+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8b9c | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
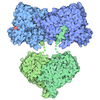
| Title | S. cerevisiae pol alpha - replisome complex | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | REPLICATION / helicase / polymerase / pol alpha / priming / replisome | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationInhibition of replication initiation of damaged DNA by RB1/E2F1 / H3-H4 histone complex chaperone activity / Unwinding of DNA / maintenance of DNA repeat elements / regulation of nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / DNA replication initiation / replication fork arrest / meiotic chromosome segregation / RNA-templated DNA biosynthetic process / Processive synthesis on the lagging strand ...Inhibition of replication initiation of damaged DNA by RB1/E2F1 / H3-H4 histone complex chaperone activity / Unwinding of DNA / maintenance of DNA repeat elements / regulation of nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / DNA replication initiation / replication fork arrest / meiotic chromosome segregation / RNA-templated DNA biosynthetic process / Processive synthesis on the lagging strand / Removal of the Flap Intermediate / MCM core complex / Assembly of the pre-replicative complex / Switching of origins to a post-replicative state / DNA strand elongation involved in mitotic DNA replication / GINS complex / MCM complex binding / mitotic DNA replication preinitiation complex assembly / nuclear DNA replication / Polymerase switching / premeiotic DNA replication / replication fork protection complex / pre-replicative complex assembly involved in nuclear cell cycle DNA replication / anaphase-promoting complex binding / alpha DNA polymerase:primase complex / Activation of the pre-replicative complex / mitotic DNA replication / DNA replication checkpoint signaling / CMG complex / establishment of mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / nuclear pre-replicative complex / DNA replication preinitiation complex / Activation of ATR in response to replication stress / MCM complex / mitotic DNA replication checkpoint signaling / lagging strand elongation / double-strand break repair via break-induced replication / mitotic DNA replication initiation / DNA replication, synthesis of primer / telomere capping / cellular response to osmotic stress / single-stranded DNA helicase activity / mitotic intra-S DNA damage checkpoint signaling / silent mating-type cassette heterochromatin formation / regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / mitotic sister chromatid cohesion / DNA biosynthetic process / DNA strand elongation involved in DNA replication / DNA synthesis involved in DNA repair / leading strand elongation / mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling / nuclear replication fork / replication fork processing / DNA replication origin binding / DNA replication initiation / Ub-specific processing proteases / subtelomeric heterochromatin formation / nuclear periphery / DNA helicase activity / telomere maintenance / replication fork / meiotic cell cycle / transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II / helicase activity / DNA-templated DNA replication / Transferases; Transferring phosphorus-containing groups; Nucleotidyltransferases / DNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / nuclear envelope / heterochromatin formation / double-strand break repair / single-stranded DNA binding / 4 iron, 4 sulfur cluster binding / DNA-directed DNA polymerase / DNA helicase / DNA-directed DNA polymerase activity / DNA replication / chromosome, telomeric region / protein stabilization / nucleotide binding / DNA repair / DNA damage response / chromatin binding / ATP hydrolysis activity / mitochondrion / DNA binding / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / metal ion binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.6 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Jones, M.L. / Yeeles, J.T.P. | ||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2023 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2023Title: How Pol α-primase is targeted to replisomes to prime eukaryotic DNA replication. Authors: Morgan L Jones / Valentina Aria / Yasemin Baris / Joseph T P Yeeles /  Abstract: During eukaryotic DNA replication, Pol α-primase generates primers at replication origins to start leading-strand synthesis and every few hundred nucleotides during discontinuous lagging-strand ...During eukaryotic DNA replication, Pol α-primase generates primers at replication origins to start leading-strand synthesis and every few hundred nucleotides during discontinuous lagging-strand replication. How Pol α-primase is targeted to replication forks to prime DNA synthesis is not fully understood. Here, by determining cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of budding yeast and human replisomes containing Pol α-primase, we reveal a conserved mechanism for the coordination of priming by the replisome. Pol α-primase binds directly to the leading edge of the CMG (CDC45-MCM-GINS) replicative helicase via a complex interaction network. The non-catalytic PRIM2/Pri2 subunit forms two interfaces with CMG that are critical for in vitro DNA replication and yeast cell growth. These interactions position the primase catalytic subunit PRIM1/Pri1 directly above the exit channel for lagging-strand template single-stranded DNA (ssDNA), revealing why priming occurs efficiently only on the lagging-strand template and elucidating a mechanism for Pol α-primase to overcome competition from RPA to initiate primer synthesis. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8b9c.cif.gz 8b9c.cif.gz | 2.5 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8b9c.ent.gz pdb8b9c.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8b9c.json.gz 8b9c.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b9/8b9c https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b9/8b9c ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b9/8b9c ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/b9/8b9c | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  15924MC  8b9aC  8b9bC  8b9dC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 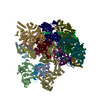
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-DNA replication licensing factor ... , 5 types, 5 molecules 23467
| #1: Protein | Mass: 98911.539 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: MCM2, YBL023C, YBL0438 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 111987.562 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: MCM3, YEL032W, SYGP-ORF23 / Production host:  |
| #3: Protein | Mass: 105138.375 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: MCM4, CDC54, HCD21, YPR019W, YP9531.13 / Production host:  |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 113110.211 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: MCM6, YGL201C / Production host:  |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 95049.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: MCM7, CDC47, YBR202W, YBR1441 / Production host:  |
-Protein , 7 types, 7 molecules 5AGPSXY
| #4: Protein | Mass: 86505.734 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: MCM5, CDC46, YLR274W, L9328.1 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #7: Protein | Mass: 62348.551 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: PRI2, YKL045W, YKL258 / Production host:  |
| #13: Protein | Mass: 75154.703 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: CDC45, SLD4, YLR103C, L8004.11 / Production host:  |
| #14: Protein | Mass: 126078.859 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: MRC1, YCL061C, YCL61C/YCL60C / Production host:  |
| #17: Protein | Mass: 51827.090 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: PRI1, YIR008C, YIB8C / Production host:  References: UniProt: P10363, Transferases; Transferring phosphorus-containing groups; Nucleotidyltransferases |
| #18: Protein | Mass: 141296.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: TOF1, YNL273W, N0636 / Production host:  |
| #19: Protein | Mass: 36588.758 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: CSM3, YMR048W, YM9796.01 / Production host:  |
-DNA polymerase alpha ... , 2 types, 2 molecules BJ
| #8: Protein | Mass: 78865.938 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: POL12, YBL035C, YBL0414 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #20: Protein | Mass: 167027.766 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: POL1, CDC17, YNL102W, N2181 / Production host:  |
-DNA replication complex GINS protein ... , 4 types, 4 molecules CDEF
| #9: Protein | Mass: 24230.576 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: PSF1, YDR013W, PZA208, YD8119.18 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #10: Protein | Mass: 25096.807 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: PSF2, YJL072C, HRF213, J1086 / Production host:  |
| #11: Protein | Mass: 24437.859 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: PSF3, YOL146W / Production host:  |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 33983.617 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Gene: SLD5, YDR489W / Production host:  |
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules QR
| #15: DNA chain | Mass: 26092.645 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
|---|---|
| #16: DNA chain | Mass: 32046.451 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  |
-Non-polymers , 3 types, 12 molecules 




| #21: Chemical | ChemComp-ANP / #22: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #23: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: S. cerevisiae replisome - pol alpha primase complex / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#20 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.6 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1500 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 39.2 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20_4459: / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 53964 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller























 PDBj
PDBj