+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3341 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Atomic cryoEM structure of Hsp90/Cdc37/Cdk4 complex | |||||||||
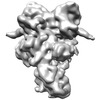
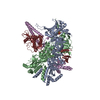
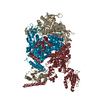
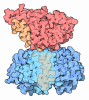
 Map data Map data | Reconstruction of Hsp90:Cdc37:Cdk4 complex. Part of series of maps, the highest resolution map being EMD-3337. This is a different subclass from the same particles as in EMD-3337, having well defined Cdk4 N-Lobe. Other relevant maps are EMD-3338, EMD-3339, EMD-3340. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Hsp90 / Cdc37 / Cdk4 / chaperone / kinase / unfolding | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcyclin D3-CDK4 complex / cyclin D1-CDK4 complex / cyclin D2-CDK4 complex / Evasion of Oncogene Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 / Evasion of Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 / citrulline metabolic process / regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II / Evasion of Oncogene Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 and CDK6 / Evasion of Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 and CDK6 / Drug-mediated inhibition of CDK4/CDK6 activity ...cyclin D3-CDK4 complex / cyclin D1-CDK4 complex / cyclin D2-CDK4 complex / Evasion of Oncogene Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 / Evasion of Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 / citrulline metabolic process / regulation of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II / Evasion of Oncogene Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 and CDK6 / Evasion of Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence Due to Defective p16INK4A binding to CDK4 and CDK6 / Drug-mediated inhibition of CDK4/CDK6 activity / regulation of type II interferon-mediated signaling pathway / regulation of type B pancreatic cell proliferation / hypoxia-inducible factor-asparagine dioxygenase / : / [protein]-asparagine 3-dioxygenase activity / HSP90-CDC37 chaperone complex / very long-chain fatty acid metabolic process / peptidyl-histidine dioxygenase activity / negative regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process / peptidyl-aspartic acid 3-dioxygenase activity / Aryl hydrocarbon receptor signalling / regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway / aryl hydrocarbon receptor complex / Cellular response to hypoxia / : / cellular response to ionomycin / positive regulation of vasculogenesis / histone methyltransferase binding / Transcriptional regulation by RUNX2 / dynein axonemal particle / carboxylic acid binding / cellular response to phorbol 13-acetate 12-myristate / receptor ligand inhibitor activity / positive regulation of type 2 mitophagy / ankyrin repeat binding / regulation of cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / ATP-dependent protein binding / protein kinase regulator activity / positive regulation of protein localization to cell surface / Notch binding / oxygen sensor activity / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity / post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression / Respiratory syncytial virus genome replication / telomerase holoenzyme complex assembly / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / Drug-mediated inhibition of ERBB2 signaling / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to trastuzumab / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to sapitinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to tesevatinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to neratinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to osimertinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to afatinib / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to AEE788 / Resistance of ERBB2 KD mutants to lapatinib / Drug resistance in ERBB2 TMD/JMD mutants / Uptake and function of diphtheria toxin / PTK6 Regulates Cell Cycle / regulation of type I interferon-mediated signaling pathway / : / TPR domain binding / dendritic growth cone / Defective binding of RB1 mutants to E2F1,(E2F2, E2F3) / Assembly and release of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) virions / protein phosphatase activator activity / Sema3A PAK dependent Axon repulsion / The NLRP3 inflammasome / regulation of protein ubiquitination / negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway / HSF1-dependent transactivation / positive regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / protein folding chaperone complex / bicellular tight junction / response to unfolded protein / NF-kappaB binding / cyclin-dependent kinase / HSF1 activation / positive regulation of myoblast differentiation / cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activity / Attenuation phase / chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly / RHOBTB2 GTPase cycle / axonal growth cone / telomere maintenance via telomerase / protein targeting / Purinergic signaling in leishmaniasis infection / cyclin-dependent protein kinase holoenzyme complex / regulation of G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / supramolecular fiber organization / heat shock protein binding / DNA polymerase binding / Signaling by ERBB2 / protein folding chaperone / peptide binding / negative regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / cellular response to interleukin-4 / ESR-mediated signaling / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / Constitutive Signaling by Overexpressed ERBB2 / cyclin binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
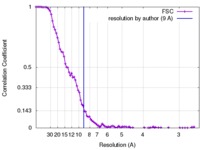
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 9.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Verba KA / Wang RYR / Arakawa A / Liu Y / Shirouzu M / Yokoyama S / Agard DA | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2016 Journal: Science / Year: 2016Title: Atomic structure of Hsp90-Cdc37-Cdk4 reveals that Hsp90 traps and stabilizes an unfolded kinase. Authors: Kliment A Verba / Ray Yu-Ruei Wang / Akihiko Arakawa / Yanxin Liu / Mikako Shirouzu / Shigeyuki Yokoyama / David A Agard /   Abstract: The Hsp90 molecular chaperone and its Cdc37 cochaperone help stabilize and activate more than half of the human kinome. However, both the mechanism by which these chaperones assist their "client" ...The Hsp90 molecular chaperone and its Cdc37 cochaperone help stabilize and activate more than half of the human kinome. However, both the mechanism by which these chaperones assist their "client" kinases and the reason why some kinases are addicted to Hsp90 while closely related family members are independent are unknown. Our structural understanding of these interactions is lacking, as no full-length structures of human Hsp90, Cdc37, or either of these proteins with a kinase have been elucidated. Here we report a 3.9 angstrom cryo-electron microscopy structure of the Hsp90-Cdc37-Cdk4 kinase complex. Surprisingly, the two lobes of Cdk4 are completely separated with the β4-β5 sheet unfolded. Cdc37 mimics part of the kinase N lobe, stabilizing an open kinase conformation by wedging itself between the two lobes. Finally, Hsp90 clamps around the unfolded kinase β5 strand and interacts with exposed N- and C-lobe interfaces, protecting the kinase in a trapped unfolded state. On the basis of this structure and an extensive amount of previously collected data, we propose unifying conceptual and mechanistic models of chaperone-kinase interactions. