+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-10864 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
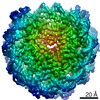
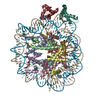
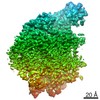
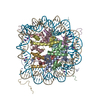
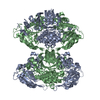
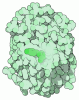
| Title | OCT4-SOX2-bound nucleosome - SHL+6 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | OCT4-SOX2 bound to SHL 6 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | nucleosome / OCT4 / SOX2 / transcription factor / TRANSCRIPTION | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationglial cell fate commitment / regulation of myofibroblast cell apoptotic process / Formation of the posterior neural plate / cell fate commitment involved in formation of primary germ layer / cardiac cell fate determination / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG repress genes related to differentiation / Formation of the anterior neural plate / endodermal-mesodermal cell signaling / regulation of asymmetric cell division / endodermal cell fate specification ...glial cell fate commitment / regulation of myofibroblast cell apoptotic process / Formation of the posterior neural plate / cell fate commitment involved in formation of primary germ layer / cardiac cell fate determination / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG repress genes related to differentiation / Formation of the anterior neural plate / endodermal-mesodermal cell signaling / regulation of asymmetric cell division / endodermal cell fate specification / response to oxygen-glucose deprivation / adenohypophysis development / heart induction / negative regulation of cell cycle G1/S phase transition / POU5F1 (OCT4), SOX2, NANOG activate genes related to proliferation / Specification of primordial germ cells / Specification of the neural plate border / pituitary gland development / Regulation of MITF-M-dependent genes involved in extracellular matrix, focal adhesion and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition / positive regulation of cell-cell adhesion / Transcriptional Regulation by MECP2 / Transcriptional regulation of pluripotent stem cells / neuronal stem cell population maintenance / Germ layer formation at gastrulation / eye development / tissue regeneration / response to growth factor / miRNA binding / negative regulation of neuron differentiation / forebrain development / inner ear development / somatic stem cell population maintenance / blastocyst development / anatomical structure morphogenesis / negative regulation of tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling pathway / BMP signaling pathway / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of MITF-M expression and activity / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / negative regulation of miRNA transcription / telomere organization / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / Interleukin-7 signaling / epigenetic regulation of gene expression / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / bioluminescence / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / innate immune response in mucosa / Defective pyroptosis / generation of precursor metabolites and energy / Negative Regulation of CDH1 Gene Transcription / positive regulation of cell differentiation / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / Deactivation of the beta-catenin transactivating complex / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / lipopolysaccharide binding / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / HDMs demethylate histones / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / brain development / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / response to wounding / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / RMTs methylate histone arginines / neuron differentiation / HCMV Early Events Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.42 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Michael AK / Kempf G | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Switzerland, 1 items Switzerland, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2020 Journal: Science / Year: 2020Title: Mechanisms of OCT4-SOX2 motif readout on nucleosomes. Authors: Alicia K Michael / Ralph S Grand / Luke Isbel / Simone Cavadini / Zuzanna Kozicka / Georg Kempf / Richard D Bunker / Andreas D Schenk / Alexandra Graff-Meyer / Ganesh R Pathare / Joscha ...Authors: Alicia K Michael / Ralph S Grand / Luke Isbel / Simone Cavadini / Zuzanna Kozicka / Georg Kempf / Richard D Bunker / Andreas D Schenk / Alexandra Graff-Meyer / Ganesh R Pathare / Joscha Weiss / Syota Matsumoto / Lukas Burger / Dirk Schübeler / Nicolas H Thomä /  Abstract: Transcription factors (TFs) regulate gene expression through chromatin where nucleosomes restrict DNA access. To study how TFs bind nucleosome-occupied motifs, we focused on the reprogramming factors ...Transcription factors (TFs) regulate gene expression through chromatin where nucleosomes restrict DNA access. To study how TFs bind nucleosome-occupied motifs, we focused on the reprogramming factors OCT4 and SOX2 in mouse embryonic stem cells. We determined TF engagement throughout a nucleosome at base-pair resolution in vitro, enabling structure determination by cryo-electron microscopy at two preferred positions. Depending on motif location, OCT4 and SOX2 differentially distort nucleosomal DNA. At one position, OCT4-SOX2 removes DNA from histone H2A and histone H3; however, at an inverted motif, the TFs only induce local DNA distortions. OCT4 uses one of its two DNA-binding domains to engage DNA in both structures, reading out a partial motif. These findings explain site-specific nucleosome engagement by the pluripotency factors OCT4 and SOX2, and they reveal how TFs distort nucleosomes to access chromatinized motifs. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_10864.map.gz emd_10864.map.gz | 32 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-10864-v30.xml emd-10864-v30.xml emd-10864.xml emd-10864.xml | 23.8 KB 23.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_10864.png emd_10864.png | 136.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-10864.cif.gz emd-10864.cif.gz | 7.2 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10864 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10864 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10864 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-10864 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6yovMC  6t90C  6t93C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_10864.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_10864.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
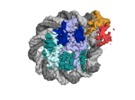
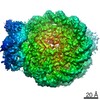
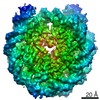
| Annotation | OCT4-SOX2 bound to SHL 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.86 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Ternary complex of OCT4-SOX2 and SHL+6 nucleosome
+Supramolecule #1: Ternary complex of OCT4-SOX2 and SHL+6 nucleosome
+Supramolecule #2: Histones
+Supramolecule #3: DNA
+Supramolecule #4: Green fluorescent protein,POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1
+Supramolecule #5: SOX2
+Macromolecule #1: Histone H3.1
+Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
+Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 1-B/E
+Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B type 1-J
+Macromolecule #5: Histone H3.1
+Macromolecule #6: Histone H4
+Macromolecule #8: Green fluorescent protein,POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1
+Macromolecule #9: Transcription factor SOX-2
+Macromolecule #7: DNA (142-MER)
+Macromolecule #10: PENTANEDIAL
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 45.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: EMDB MAP EMDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.42 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: cryoSPARC (ver. v2) / Number images used: 71284 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: RANDOM ASSIGNMENT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















 Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)
Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper)