+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 | データベース: EMDB / ID: EMD-0256 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| タイトル | Natural tetrameric form of human butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) | |||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | Map after post-processing procedure in RELION 2.1. Contour level was selected based on visualization in Chimera 1.11.2. | |||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||
| 生物種 |  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) | |||||||||
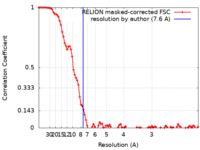
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 7.6 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Baymukhametov TN / Chesnokov YM / Boyko KM / Hons M / Lipkin AV / Lushchekina SV / Konarev PV / Masson P / Vasiliev AL / Popov VO / Kovalchuk MV | |||||||||
| 資金援助 |  ロシア, 2件 ロシア, 2件
| |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Biochimie / 年: 2019 ジャーナル: Biochimie / 年: 2019タイトル: 3D structure of the natural tetrameric form of human butyrylcholinesterase as revealed by cryoEM, SAXS and MD. 著者: Konstantin M Boyko / Timur N Baymukhametov / Yury M Chesnokov / Michael Hons / Sofya V Lushchekina / Petr V Konarev / Alexey V Lipkin / Alexandre L Vasiliev / Patrick Masson / Vladimir O ...著者: Konstantin M Boyko / Timur N Baymukhametov / Yury M Chesnokov / Michael Hons / Sofya V Lushchekina / Petr V Konarev / Alexey V Lipkin / Alexandre L Vasiliev / Patrick Masson / Vladimir O Popov / Michail V Kovalchuk /   要旨: Human plasma butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) is an endogenous bioscavenger that hydrolyzes numerous medicamentous and poisonous esters and scavenges potent organophosphorus nerve agents. BChE is thus a ...Human plasma butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) is an endogenous bioscavenger that hydrolyzes numerous medicamentous and poisonous esters and scavenges potent organophosphorus nerve agents. BChE is thus a marker for the diagnosis of OP poisoning. It is also considered a therapeutic target against Alzheimer's disease. Although the X-ray structure of a partially deglycosylated monomer of human BChE was solved 15 years ago, all attempts to determine the 3D structure of the natural full-length glycosylated tetrameric human BChE have been unsuccessful so far. Here, a combination of three complementary structural methods-single-particle cryo-electron microscopy, molecular dynamics and small-angle X-ray scattering-were implemented to elucidate the overall structural and spatial organization of the natural tetrameric human plasma BChE. A 7.6 Å cryoEM map clearly shows the major features of the enzyme: a dimer of dimers with a nonplanar monomer arrangement, in which the interconnecting super helix complex PRAD-(WAT)-peptide C-terminal tail is located in the center of the tetramer, nearly perpendicular to its plane, and is plunged deep between the four subunits. Molecular dynamics simulations allowed optimization of the geometry of the molecule and reconstruction of the structural features invisible in the cryoEM density, i.e., glycan chains and glycan interdimer contact areas, as well as intermonomer disulfide bridges at the C-terminal tail. Finally, SAXS data were used to confirm the consistency of the obtained model with the experimental data. The tetramer organization of BChE is unique in that the four subunits are joined at their C-termini through noncovalent contacts with a short polyproline-rich peptide. This tetramer structure could serve as a model for the design of highly stable glycosylated tetramers. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
| ムービー |
 ムービービューア ムービービューア |
|---|---|
| 構造ビューア | EMマップ:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| 添付画像 |
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_0256.map.gz emd_0256.map.gz | 5.8 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-0256-v30.xml emd-0256-v30.xml emd-0256.xml emd-0256.xml | 14.4 KB 14.4 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| FSC (解像度算出) |  emd_0256_fsc.xml emd_0256_fsc.xml | 9.2 KB | 表示 |  FSCデータファイル FSCデータファイル |
| 画像 |  emd_0256.png emd_0256.png | 71 KB | ||