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3341.map.gz emd_3341.map.gz | 60 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3341-v30.xml emd-3341-v30.xml emd-3341.xml emd-3341.xml | 16.9 KB 16.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_3341_fsc.xml emd_3341_fsc.xml | 10.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_3341.tif emd_3341.tif | 135.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3341 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3341 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3341 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3341 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5fwlMC  5jwlM  3337C 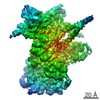 3338C  3339C  3340C  3342C  3343C  3344C  5fwkC  5fwmC  5fwpC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3341.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 62.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3341.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 62.5 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Reconstruction of Hsp90:Cdc37:Cdk4 complex. Part of series of maps, the highest resolution map being EMD-3337. This is a different subclass from the same particles as in EMD-3337, having well defined Cdk4 N-Lobe. Other relevant maps are EMD-3338, EMD-3339, EMD-3340. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.315 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of Human Hsp90 beta, human Cdc37 and human Cdk4
| Entire | Name: Complex of Human Hsp90 beta, human Cdc37 and human Cdk4 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Complex of Human Hsp90 beta, human Cdc37 and human Cdk4
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of Human Hsp90 beta, human Cdc37 and human Cdk4 type: sample / ID: 1000 / Details: All three proteins were co-expressed in Sf9 cells. Oligomeric state: One Hsp90 homodimer binds to one Cdc37 and one Cdk4 Number unique components: 3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 245 KDa / Theoretical: 245 KDa / Method: As cloned, verified by SDS-PAGE |
-Macromolecule #1: Heat Shock Protein HSP 90 beta
| Macromolecule | Name: Heat Shock Protein HSP 90 beta / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: Hsp90 / Number of copies: 2 / Oligomeric state: Dimer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Location in cell: cytoplasm Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Location in cell: cytoplasm |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 83 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta / GO: citrulline metabolic process / InterPro: Heat shock protein Hsp90 family |
-Macromolecule #2: Hsp90 co-chaperone Cdc37
| Macromolecule | Name: Hsp90 co-chaperone Cdc37 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Name.synonym: Cdc37 / Number of copies: 1 / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Location in cell: throughout Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Location in cell: throughout |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 44.5 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Hsp90 co-chaperone Cdc37 / GO: GO: 0000002 |
-Macromolecule #3: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4
| Macromolecule | Name: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Name.synonym: Cdk4 / Number of copies: 1 / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Location in cell: throughout Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Location in cell: throughout |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 33.7 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 / GO: very long-chain fatty acid metabolic process / InterPro: Protein kinase domain |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.27 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Details: 20mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 150 mM NaCl, 10 mM KCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 20 mM Na2MoO4, 2mM DTT, 0.085mM DDM |
| Grid | Details: Glow discharged for 30 sec, C-flat 400 mesh 1.2/1.3 thick carbon grids (Protochips) |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 90 % / Chamber temperature: 95 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III / Method: Single blot from 4 to 6 seconds, at 20C |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Alignment procedure | Legacy - Astigmatism: At high mag via FT. |
| Date | Nov 25, 2014 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 3718 / Average electron dose: 44 e/Å2 / Details: 38 frames, 7.6 seconds total exposure / Bits/pixel: 8 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.4 µm / Nominal magnification: 22500 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - #0 - Chain ID: A / Chain - #1 - Chain ID: B / Chain - #2 - Chain ID: E / Chain - #3 - Chain ID: K |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: Chimera, Rosetta |
| Details | Residues 5-85 (N-lobe) of Cdk4 from 3G33 were fit in Chimera as rigid body into EMD-3341. Such fit N-lobe of Cdk4 was further tweaked in Coot in the context of 5FWK to join the Cdk4 chain and minimize clashes for each of the maps. To relieve atomic clashes or bond length/angle distortions at the linker regions, these models were subjected to "Cartesian space relax" protocol within corresponding density maps using Rosetta. Final models were selected using the combined score of Rosetta all-atom physically-realistic score and electron density score. |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Overall B value: 200 Target criteria: cross correlation of fit into the density with Rosetta force field score |
| Output model |  PDB-5fwl:  PDB-5jwl: |
-Atomic model buiding 2
| Initial model | PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: Chimera, Rosetta |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Overall B value: 200 Target criteria: cross correlation of fit into the density with Rosetta force field score |
| Output model |  PDB-5fwl:  PDB-5jwl: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)