[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-1n4h: Characterization of ligands for the orphan nuclear receptor RORbeta -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 1n4h | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Characterization of ligands for the orphan nuclear receptor RORbeta | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HORMONE/GROWTH FACTOR / Alpha-helical sandwich / Protein-peptide-ligand complex / HORMONE-GROWTH FACTOR COMPLEX | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationretinal rod cell development / melatonin receptor activity / amacrine cell differentiation / retinal rod cell differentiation / retinal cone cell development / Nuclear Receptor transcription pathway / eye photoreceptor cell development / labyrinthine layer morphogenesis / positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter by galactose / regulation of thyroid hormone receptor signaling pathway ...retinal rod cell development / melatonin receptor activity / amacrine cell differentiation / retinal rod cell differentiation / retinal cone cell development / Nuclear Receptor transcription pathway / eye photoreceptor cell development / labyrinthine layer morphogenesis / positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter by galactose / regulation of thyroid hormone receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of female receptivity / NR1H2 & NR1H3 regulate gene expression to control bile acid homeostasis / male mating behavior / hypothalamus development / cellular response to Thyroglobulin triiodothyronine / Synthesis of bile acids and bile salts / progesterone receptor signaling pathway / Synthesis of bile acids and bile salts via 27-hydroxycholesterol / Endogenous sterols / Synthesis of bile acids and bile salts via 7alpha-hydroxycholesterol / response to retinoic acid / negative regulation of osteoblast differentiation / estrous cycle / nuclear retinoid X receptor binding / histone acetyltransferase activity / Transcriptional regulation of brown and beige adipocyte differentiation by EBF2 / Recycling of bile acids and salts / histone acetyltransferase / cellular response to hormone stimulus / NR1H3 & NR1H2 regulate gene expression linked to cholesterol transport and efflux / estrogen receptor signaling pathway / response to hormone / cellular response to retinoic acid / lactation / : / positive regulation of adipose tissue development / Regulation of lipid metabolism by PPARalpha / peroxisome proliferator activated receptor signaling pathway / positive regulation of neuron differentiation / regulation of cellular response to insulin stimulus / visual perception / BMAL1:CLOCK,NPAS2 activates circadian expression / SUMOylation of transcription cofactors / response to progesterone / Activation of gene expression by SREBF (SREBP) / cerebellum development / nuclear estrogen receptor binding / nuclear receptor binding / RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / hippocampus development / mRNA transcription by RNA polymerase II / Heme signaling / PPARA activates gene expression / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / Cytoprotection by HMOX1 / circadian rhythm / regulation of circadian rhythm / cerebral cortex development / Transcriptional regulation of white adipocyte differentiation / RNA polymerase II transcription regulator complex / male gonad development / nuclear receptor activity / sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding / : / response to estradiol / HATs acetylate histones / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / retina development in camera-type eye / DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / transcription regulator complex / sequence-specific DNA binding / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / transcription coactivator activity / protein dimerization activity / positive regulation of apoptotic process / RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding / DNA-binding transcription factor activity / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / chromatin binding / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / chromatin / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / protein-containing complex binding / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.1 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.1 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Stehlin-Gaon, C. / Willmann, D. / Sanglier, S. / Van Dorsselaer, A. / Renaud, J.-P. / Moras, D. / Schuele, R. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat.Struct.Biol. / Year: 2003 Journal: Nat.Struct.Biol. / Year: 2003Title: All-trans retinoic acid is a ligand for the orphan nuclear receptor RORbeta Authors: Stehlin-Gaon, C. / Willmann, D. / Zeyer, D. / Sanglier, S. / Van Dorsselaer, A. / Renaud, J.-P. / Moras, D. / Schuele, R. #1:  Journal: Embo J. / Year: 2001 Journal: Embo J. / Year: 2001Title: X-Ray Structure Of The Orphan Nuclear Receptor RORbeta Ligand-Binding Domain In The Active Conformation Authors: Stehlin, C. / Wurtz, J.M. / Steinmetz, A. / Greiner, E. / Schule, R. / Moras, D. / Renaud, J.P. #2:  Journal: Nature / Year: 1995 Journal: Nature / Year: 1995Title: Crystal structure of the RAR-gamma ligand-binding domain bound to all-trans retinoic acid Authors: Renaud, J.P. / Rochel, N. / Ruff, M. / Vivat, V. / Chambon, P. / Gronemeyer, H. / Moras, D. | ||||||
| History |
| ||||||
| Remark 300 | BIOMOLECULE: 1 THIS ENTRY CONTAINS THE CRYSTALLOGRAPHIC ASYMMETRIC UNIT WHICH CONSISTS OF 2 CHAIN(S) ...BIOMOLECULE: 1 THIS ENTRY CONTAINS THE CRYSTALLOGRAPHIC ASYMMETRIC UNIT WHICH CONSISTS OF 2 CHAIN(S). THE BIOLOGICAL UNIT IS UNKNOWN. |
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  1n4h.cif.gz 1n4h.cif.gz | 67 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb1n4h.ent.gz pdb1n4h.ent.gz | 49 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  1n4h.json.gz 1n4h.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n4/1n4h https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n4/1n4h ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n4/1n4h ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/n4/1n4h | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  1nq7C  1k4wS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 29593.297 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: Ligand-Binding Domain Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1776.072 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Fragment: NR-2 box / Source method: obtained synthetically Details: The peptide was chemically synthesized. The sequence of the peptide is naturally found in Homo Sapiens (human). References: GenBank: 1906028, UniProt: Q15788*PLUS |
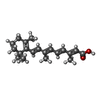
| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-REA / |
| #4: Water | ChemComp-HOH / |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.56 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 52.01 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 295 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 8 Details: PEG 6000, pH 8.0, VAPOR DIFFUSION, HANGING DROP, temperature 295K |
| Crystal grow | *PLUS Method: unknown / Details: Potier, N., (2003) Protein Sci., 12, 725. |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  ESRF ESRF  / Beamline: BM14 / Wavelength: 0.976205 Å / Beamline: BM14 / Wavelength: 0.976205 Å |
| Detector | Type: MARRESEARCH / Detector: CCD / Date: Nov 11, 2001 |
| Radiation | Monochromator: Si 111 CHANNEL / Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.976205 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.1→20 Å / Num. obs: 19390 / Observed criterion σ(I): 3 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.1→2.17 Å |
| Reflection | *PLUS Highest resolution: 2.1 Å / Num. obs: 19344 / % possible obs: 100 % / Redundancy: 6.6 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.045 |
| Reflection shell | *PLUS Highest resolution: 2.1 Å / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.175 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 8 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: PDB entry 1k4W Resolution: 2.1→20 Å / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 3
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine analyze | Luzzati coordinate error obs: 0.27 Å / Luzzati d res low obs: 5 Å / Luzzati sigma a obs: 0.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.1→20 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Xplor file |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | *PLUS Highest resolution: 2.1 Å / % reflection Rfree: 5 % / Rfactor Rfree: 0.233 / Rfactor Rwork: 0.208 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints | *PLUS
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj