+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20030 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
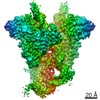
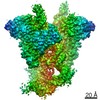
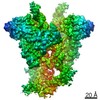
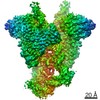
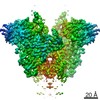
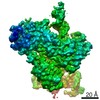
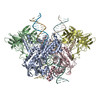
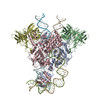
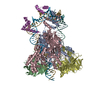
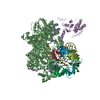
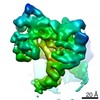
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of mouse RAG1/2 PRC complex (DNA0) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | structure of mouse RAG1/2 PRC complex | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | V(D)J recombination / DNA Transposition / RAG / SCID / RECOMBINATION / RECOMBINATION-DNA complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information: / positive regulation of myeloid progenitor cell differentiation / regulation of tolerance induction / calcium-dependent protein kinase regulator activity / regulation of T cell mediated immune response to tumor cell / positive regulation of mismatch repair / negative regulation of apoptotic cell clearance / plasmacytoid dendritic cell activation / negative regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / T-helper 1 cell activation ...: / positive regulation of myeloid progenitor cell differentiation / regulation of tolerance induction / calcium-dependent protein kinase regulator activity / regulation of T cell mediated immune response to tumor cell / positive regulation of mismatch repair / negative regulation of apoptotic cell clearance / plasmacytoid dendritic cell activation / negative regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex assembly / T-helper 1 cell activation / mature B cell differentiation involved in immune response / T-helper 1 cell differentiation / positive regulation of myeloid cell differentiation / myeloid dendritic cell activation / positive regulation of toll-like receptor 2 signaling pathway / positive regulation of dendritic cell differentiation / DNA recombinase complex / C-X-C chemokine binding / negative regulation of CD4-positive, alpha-beta T cell differentiation / positive regulation of toll-like receptor 9 signaling pathway / B cell homeostatic proliferation / neutrophil clearance / endodeoxyribonuclease complex / negative regulation of T cell differentiation in thymus / positive regulation of glycogen catabolic process / DN2 thymocyte differentiation / pre-B cell allelic exclusion / DNA geometric change / positive regulation of toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway / endothelial cell chemotaxis / positive regulation of organ growth / RAGE receptor binding / eye development / Regulation of TLR by endogenous ligand / positive regulation of interleukin-1 production / regulation of behavioral fear response / bubble DNA binding / V(D)J recombination / negative regulation of T cell apoptotic process / myeloid cell differentiation / alphav-beta3 integrin-HMGB1 complex / myeloid progenitor cell differentiation / Apoptosis induced DNA fragmentation / phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate binding / inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus / negative regulation of thymocyte apoptotic process / MyD88 deficiency (TLR2/4) / macrophage activation involved in immune response / positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis / positive regulation of monocyte chemotactic protein-1 production / histone H3K4me3 reader activity / regulation of nucleotide-excision repair / endothelial cell proliferation / positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation / phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding / positive regulation of chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 production / cellular response to interleukin-7 / glycogen catabolic process / apoptotic cell clearance / IRAK4 deficiency (TLR2/4) / regulation of T cell differentiation / MyD88:MAL(TIRAP) cascade initiated on plasma membrane / dendritic cell chemotaxis / positive regulation of DNA binding / DNA binding, bending / organ growth / supercoiled DNA binding / positive regulation of T cell differentiation / T cell lineage commitment / positive regulation of wound healing / phosphatidylserine binding / B cell lineage commitment / positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis / chemoattractant activity / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment / phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding / T cell homeostasis / TRAF6 mediated NF-kB activation / negative regulation of type II interferon production / DNA topological change / negative regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration / Advanced glycosylation endproduct receptor signaling / positive regulation of interferon-alpha production / positive regulation of activated T cell proliferation / positive regulation of interleukin-10 production / T cell differentiation / positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration / Pyroptosis / protein kinase activator activity / protein autoubiquitination / four-way junction DNA binding / condensed chromosome / DNA polymerase binding / phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding / transcription repressor complex / positive regulation of interleukin-12 production / phosphatidylinositol binding / positive regulation of autophagy / activation of innate immune response / lung development Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chen X / Cui Y / Zhou ZH / Yang W / Gellert M | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2020 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2020Title: Cutting antiparallel DNA strands in a single active site. Authors: Xuemin Chen / Yanxiang Cui / Robert B Best / Huaibin Wang / Z Hong Zhou / Wei Yang / Martin Gellert /  Abstract: A single enzyme active site that catalyzes multiple reactions is a well-established biochemical theme, but how one nuclease site cleaves both DNA strands of a double helix has not been well ...A single enzyme active site that catalyzes multiple reactions is a well-established biochemical theme, but how one nuclease site cleaves both DNA strands of a double helix has not been well understood. In analyzing site-specific DNA cleavage by the mammalian RAG1-RAG2 recombinase, which initiates V(D)J recombination, we find that the active site is reconfigured for the two consecutive reactions and the DNA double helix adopts drastically different structures. For initial nicking of the DNA, a locally unwound and unpaired DNA duplex forms a zipper via alternating interstrand base stacking, rather than melting as generally thought. The second strand cleavage and formation of a hairpin-DNA product requires a global scissor-like movement of protein and DNA, delivering the scissile phosphate into the rearranged active site. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20030.map.gz emd_20030.map.gz | 5.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20030-v30.xml emd-20030-v30.xml emd-20030.xml emd-20030.xml | 21 KB 21 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20030.png emd_20030.png | 56.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20030.cif.gz emd-20030.cif.gz | 7.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20030 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20030 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20030 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20030 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6oemMC  6oenC  6oeoC  6oepC  6oeqC  6oerC  6v0vC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20030.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20030.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | structure of mouse RAG1/2 PRC complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.07 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : RAG1/2 pre-reaction complex
+Supramolecule #1: RAG1/2 pre-reaction complex
+Macromolecule #1: V(D)J recombination-activating protein 1
+Macromolecule #2: V(D)J recombination-activating protein 2
+Macromolecule #7: High mobility group protein B1
+Macromolecule #3: DNA (57-MER)
+Macromolecule #4: DNA (46-MER)
+Macromolecule #5: DNA (46-MER)
+Macromolecule #6: DNA (57-MER)
+Macromolecule #8: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #9: ZINC ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 57.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















