+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20952 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | K.lactis 80S ribosome with p/PE tRNA and eIF5B | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | translation / ribosome / initiation / eIF5B | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationprotein-synthesizing GTPase / GDP-dissociation inhibitor activity / response to cycloheximide / cleavage in ITS2 between 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA of tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / preribosome, large subunit precursor / ribosomal large subunit export from nucleus / translational elongation / 90S preribosome / ribosomal subunit export from nucleus / protein-RNA complex assembly ...protein-synthesizing GTPase / GDP-dissociation inhibitor activity / response to cycloheximide / cleavage in ITS2 between 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA of tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / preribosome, large subunit precursor / ribosomal large subunit export from nucleus / translational elongation / 90S preribosome / ribosomal subunit export from nucleus / protein-RNA complex assembly / maturation of LSU-rRNA / endonucleolytic cleavage in ITS1 to separate SSU-rRNA from 5.8S rRNA and LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / translation regulator activity / translation initiation factor activity / cellular response to amino acid starvation / maturation of LSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / maturation of SSU-rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / maturation of SSU-rRNA / translational initiation / small-subunit processome / rRNA processing / large ribosomal subunit / ribosome biogenesis / ribosome binding / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / ribosomal large subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / protein ubiquitination / ribosome / translation / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / ribonucleoprotein complex / response to antibiotic / GTPase activity / mRNA binding / GTP binding / nucleolus / mitochondrion / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / metal ion binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Kluyveromyces lactis (yeast) / Kluyveromyces lactis (yeast) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Fernandez IS / Huang BY | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2020Title: Long-range interdomain communications in eIF5B regulate GTP hydrolysis and translation initiation. Authors: Bridget Y Huang / Israel S Fernández /  Abstract: Translation initiation controls protein synthesis by regulating the delivery of the first aminoacyl-tRNA to messenger RNAs (mRNAs). In eukaryotes, initiation is sophisticated, requiring dozens of ...Translation initiation controls protein synthesis by regulating the delivery of the first aminoacyl-tRNA to messenger RNAs (mRNAs). In eukaryotes, initiation is sophisticated, requiring dozens of protein factors and 2 GTP-regulated steps. The GTPase eIF5B gates progression to elongation during the second GTP-regulated step. Using electron cryomicroscopy (cryo-EM), we imaged an in vitro initiation reaction which is set up with purified yeast components and designed to stall with eIF5B and a nonhydrolyzable GTP analog. A high-resolution reconstruction of a "dead-end" intermediate at 3.6 Å allowed us to visualize eIF5B in its ribosome-bound conformation. We identified a stretch of residues in eIF5B, located close to the γ-phosphate of GTP and centered around the universally conserved tyrosine 837 ( numbering), that contacts the catalytic histidine of eIF5B (H480). Site-directed mutagenesis confirmed the essential role that these residues play in regulating ribosome binding, GTP hydrolysis, and translation initiation both in vitro and in vivo. Our results illustrate how eIF5B transmits the presence of a properly delivered initiator aminoacyl-tRNA at the P site to the distant GTPase center through interdomain communications and underscore the importance of the multidomain architecture in translation factors to sense and communicate ribosomal states. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20952.map.gz emd_20952.map.gz | 227.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20952-v30.xml emd-20952-v30.xml emd-20952.xml emd-20952.xml | 100.1 KB 100.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20952.png emd_20952.png | 165.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-20952.cif.gz emd-20952.cif.gz | 19.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20952 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20952 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20952 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20952 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6uz7MC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20952.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20952.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.07 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Kluyveromyces lactis 80S ribosome in complex with eIF5B
