 / Isotropic thermal model: RESTRAINED / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Solvent model: FLAT MODEL / Bsol: 61.5472 Å2 / ksol: 0.395503 e/Å3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 29.5 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine analyze |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 1.65→24.77 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 1.65→1.75 Å / Rfactor Rfree error: 0.024 / Total num. of bins used: 6
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Xplor file |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints | *PLUS
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj


