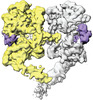
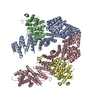
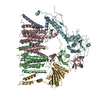
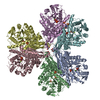
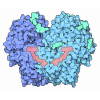
登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-25523タイトル Cryo-EM structure of the extracellular module of the full-length EGFR bound to EGF. "tips-separated" conformation WT:EGF_separated 複合体 : full-length human EGFR:EGF complexタンパク質・ペプチド : Epidermal growth factor receptorタンパク質・ペプチド : Epidermal growth factor / / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト)手法 / / 解像度 : 3.3 Å Huang Y / Ognjenovic J 資金援助 Organization Grant number 国 Canada Excellence Research Chair Award Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI)
ジャーナル : Elife / 年 : 2021タイトル : A molecular mechanism for the generation of ligand-dependent differential outputs by the epidermal growth factor receptor.著者 : Yongjian Huang / Jana Ognjenovic / Deepti Karandur / Kate Miller / Alan Merk / Sriram Subramaniam / John Kuriyan / 要旨 : The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that couples the binding of extracellular ligands, such as EGF and transforming growth factor-α (TGF-α), to the initiation ... The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a receptor tyrosine kinase that couples the binding of extracellular ligands, such as EGF and transforming growth factor-α (TGF-α), to the initiation of intracellular signaling pathways. EGFR binds to EGF and TGF-α with similar affinity, but generates different signals from these ligands. To address the mechanistic basis of this phenomenon, we have carried out cryo-EM analyses of human EGFR bound to EGF and TGF-α. We show that the extracellular module adopts an ensemble of dimeric conformations when bound to either EGF or TGF-α. The two extreme states of this ensemble represent distinct ligand-bound quaternary structures in which the membrane-proximal tips of the extracellular module are either juxtaposed or separated. EGF and TGF-α differ in their ability to maintain the conformation with the membrane-proximal tips of the extracellular module separated, and this conformation is stabilized preferentially by an oncogenic EGFR mutation. Close proximity of the transmembrane helices at the junction with the extracellular module has been associated previously with increased EGFR activity. Our results show how EGFR can couple the binding of different ligands to differential modulation of this proximity, thereby suggesting a molecular mechanism for the generation of ligand-sensitive differential outputs in this receptor family. 履歴 登録 2021年11月24日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2021年12月22日 - マップ公開 2021年12月22日 - 更新 2024年10月16日 - 現状 2024年10月16日 処理サイト : RCSB / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) データ登録者
データ登録者 米国, 2件
米国, 2件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Elife / 年: 2021
ジャーナル: Elife / 年: 2021

 構造の表示
構造の表示 ムービービューア
ムービービューア SurfView
SurfView Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_25523.map.gz
emd_25523.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-25523-v30.xml
emd-25523-v30.xml emd-25523.xml
emd-25523.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_25523.png
emd_25523.png emd-25523.cif.gz
emd-25523.cif.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25523
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25523 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25523
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-25523 emd_25523_validation.pdf.gz
emd_25523_validation.pdf.gz EMDB検証レポート
EMDB検証レポート emd_25523_full_validation.pdf.gz
emd_25523_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_25523_validation.xml.gz
emd_25523_validation.xml.gz emd_25523_validation.cif.gz
emd_25523_validation.cif.gz https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25523
https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25523 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25523
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-25523 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_25523.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 103 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_25523.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 103 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト)
 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー

































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















