+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-1908 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Unique structure of iC3b by 3D-Electron Microscopy | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | 3D structure of iC3b, a component of the complement alternative pathway | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | iC3b / C3b / complement / 3D-electron microscopy / SAXS | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 24.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Alcorlo M / Martinez-Barricarte R / Fernandez FJ / Rodriguez-Gallego C / Round A / Vega MC / Harris CL / Rodriguez-de-Cordoba S / Llorca O | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2011 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2011Title: Unique structure of iC3b resolved at a resolution of 24 Å by 3D-electron microscopy. Authors: Martin Alcorlo / Ruben Martínez-Barricarte / Francisco J Fernández / César Rodríguez-Gallego / Adam Round / M Cristina Vega / Claire L Harris / Santiago Rodríguez de Cordoba / Oscar Llorca /  Abstract: Activation of C3, deposition of C3b on the target surface, and subsequent amplification by formation of a C3-cleaving enzyme (C3-convertase; C3bBb) triggers the effector functions of complement that ...Activation of C3, deposition of C3b on the target surface, and subsequent amplification by formation of a C3-cleaving enzyme (C3-convertase; C3bBb) triggers the effector functions of complement that result in inflammation and cell lysis. Concurrently, surface-bound C3b is proteolyzed to iC3b by factor I and appropriate cofactors. iC3b then interacts with the complement receptors (CR) of the Ig superfamily, CR2 (CD21), CR3 (CD11b/CD18), and CR4 (CD11c/CD18) on leukocytes, down-modulating inflammation, enhancing B cell-mediated immunity, and targeting pathogens for clearance by phagocytosis. Using EM and small-angle X-ray scattering, we now present a medium-resolution structure of iC3b (24 Å). iC3b displays a unique conformation with structural features distinct from any other C3 fragment. The macroglobulin ring in iC3b is similar to that in C3b, whereas the TED (thioester-containing domain) domain and the remnants of the CUB (complement protein subcomponents C1r/C1s, urchin embryonic growth factor and bone morphogenetic protein 1) domain have moved to locations more similar to where they were in native C3. A consequence of this large conformational change is the disruption of the factor B binding site, which renders iC3b unable to assemble a C3-convertase. This structural model also justifies the decreased interaction between iC3b and complement regulators and the recognition of iC3b by the CR of the Ig superfamily, CR2, CR3, and CR4. These data further illustrate the extraordinary conformational versatility of C3 to accommodate a great diversity of functional activities. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_1908.map.gz emd_1908.map.gz | 1.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-1908-v30.xml emd-1908-v30.xml emd-1908.xml emd-1908.xml | 9.8 KB 9.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  EMDB-1908_image.tif EMDB-1908_image.tif | 742.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1908 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1908 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1908 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-1908 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Similar structure data |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_1908.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_1908.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 1.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | 3D structure of iC3b, a component of the complement alternative pathway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 4.2 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human iC3b
| Entire | Name: Human iC3b |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Human iC3b
| Supramolecule | Name: Human iC3b / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Oligomeric state: Monomer / Number unique components: 1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 181 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Complement component iC3b
| Macromolecule | Name: Complement component iC3b / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: iC3b / Number of copies: 1 / Oligomeric state: Monomer / Recombinant expression: No |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Tissue: Plasma Homo sapiens (human) / synonym: Human / Tissue: Plasma |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 181 KDa |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1.1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 / Details: 150 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris-HCL |
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Details: 1% w/v uranyl acetate |
| Grid | Details: Carbon-coated 400 mesh copper grid |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NONE / Instrument: OTHER |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | JEOL 1230 |
|---|---|
| Alignment procedure | Legacy - Astigmatism: Objective lens astigmatism was corrected at 80,000 times magnification |
| Image recording | Category: FILM / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM / Digitization - Scanner: OTHER / Digitization - Sampling interval: 10.5 µm / Number real images: 112 / Average electron dose: 10 e/Å2 Details: Images scanned with Minolta Dimage Scan Multi Pro scanner at 2400 dpi and averaged to a final 4.2 Angstroms pixel at the specimen Bits/pixel: 16 |
| Tilt angle min | 0 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 100 kV / Electron source: TUNGSTEN HAIRPIN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.9 mm / Nominal defocus max: 1.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 50000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: Eucentric / Specimen holder model: JEOL / Tilt angle max: 47 |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Details | The particles were selected manually with Boxer (Eman) |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 24.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: Xmipp,EMAN / Number images used: 29730 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: Situs |
| Details | Protocol: Rigid Body |
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Target criteria: Cross-correlation |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera
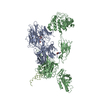
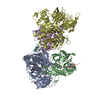

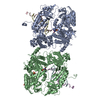
 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)






















