[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-15341: Human replisome bound by pol alpha, engaged on fork DNA containin... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
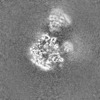
| Title | Human replisome bound by pol alpha, engaged on fork DNA containing a 60 nt lagging strand. | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Human replisome bound by pol alpha, engaged on fork DNA containing a 60 nt lagging strand. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Replication / helicase / polymerase / pol alpha / priming | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcellular response to bleomycin / DNA primase AEP / ribonucleotide binding / DNA secondary structure binding / regulation of nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / detection of abiotic stimulus / replication fork arrest / Switching of origins to a post-replicative state / Unwinding of DNA / cell cycle phase transition ...cellular response to bleomycin / DNA primase AEP / ribonucleotide binding / DNA secondary structure binding / regulation of nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / detection of abiotic stimulus / replication fork arrest / Switching of origins to a post-replicative state / Unwinding of DNA / cell cycle phase transition / DNA replication initiation / DNA strand elongation involved in mitotic DNA replication / GINS complex / mitotic DNA replication preinitiation complex assembly / activation of protein kinase activity / DNA/RNA hybrid binding / replication fork protection complex / Inhibition of replication initiation of damaged DNA by RB1/E2F1 / regulation of phosphorylation / cellular response to cisplatin / nuclear origin of replication recognition complex / alpha DNA polymerase:primase complex / Telomere C-strand synthesis initiation / anaphase-promoting complex binding / regulation of type I interferon production / cellular response to hydroxyurea / mitotic DNA replication / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in DNA replication, damage repair and senescence / Polymerase switching / CMG complex / DNA replication checkpoint signaling / Processive synthesis on the lagging strand / DNA replication preinitiation complex / MCM complex / Removal of the Flap Intermediate / mitotic DNA replication checkpoint signaling / lagging strand elongation / double-strand break repair via break-induced replication / mitotic DNA replication initiation / DNA replication, synthesis of primer / Polymerase switching on the C-strand of the telomere / mitotic intra-S DNA damage checkpoint signaling / regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / inner cell mass cell proliferation / DNA strand elongation involved in DNA replication / Apoptotic cleavage of cellular proteins / branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube / positive regulation of double-strand break repair / DNA synthesis involved in DNA repair / leading strand elongation / G1/S-Specific Transcription / mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / nuclear replication fork / replication fork processing / DNA replication origin binding / cochlea development / DNA replication initiation / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / response to UV / positive regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination / cellular response to interleukin-4 / lung development / DNA helicase activity / cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus / DNA damage checkpoint signaling / morphogenesis of an epithelium / Defective pyroptosis / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / enzyme activator activity / peptidyl-serine phosphorylation / helicase activity / circadian rhythm / regulation of circadian rhythm / double-strand break repair via nonhomologous end joining / DNA-templated DNA replication / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / multicellular organism growth / nuclear matrix / protein import into nucleus / Orc1 removal from chromatin / cellular senescence / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / nuclear envelope / mitotic cell cycle / nucleosome assembly / single-stranded DNA binding / site of double-strand break / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / histone binding / DNA-directed DNA polymerase / DNA helicase / DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / DNA replication / chromosome, telomeric region / cell population proliferation / Ub-specific processing proteases / cilium / ciliary basal body Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
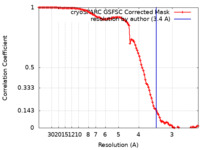
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Jones ML / Yeeles JTP | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1 items United Kingdom, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2023 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2023Title: How Pol α-primase is targeted to replisomes to prime eukaryotic DNA replication. Authors: Morgan L Jones / Valentina Aria / Yasemin Baris / Joseph T P Yeeles /  Abstract: During eukaryotic DNA replication, Pol α-primase generates primers at replication origins to start leading-strand synthesis and every few hundred nucleotides during discontinuous lagging-strand ...During eukaryotic DNA replication, Pol α-primase generates primers at replication origins to start leading-strand synthesis and every few hundred nucleotides during discontinuous lagging-strand replication. How Pol α-primase is targeted to replication forks to prime DNA synthesis is not fully understood. Here, by determining cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of budding yeast and human replisomes containing Pol α-primase, we reveal a conserved mechanism for the coordination of priming by the replisome. Pol α-primase binds directly to the leading edge of the CMG (CDC45-MCM-GINS) replicative helicase via a complex interaction network. The non-catalytic PRIM2/Pri2 subunit forms two interfaces with CMG that are critical for in vitro DNA replication and yeast cell growth. These interactions position the primase catalytic subunit PRIM1/Pri1 directly above the exit channel for lagging-strand template single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), revealing why priming occurs efficiently only on the lagging-strand template and elucidating a mechanism for Pol α-primase to overcome competition from RPA to initiate primer synthesis. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_15341.map.gz emd_15341.map.gz | 6.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-15341-v30.xml emd-15341-v30.xml emd-15341.xml emd-15341.xml | 11.8 KB 11.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_15341_fsc.xml emd_15341_fsc.xml | 11.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
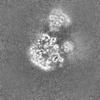
| Images |  emd_15341.png emd_15341.png | 105.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_15341_half_map_1.map.gz emd_15341_half_map_1.map.gz emd_15341_half_map_2.map.gz emd_15341_half_map_2.map.gz | 115.9 MB 115.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15341 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15341 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15341 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-15341 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8b9dMC  8b9aC  8b9bC  8b9cC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_15341.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_15341.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Human replisome bound by pol alpha, engaged on fork DNA containing a 60 nt lagging strand. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.2363 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
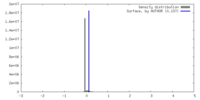
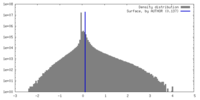
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Half map A
| File | emd_15341_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half map B
| File | emd_15341_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half map B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Replisome - pol alpha complex
| Entire | Name: Replisome - pol alpha complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Replisome - pol alpha complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Replisome - pol alpha complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 Details: S. cerevisiae pol alpha bound to the core replisome engaged with a fork DNA substrate containing a 60 nucleotide lagging strand. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.6 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 40.184 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)