+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-4971 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Structure of inner kinetochore CCAN complex | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | The map of CCAN complex with mask3. | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of meiotic DNA double-strand break formation involved in reciprocal meiotic recombination / COMA complex / maintenance of meiotic sister chromatid cohesion / : / Mis6-Sim4 complex / meiotic sister chromatid segregation / establishment of meiotic sister chromatid cohesion / ascospore formation / attachment of spindle microtubules to kinetochore / CENP-A containing chromatin assembly ...negative regulation of meiotic DNA double-strand break formation involved in reciprocal meiotic recombination / COMA complex / maintenance of meiotic sister chromatid cohesion / : / Mis6-Sim4 complex / meiotic sister chromatid segregation / establishment of meiotic sister chromatid cohesion / ascospore formation / attachment of spindle microtubules to kinetochore / CENP-A containing chromatin assembly / protein localization to chromosome, centromeric region / kinetochore assembly / outer kinetochore / establishment of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / protein localization to kinetochore / spindle pole body / mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint signaling / DNA replication initiation / meiotic cell cycle / chromosome segregation / kinetochore / cell division / structural molecule activity / nucleus / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.8 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yan K / Yang J / Zhang Z / McLaughlin SH / Chang L / Fasci D / Heck AJR / Barford D | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 3 items United Kingdom, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2019 Journal: Nature / Year: 2019Title: Structure of the inner kinetochore CCAN complex assembled onto a centromeric nucleosome. Authors: Kaige Yan / Jing Yang / Ziguo Zhang / Stephen H McLaughlin / Leifu Chang / Domenico Fasci / Ann E Ehrenhofer-Murray / Albert J R Heck / David Barford /     Abstract: In eukaryotes, accurate chromosome segregation in mitosis and meiosis maintains genome stability and prevents aneuploidy. Kinetochores are large protein complexes that, by assembling onto specialized ...In eukaryotes, accurate chromosome segregation in mitosis and meiosis maintains genome stability and prevents aneuploidy. Kinetochores are large protein complexes that, by assembling onto specialized Cenp-A nucleosomes, function to connect centromeric chromatin to microtubules of the mitotic spindle. Whereas the centromeres of vertebrate chromosomes comprise millions of DNA base pairs and attach to multiple microtubules, the simple point centromeres of budding yeast are connected to individual microtubules. All 16 budding yeast chromosomes assemble complete kinetochores using a single Cenp-A nucleosome (Cenp-A), each of which is perfectly centred on its cognate centromere. The inner and outer kinetochore modules are responsible for interacting with centromeric chromatin and microtubules, respectively. Here we describe the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae inner kinetochore module, the constitutive centromere associated network (CCAN) complex, assembled onto a Cenp-A nucleosome (CCAN-Cenp-A). The structure explains the interdependency of the constituent subcomplexes of CCAN and shows how the Y-shaped opening of CCAN accommodates Cenp-A to enable specific CCAN subunits to contact the nucleosomal DNA and histone subunits. Interactions with the unwrapped DNA duplex at the two termini of Cenp-A are mediated predominantly by a DNA-binding groove in the Cenp-L-Cenp-N subcomplex. Disruption of these interactions impairs assembly of CCAN onto Cenp-A. Our data indicate a mechanism of Cenp-A nucleosome recognition by CCAN and how CCAN acts as a platform for assembly of the outer kinetochore to link centromeres to the mitotic spindle for chromosome segregation. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_4971.map.gz emd_4971.map.gz | 6.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-4971-v30.xml emd-4971-v30.xml emd-4971.xml emd-4971.xml | 10.2 KB 10.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_4971.png emd_4971.png | 61.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4971 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4971 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4971 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4971 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 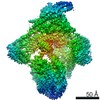 4579C  4580C  4581C  6qldC  6qleC  6qlfC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_4971.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_4971.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | The map of CCAN complex with mask3. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.09 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Inner kinetochore CCAN complex
| Entire | Name: Inner kinetochore CCAN complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Inner kinetochore CCAN complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Inner kinetochore CCAN complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#11 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  unidentified baculovirus / Recombinant cell: High Five unidentified baculovirus / Recombinant cell: High Five |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 32.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: NONE / Details: Reconstruction using SIMPLE_prime |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 618459 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