| マスクデータ |  emd_0256_msk_1.map emd_0256_msk_1.map | 64 MB |  マスクマップ マスクマップ | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0256 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0256 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0256 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-0256 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_0256_validation.pdf.gz emd_0256_validation.pdf.gz | 253.4 KB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_0256_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_0256_full_validation.pdf.gz | 252.6 KB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_0256_validation.xml.gz emd_0256_validation.xml.gz | 11.1 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0256 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0256 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0256 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-0256 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_0256.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 64 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_0256.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 64 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 注釈 | Map after post-processing procedure in RELION 2.1. Contour level was selected based on visualization in Chimera 1.11.2. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 1.067 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
CCP4マップ ヘッダ情報:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-添付データ
-マスク #1
| ファイル |  emd_0256_msk_1.map emd_0256_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
| 密度ヒストグラム |
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : Natural tetrameric form of human butyrylcholinesterase
| 全体 | 名称: Natural tetrameric form of human butyrylcholinesterase |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: Natural tetrameric form of human butyrylcholinesterase
| 超分子 | 名称: Natural tetrameric form of human butyrylcholinesterase タイプ: complex / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 / 含まれる分子: all |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 335 KDa |
-分子 #1: Natural tetrameric form of human butyrylcholinesterase
| 分子 | 名称: Natural tetrameric form of human butyrylcholinesterase タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 詳細: Glycan chains are attached to the following residues: 17,57,106, 241, 256, 341, 455, 481, 486. 光学異性体: LEVO / EC番号: cholinesterase |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト) |
| 配列 | 文字列: MHSKVTIICI RFLFWFLLLC MLIGKSHTED DIIIATKNGK VRGMNLTVFG GTVTAFLGIP YAQPPLGRL RFKKPQSLTK WSDIWNATKY ANSCCQNIDQ SFPGFHGSEM WNPNTDLSED C LYLNVWIP APKPKNATVL IWIYGGGFQT GTSSLHVYDG KFLARVERVI ...文字列: MHSKVTIICI RFLFWFLLLC MLIGKSHTED DIIIATKNGK VRGMNLTVFG GTVTAFLGIP YAQPPLGRL RFKKPQSLTK WSDIWNATKY ANSCCQNIDQ SFPGFHGSEM WNPNTDLSED C LYLNVWIP APKPKNATVL IWIYGGGFQT GTSSLHVYDG KFLARVERVI VVSMNYRVGA LG FLALPGN PEAPGNMGLF DQQLALQWVQ KNIAAFGGNP KSVTLFGESA GAASVSLHLL SPG SHSLFT RAILQSGSFN APWAVTSLYE ARNRTLNLAK LTGCSRENET EIIKCLRNKD PQEI LLNEA FVVPYGTPLS VNFGPTVDGD FLTDMPDILL ELGQFKKTQI LVGVNKDEGT AFLVY GAPG FSKDNNSIIT RKEFQEGLKI FFPGVSEFGK ESILFHYTDW VDDQRPENYR EALGDV VGD YNFICPALEF TKKFSEWGNN AFFYYFEHRS SKLPWPEWMG VMHGYEIEFV FGLPLER RD NYTKAEEILS RSIVKRWANF AKYGNPNETQ NNSTSWPVFK STEQKYLTLN TESTRIMT K LRAQQCRFWT SFFPKVLEMT GNIDEAEWEW KAGFHRWNNY MMDWKNQFND YTSKKESCVG L |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 濃度 | 0.3 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 緩衝液 | pH: 8 |
| グリッド | 材質: COPPER / メッシュ: 300 / 前処理 - タイプ: GLOW DISCHARGE / 前処理 - 雰囲気: AIR / 前処理 - 気圧: 0.026 kPa |
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE / チャンバー内湿度: 100 % / チャンバー内温度: 277.15 K / 装置: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / 詳細: Blot for 1 second before plunging. |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| 特殊光学系 | エネルギーフィルター - 名称: GIF Quantum LS / エネルギーフィルター - スリット幅: 20 eV |
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) 検出モード: COUNTING / デジタル化 - サイズ - 横: 3838 pixel / デジタル化 - サイズ - 縦: 3710 pixel / デジタル化 - 画像ごとのフレーム数: 1-28 / 撮影したグリッド数: 1 / 実像数: 1500 / 平均露光時間: 7.0 sec. / 平均電子線量: 42.0 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 300 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 倍率(補正後): 46860 / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 0.003 µm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 0.001 µm / 倍率(公称値): 130000 |
| 試料ステージ | 試料ホルダーモデル: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER ホルダー冷却材: NITROGEN |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
+ 画像解析
画像解析
-原子モデル構築 1
| 精密化 | プロトコル: RIGID BODY FIT |
|---|
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)