+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-14191 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
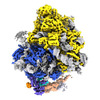
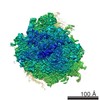
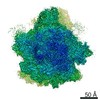
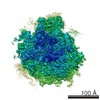
| Title | Ternary complex of ribosome nascent chain with SRP and NAC | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Ternary ribosome-nascent chain, SRP and NAC complex | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Ribosome / SRP / NAC / nascent chain / co-translational / Endoplasmic reticulum / co-translational protein targeting / co-translational folding | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationPI3K Cascade / PIP3 activates AKT signaling / FLT3 Signaling / Negative regulation of FLT3 / FLT3 signaling through SRC family kinases / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / negative regulation of protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum / nascent polypeptide-associated complex / negative regulation of striated muscle cell apoptotic process / regulation of skeletal muscle fiber development ...PI3K Cascade / PIP3 activates AKT signaling / FLT3 Signaling / Negative regulation of FLT3 / FLT3 signaling through SRC family kinases / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / negative regulation of protein localization to endoplasmic reticulum / nascent polypeptide-associated complex / negative regulation of striated muscle cell apoptotic process / regulation of skeletal muscle fiber development / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, signal sequence recognition / endoplasmic reticulum signal peptide binding / PI5P, PP2A and IER3 Regulate PI3K/AKT Signaling / positive regulation of cell proliferation involved in heart morphogenesis / positive regulation of skeletal muscle tissue growth / signal recognition particle, endoplasmic reticulum targeting / Major pathway of rRNA processing in the nucleolus and cytosol / GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit / L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) / cardiac ventricle development / signal recognition particle binding / signal recognition particle / cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / granulocyte differentiation / protein targeting to ER / signal-recognition-particle GTPase / dendritic cell differentiation / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, translocation / 7S RNA binding / heart trabecula morphogenesis / skeletal muscle tissue regeneration / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / exocrine pancreas development / ribosomal subunit / embryonic hemopoiesis / ubiquitin ligase inhibitor activity / SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane / positive regulation of signal transduction by p53 class mediator / ribonucleoprotein complex binding / protein-RNA complex assembly / rough endoplasmic reticulum / MDM2/MDM4 family protein binding / neutrophil chemotaxis / cytosolic ribosome / maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / B cell differentiation / ribosomal large subunit biogenesis / cytokine activity / wound healing / receptor tyrosine kinase binding / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / GDP binding / protein transport / large ribosomal subunit / regulation of translation / 5S rRNA binding / ribosomal large subunit assembly / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / defense response to Gram-negative bacterium / killing of cells of another organism / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / in utero embryonic development / cytoplasmic translation / transcription coactivator activity / tRNA binding / postsynaptic density / rRNA binding / nuclear speck / nuclear body / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / response to xenobiotic stimulus / ribonucleoprotein complex / protein domain specific binding / focal adhesion / GTPase activity / mRNA binding / positive regulation of cell population proliferation / synapse / GTP binding / nucleolus / cell surface / endoplasmic reticulum / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / ATP hydrolysis activity / extracellular space / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / zinc ion binding / nucleus / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.83 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Jomaa A / Gamerdinger M / Hsieh H / Wallisch A / Chandrasekaran V / Ulusoy Z / Scaiola A / Hegde R / Shan S / Ban N / Deuerling E | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Switzerland, 1 items Switzerland, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2022 Journal: Science / Year: 2022Title: Mechanism of signal sequence handover from NAC to SRP on ribosomes during ER-protein targeting. Authors: Ahmad Jomaa / Martin Gamerdinger / Hao-Hsuan Hsieh / Annalena Wallisch / Viswanathan Chandrasekaran / Zeynel Ulusoy / Alain Scaiola / Ramanujan S Hegde / Shu-Ou Shan / Nenad Ban / Elke Deuerling /     Abstract: The nascent polypeptide-associated complex (NAC) interacts with newly synthesized proteins at the ribosomal tunnel exit and competes with the signal recognition particle (SRP) to prevent mistargeting ...The nascent polypeptide-associated complex (NAC) interacts with newly synthesized proteins at the ribosomal tunnel exit and competes with the signal recognition particle (SRP) to prevent mistargeting of cytosolic and mitochondrial polypeptides to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). How NAC antagonizes SRP and how this is overcome by ER targeting signals are unknown. Here, we found that NAC uses two domains with opposing effects to control SRP access. The core globular domain prevented SRP from binding to signal-less ribosomes, whereas a flexibly attached domain transiently captured SRP to permit scanning of nascent chains. The emergence of an ER-targeting signal destabilized NAC's globular domain and facilitated SRP access to the nascent chain. These findings elucidate how NAC hands over the signal sequence to SRP and imparts specificity of protein localization. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_14191.map.gz emd_14191.map.gz | 321.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-14191-v30.xml emd-14191-v30.xml emd-14191.xml emd-14191.xml | 78.7 KB 78.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_14191.png emd_14191.png | 173.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-14191.cif.gz emd-14191.cif.gz | 16.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14191 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14191 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14191 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-14191 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_14191_validation.pdf.gz emd_14191_validation.pdf.gz | 782.4 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_14191_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_14191_full_validation.pdf.gz | 782 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_14191_validation.xml.gz emd_14191_validation.xml.gz | 7.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_14191_validation.cif.gz emd_14191_validation.cif.gz | 8.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-14191 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-14191 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-14191 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-14191 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7qwqMC  7qwrC  7qwsC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_14191.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 343 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_14191.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 343 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Ternary ribosome-nascent chain, SRP and NAC complex | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.08 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
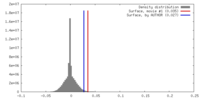
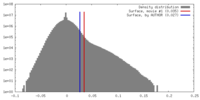
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Ternary ribosome-nascent chain SRP NAC complex
+Supramolecule #1: Ternary ribosome-nascent chain SRP NAC complex
+Supramolecule #2: Ribosome
+Supramolecule #3: SRP RNA 7SL
+Supramolecule #4: Signal recognition particle proteins
+Supramolecule #5: Nascent chain preprolactin
+Supramolecule #6: Isoform 2 of Transcription factor BTF3
+Macromolecule #1: SRP RNA 7SL
+Macromolecule #9: 28S rRNA
+Macromolecule #47: 5S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #49: 5.8S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #2: Signal recognition particle 19 kDa protein
+Macromolecule #3: Nascent chain preprolactin
+Macromolecule #4: Isoform 2 of Transcription factor BTF3
+Macromolecule #5: Signal recognition particle subunit SRP68
+Macromolecule #6: Signal recognition particle 54 kDa protein
+Macromolecule #7: L8
+Macromolecule #8: 60S ribosomal protein L29
+Macromolecule #10: uL3
+Macromolecule #11: 60S ribosomal protein L30
+Macromolecule #12: 60S ribosomal protein L4
+Macromolecule #13: Ribosomal protein L31
+Macromolecule #14: Ribosomal_L18_c domain-containing protein
+Macromolecule #15: Ribosomal protein L32
+Macromolecule #16: 60S ribosomal protein L6
+Macromolecule #17: 60S ribosomal protein L35a
+Macromolecule #18: uL30
+Macromolecule #19: 60S ribosomal protein L34
+Macromolecule #20: 60S ribosomal protein L7a
+Macromolecule #21: 60S ribosomal protein L35
+Macromolecule #22: 60S ribosomal protein L9
+Macromolecule #23: 60S ribosomal protein L36
+Macromolecule #24: 60S ribosomal protein L10
+Macromolecule #25: Ribosomal protein L37
+Macromolecule #26: Ribosomal protein L11
+Macromolecule #27: 60S ribosomal protein L38
+Macromolecule #28: 60S ribosomal protein L13
+Macromolecule #29: Ribosomal protein L39
+Macromolecule #30: 60S ribosomal protein L14
+Macromolecule #31: Ubiquitin A-52 residue ribosomal protein fusion product 1
+Macromolecule #32: Ribosomal protein L15
+Macromolecule #33: 60s ribosomal protein l41
+Macromolecule #34: 60S ribosomal protein L13a
+Macromolecule #35: eL42
+Macromolecule #36: 60S ribosomal protein L17
+Macromolecule #37: eL43
+Macromolecule #38: eL18
+Macromolecule #39: 60S ribosomal protein L28
+Macromolecule #40: 60S ribosomal protein L19
+Macromolecule #41: 60S ribosomal protein L18a
+Macromolecule #42: 60S ribosomal protein L21
+Macromolecule #43: Ribosomal protein L22
+Macromolecule #44: Ribosomal protein L23
+Macromolecule #45: Ribosomal protein L24
+Macromolecule #46: Ribosomal_L23eN domain-containing protein
+Macromolecule #48: Ribosomal protein L26
+Macromolecule #50: 60S ribosomal protein L27
+Macromolecule #51: 60S ribosomal protein L27a
+Macromolecule #52: Nascent polypeptide-associated complex subunit alpha
+Macromolecule #53: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #54: ZINC ION
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 15 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.83 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 51843 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)