[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-23147: The structure of an infectious immature flavivirus redefines vira... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-23147 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
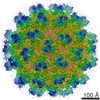
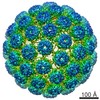
| Title | The structure of an infectious immature flavivirus redefines viral architecture and maturation | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Local-resolution filtered map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Flavivirus / glycoprotein / fusion / VIRUS | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationribonucleoside triphosphate phosphatase activity / viral capsid / double-stranded RNA binding / methyltransferase cap1 activity / mRNA 5'-cap (guanine-N7-)-methyltransferase activity / RNA helicase activity / protein dimerization activity / host cell endoplasmic reticulum membrane / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / serine-type endopeptidase activity ...ribonucleoside triphosphate phosphatase activity / viral capsid / double-stranded RNA binding / methyltransferase cap1 activity / mRNA 5'-cap (guanine-N7-)-methyltransferase activity / RNA helicase activity / protein dimerization activity / host cell endoplasmic reticulum membrane / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / serine-type endopeptidase activity / viral RNA genome replication / RNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / symbiont entry into host cell / virion attachment to host cell / host cell nucleus / virion membrane / structural molecule activity / proteolysis / extracellular region / ATP binding / metal ion binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Binjari virus Binjari virus | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hardy JM / Venugopal HV | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Australia, 1 items Australia, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2021 Journal: Sci Adv / Year: 2021Title: The structure of an infectious immature flavivirus redefines viral architecture and maturation. Authors: Natalee D Newton / Joshua M Hardy / Naphak Modhiran / Leon E Hugo / Alberto A Amarilla / Summa Bibby / Hariprasad Venugopal / Jessica J Harrison / Renee J Traves / Roy A Hall / Jody Hobson- ...Authors: Natalee D Newton / Joshua M Hardy / Naphak Modhiran / Leon E Hugo / Alberto A Amarilla / Summa Bibby / Hariprasad Venugopal / Jessica J Harrison / Renee J Traves / Roy A Hall / Jody Hobson-Peters / Fasséli Coulibaly / Daniel Watterson /  Abstract: Flaviviruses are the cause of severe human diseases transmitted by mosquitoes and ticks. These viruses use a potent fusion machinery to enter target cells that needs to be restrained during viral ...Flaviviruses are the cause of severe human diseases transmitted by mosquitoes and ticks. These viruses use a potent fusion machinery to enter target cells that needs to be restrained during viral assembly and egress. A molecular chaperone, premembrane (prM) maintains the virus particles in an immature, fusion-incompetent state until they exit the cell. Taking advantage of an insect virus that produces particles that are both immature and infectious, we determined the structure of the first immature flavivirus with a complete spike by cryo-electron microscopy. Unexpectedly, the prM chaperone forms a supporting pillar that maintains the immature spike in an asymmetric and upright state, primed for large rearrangements upon acidification. The collapse of the spike along a path defined by the prM chaperone is required, and its inhibition by a multivalent immunoglobulin M blocks infection. The revised architecture and collapse model are likely to be conserved across flaviviruses. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23147.map.gz emd_23147.map.gz | 270 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23147-v30.xml emd-23147-v30.xml emd-23147.xml emd-23147.xml | 16.7 KB 16.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_23147.png emd_23147.png | 302.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-23147.cif.gz emd-23147.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23147 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23147 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23147 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23147 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_23147_validation.pdf.gz emd_23147_validation.pdf.gz | 604.6 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_23147_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_23147_full_validation.pdf.gz | 604.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_23147_validation.xml.gz emd_23147_validation.xml.gz | 7.8 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_23147_validation.cif.gz emd_23147_validation.cif.gz | 9.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23147 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23147 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23147 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-23147 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7l30MC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23147.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23147.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 512 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Local-resolution filtered map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.34 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
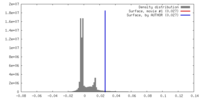
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Binjari virus
| Entire | Name:  Binjari virus Binjari virus |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Binjari virus
| Supramolecule | Name: Binjari virus / type: virus / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: M and E from Binjari virus form a complex that assembles into anti-parallel dimers, (M-E)2, in the T=3 icosahedral particle. NCBI-ID: 2305258 / Sci species name: Binjari virus / Sci species strain: BFTA20 / Virus type: VIRION / Virus isolate: SPECIES / Virus enveloped: Yes / Virus empty: No |
|---|---|
| Host (natural) | Organism:  Ochlerotatus normanensis (mosquito) Ochlerotatus normanensis (mosquito) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22 MDa |
| Virus shell | Shell ID: 1 / Diameter: 470.0 Å / T number (triangulation number): 3 |
-Macromolecule #1: Envelope protein E
| Macromolecule | Name: Envelope protein E / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Binjari virus Binjari virus |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 53.495086 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: NQCLDVQSRD FVQGVSGGTW VDVVLDHDNC ITIVADGKPS FDIRLSKMSM SKFAEYKRYC LQATMSDVTS IVACPGAGDA HNDKSKNHE YICKAVNNDR GWGNGCVLFG KGSMETCGKF ECKKKMAGKL VARENVESVV TVHVHGASAT DTKGVDTAST A KATITPKA ...String: NQCLDVQSRD FVQGVSGGTW VDVVLDHDNC ITIVADGKPS FDIRLSKMSM SKFAEYKRYC LQATMSDVTS IVACPGAGDA HNDKSKNHE YICKAVNNDR GWGNGCVLFG KGSMETCGKF ECKKKMAGKL VARENVESVV TVHVHGASAT DTKGVDTAST A KATITPKA SVATLNLNDF GSLEVDCSTD VGMDFGEIVV ADMSGKWWIV NKDWFNELAL PWSTASTTAE VWQARDRLVE FG WPHAAKQ NIYDIGDQEG AVTAAIAQAP MAKWESDKVE LISGILKCKV KLGNLKLRGV TYSMCAQTFT TETRPADTGH GTV AFKVKY VGTDVPCRVP LHIIDSDGGV AAGRVITAHP FVMKQNDYII LEVEPPFGDS KIEIGTGTTK LVEAWHRKGS SIGN AFTAT YKGITKLTVL GEHAWDFNSL GGFGASLGKA VHTLFGGVFR VMFGGMGWLT KIFVGAVLVW LGLGAHDKTI ATTMI LVGS ILMYMAVTVG ALS UniProtKB: Genome polyprotein |
-Macromolecule #2: prM protein
| Macromolecule | Name: prM protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Binjari virus Binjari virus |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.946809 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: ATLRTVGDLT WLNVSTTDVG KWIRVENRHG KGECFVTATD VGTWCSDSVG YECPQIAPAY DPEDLDCYCR NTSTYVTYGR CKNGRSGRS RSKRAITIAP HGEAGLRVGS TKHWTSRATP QRYLMRVEKW VLRHPLPALV LVVLGWMMGR SHGQRAMYIV L MLLVAPSY G UniProtKB: Genome polyprotein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 4 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
| ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Details: 0 second wait time 2.5 second blot time -4 blot force 1 second drain time. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 6226 / Average exposure time: 12.8 sec. / Average electron dose: 43.2768 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated defocus max: 4.3 µm / Calibrated defocus min: 0.1 µm / Calibrated magnification: 105000 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






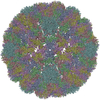
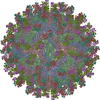

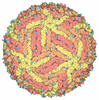
 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)