+Supramolecule #1: Kluyveromyces lactis 80S ribosome in complex with eIF5B
+Macromolecule #1: 25S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #2: RNA (121-MER)
+Macromolecule #3: 5.8S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #81: 18S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #83: RNA (76-MER)
+Macromolecule #4: KLLA0D16027p
+Macromolecule #5: 60S ribosomal protein L3
+Macromolecule #6: KLLA0B07139p
+Macromolecule #7: KLLA0D06941p
+Macromolecule #8: KLLA0B04686p
+Macromolecule #9: KLLA0D03410p
+Macromolecule #10: KLLA0E00573p
+Macromolecule #11: KLLA0F04499p
+Macromolecule #12: KLLA0D05643p
+Macromolecule #13: KLLA0F08261p
+Macromolecule #14: 60S ribosomal protein L13
+Macromolecule #15: KLLA0B13409p
+Macromolecule #16: Ribosomal protein L15
+Macromolecule #17: KLLA0F04675p
+Macromolecule #18: KLLA0A06336p
+Macromolecule #19: KLLA0A07227p
+Macromolecule #20: KLLA0E12453p
+Macromolecule #21: 60S ribosomal protein L20
+Macromolecule #22: KLLA0E23651p
+Macromolecule #23: KLLA0D05181p
+Macromolecule #24: KLLA0E06997p
+Macromolecule #25: 60S ribosomal protein L24
+Macromolecule #26: 60S ribosomal protein L25
+Macromolecule #27: KLLA0B05742p
+Macromolecule #28: KLLA0E03455p
+Macromolecule #29: RPL28
+Macromolecule #30: 60S ribosomal protein L29
+Macromolecule #31: 60S ribosomal protein L30
+Macromolecule #32: KLLA0B02937p
+Macromolecule #33: KLLA0E06843p
+Macromolecule #34: KLLA0D07405p
+Macromolecule #35: KLLA0C08371p
+Macromolecule #36: KLLA0F05247p
+Macromolecule #37: 60S ribosomal protein L36
+Macromolecule #38: Ribosomal protein L37
+Macromolecule #39: KLLA0C18216p
+Macromolecule #40: 60S ribosomal protein L39
+Macromolecule #41: Ubiquitin fusion protein
+Macromolecule #42: 60S ribosomal protein L41
+Macromolecule #43: 60S ribosomal protein L44
+Macromolecule #44: KLLA0E05941p
+Macromolecule #45: Ribosomal protein
+Macromolecule #46: 60S acidic ribosomal protein P0
+Macromolecule #47: GDPCP
+Macromolecule #48: 40S ribosomal protein S0
+Macromolecule #49: 40S ribosomal protein S1
+Macromolecule #50: KLLA0F09812p
+Macromolecule #51: KLLA0D08305p
+Macromolecule #52: 40S ribosomal protein S4
+Macromolecule #53: KLLA0D10659p
+Macromolecule #54: 40S ribosomal protein S6
+Macromolecule #55: 40S ribosomal protein S7
+Macromolecule #56: 40S ribosomal protein S8
+Macromolecule #57: KLLA0E23673p
+Macromolecule #58: KLLA0B08173p
+Macromolecule #59: KLLA0A10483p
+Macromolecule #60: 40S ribosomal protein S12
+Macromolecule #61: KLLA0F18040p
+Macromolecule #62: 40S ribosomal protein S14
+Macromolecule #63: KLLA0F07843p
+Macromolecule #64: 40S ribosomal protein S16
+Macromolecule #65: KLLA0B01474p
+Macromolecule #66: KLLA0B01562p
+Macromolecule #67: KLLA0A07194p
+Macromolecule #68: KLLA0F25542p
+Macromolecule #69: 40S ribosomal protein S21
+Macromolecule #70: 40S ribosomal protein S22
+Macromolecule #71: RPS23
+Macromolecule #72: 40S ribosomal protein S24
+Macromolecule #73: 40S ribosomal protein S25
+Macromolecule #74: 40S ribosomal protein S26
+Macromolecule #75: 40S ribosomal protein S27
+Macromolecule #76: 40S ribosomal protein S28
+Macromolecule #77: 40S ribosomal protein S29
+Macromolecule #78: 40S ribosomal protein S30
+Macromolecule #79: Ubiquitin-40S ribosomal protein S27a
+Macromolecule #80: KLLA0E12277p
+Macromolecule #82: KLLA0F23265p
+Macromolecule #84: ZINC ION
+Macromolecule #85: PHOSPHOMETHYLPHOSPHONIC ACID GUANYLATE ESTER
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 6 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: GOLD / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Support film - Film thickness: 3 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





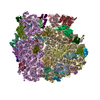
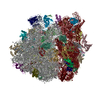
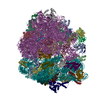











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)