[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-30083: Human apo ferritin chain A frozen on TEM grid with amorphous carb... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-30083 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
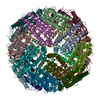
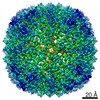
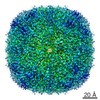
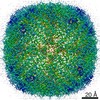
| Title | Human apo ferritin chain A frozen on TEM grid with amorphous carbon supporting film | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Human apo ferritin chain A frozen on TEM grid with amorphous carbon supporting film | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Apoferritin heavy chain / Homo sapiens / METAL TRANSPORT / OXIDOREDUCTASE | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationiron ion sequestering activity / ferritin complex / Scavenging by Class A Receptors / negative regulation of ferroptosis / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / ferroxidase / autolysosome / ferroxidase activity / negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation / ferric iron binding ...iron ion sequestering activity / ferritin complex / Scavenging by Class A Receptors / negative regulation of ferroptosis / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / ferroxidase / autolysosome / ferroxidase activity / negative regulation of fibroblast proliferation / ferric iron binding / autophagosome / iron ion transport / ferrous iron binding / Iron uptake and transport / tertiary granule lumen / ficolin-1-rich granule lumen / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / immune response / iron ion binding / negative regulation of cell population proliferation / Neutrophil degranulation / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / identical protein binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.6 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Huang X / Zhang L | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 4 items China, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Prog Biophys Mol Biol / Year: 2020 Journal: Prog Biophys Mol Biol / Year: 2020Title: Amorphous nickel titanium alloy film: A new choice for cryo electron microscopy sample preparation. Authors: Xiaojun Huang / Lei Zhang / Zuoling Wen / Hui Chen / Shuoguo Li / Gang Ji / Chang-Cheng Yin / Fei Sun /  Abstract: Cryo-electron microscopy (cryoEM) has become one of the most important approach for structural biology. However, barriers are still there for an increased successful rate, a better resolution and ...Cryo-electron microscopy (cryoEM) has become one of the most important approach for structural biology. However, barriers are still there for an increased successful rate, a better resolution and improved efficiency from sample preparation, data collection to image processing. CryoEM sample preparation is one of the bottlenecks with many efforts made recently, including the optimization of supporting substrate (e.g. ultra-thin carbon, graphene, pure gold, 2d crystal of streptavidin, and affinity modification), which was aimed to solve air-water interface problem, or reduce beam induced motion (BIM), or change particle distribution in the grid hole. Here, we report another effort of developing a new supporting substrate, the amorphous nickel-titanium alloy (ANTA) film, for cryoEM sample preparation as a layer of holey supporting film covering on TEM grid. Our investigations showed advantages of ANTA film in comparison with conventional carbon film, including much better electron conductivity and trace non-specific interaction with protein. These advantages yield less BIM and significantly improved particle distribution during cryoEM experiment of human apo-ferritn, thus resulting an improved reconstruction resolution from a reduced number of micrographs and particles. Unlike the pure gold film, the usage of the ANTA film is just same with the carbon film, compatible to conventional automatic cryoEM data collection procedure. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_30083.map.gz emd_30083.map.gz | 13.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-30083-v30.xml emd-30083-v30.xml emd-30083.xml emd-30083.xml | 12.5 KB 12.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_30083_fsc.xml emd_30083_fsc.xml | 10.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_30083.png emd_30083.png | 263.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-30083.cif.gz emd-30083.cif.gz | 5.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30083 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30083 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30083 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30083 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6m52MC  6m54C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-10405 (Title: Human apo ferritin frozen on TEM grid with amorphous carbon supporting film EMPIAR-10405 (Title: Human apo ferritin frozen on TEM grid with amorphous carbon supporting filmData size: 226.5 Data #1: Human apo ferritin frozen on TEM grid with amorphous carbon supporting film [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_30083.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_30083.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 91.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Human apo ferritin chain A frozen on TEM grid with amorphous carbon supporting film | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.87 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : apoferritin heavy chain, 24 homologous polymer
| Entire | Name: apoferritin heavy chain, 24 homologous polymer |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: apoferritin heavy chain, 24 homologous polymer
| Supramolecule | Name: apoferritin heavy chain, 24 homologous polymer / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 Details: frozen on TEM grid with amorphous carbon supporting film |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 440 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Ferritin heavy chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Ferritin heavy chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 24 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: ferroxidase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 21.255656 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MTTASTSQVR QNYHQDSEAA INRQINLELY ASYVYLSMSY YFDRDDVALK NFAKYFLHQS HEEREHAEKL MKLQNQRGGR IFLQDIKKP DCDDWESGLN AMECALHLEK NVNQSLLELH KLATDKNDPH LCDFIETHYL NEQVKAIKEL GDHVTNLRKM G APESGLAE YLFDKHTLGD SDNES UniProtKB: Ferritin heavy chain |
-Macromolecule #2: FE (II) ION
| Macromolecule | Name: FE (II) ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: FE2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 55.845 Da |
-Macromolecule #3: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.3 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| |||||||||
| Grid | Model: Homemade / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY ARRAY / Support film - Film thickness: 25 / Pretreatment - Type: PLASMA CLEANING / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: OTHER | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: LEICA EM GP |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller













 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)























