[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
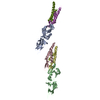
Yorodumi- SASDB93: Human dystrophin central domain repeats 16 to 19 (Dystrophin cent... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: SASBDB / ID: SASDB93 |
|---|---|
 Sample Sample | Human dystrophin central domain repeats 16 to 19
|
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of muscle system process / regulation of cellular response to growth factor stimulus / syntrophin complex / cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of skeletal muscle contraction / dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex / synaptic signaling / cell-substrate junction / peptide biosynthetic process / motile cilium assembly ...regulation of muscle system process / regulation of cellular response to growth factor stimulus / syntrophin complex / cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of skeletal muscle contraction / dystrophin-associated glycoprotein complex / synaptic signaling / cell-substrate junction / peptide biosynthetic process / motile cilium assembly / dystroglycan binding / regulation of skeletal muscle contraction by regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion / vinculin binding / regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transport / costamere / Formation of the dystrophin-glycoprotein complex (DGC) / muscle cell development / regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport / Striated Muscle Contraction / filopodium membrane / structural constituent of muscle / muscle organ development / muscle cell cellular homeostasis / myosin binding / maintenance of blood-brain barrier / nitric-oxide synthase binding / neuron projection terminus / Non-integrin membrane-ECM interactions / neuron development / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / skeletal muscle tissue development / cardiac muscle contraction / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / response to muscle stretch / positive regulation of neuron differentiation / regulation of heart rate / filopodium / positive regulation of neuron projection development / sarcolemma / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / Z disc / intracellular protein localization / actin binding / protein-containing complex assembly / cytoskeleton / postsynaptic membrane / membrane raft / synapse / cell surface / protein-containing complex / zinc ion binding / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function |
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2018 Journal: J Biol Chem / Year: 2018Title: Dystrophin's central domain forms a complex filament that becomes disorganized by in-frame deletions. Authors: Olivier Delalande / Anne-Elisabeth Molza / Raphael Dos Santos Morais / Angélique Chéron / Émeline Pollet / Céline Raguenes-Nicol / Christophe Tascon / Emmanuel Giudice / Marine Guilbaud ...Authors: Olivier Delalande / Anne-Elisabeth Molza / Raphael Dos Santos Morais / Angélique Chéron / Émeline Pollet / Céline Raguenes-Nicol / Christophe Tascon / Emmanuel Giudice / Marine Guilbaud / Aurélie Nicolas / Arnaud Bondon / France Leturcq / Nicolas Férey / Marc Baaden / Javier Perez / Pierre Roblin / France Piétri-Rouxel / Jean-François Hubert / Mirjam Czjzek / Elisabeth Le Rumeur /  Abstract: Dystrophin, encoded by the gene, is critical for maintaining plasma membrane integrity during muscle contraction events. Mutations in the gene disrupting the reading frame prevent dystrophin ...Dystrophin, encoded by the gene, is critical for maintaining plasma membrane integrity during muscle contraction events. Mutations in the gene disrupting the reading frame prevent dystrophin production and result in severe Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD); in-frame internal deletions allow production of partly functional internally deleted dystrophin and result in less severe Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD). Many known BMD deletions occur in dystrophin's central domain, generally considered to be a monotonous rod-shaped domain based on the knowledge of spectrin family proteins. However, the effects caused by these deletions, ranging from asymptomatic to severe BMD, argue against the central domain serving only as a featureless scaffold. We undertook structural studies combining small-angle X-ray scattering and molecular modeling in an effort to uncover the structure of the central domain, as dystrophin has been refractory to characterization. We show that this domain appears to be a tortuous and complex filament that is profoundly disorganized by the most severe BMD deletion (loss of exons 45-47). Despite the preservation of large parts of the binding site for neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) in this deletion, computational approaches failed to recreate the association of dystrophin with nNOS. This observation is in agreement with a strong decrease of nNOS immunolocalization in muscle biopsies, a parameter related to the severity of BMD phenotypes. The structural description of the whole dystrophin central domain we present here is a first necessary step to improve the design of microdystrophin constructs toward the goal of a successful gene therapy for DMD. |
 Contact author Contact author |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Data source
| SASBDB page |  SASDB93 SASDB93 |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- External links
External links
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
|---|
-Models
| Model #438 |  Type: atomic / Radius of dummy atoms: 1.90 A / Chi-square value: 10.843849  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
|---|
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: Human dystrophin central domain repeats 16 to 19 |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: 20 mM Tris 150 mM NaCl 1 mM EDTA 2% glycerol 5% acetonitrile Concentration: 20.00 mM / pH: 7.5 Composition: 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 2% glycerol, 5% acetonitrile |
| Entity #289 | Name: Dystrophin 1994-2420 / Type: protein / Description: Dystrophin central domain repeats 16 to 19. / Formula weight: 50.058 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Homo sapiens / References: UniProt: P11532 Sequence: GSsyvpstyl teithvsqal leveqllnap dlcakdfedl fkqeeslkni kdslqqssgr idiihskkta alqsatpver vklqealsql dfqwekvnkm ykdrqgrfdr svekwrrfhy dikifnqwlt eaeqflrktq ipenwehaky kwylkelqdg igqrqtvvrt ...Sequence: GSsyvpstyl teithvsqal leveqllnap dlcakdfedl fkqeeslkni kdslqqssgr idiihskkta alqsatpver vklqealsql dfqwekvnkm ykdrqgrfdr svekwrrfhy dikifnqwlt eaeqflrktq ipenwehaky kwylkelqdg igqrqtvvrt lnatgeeiiq qssktdasil qeklgslnlr wqevckqlsd rkkrleeqkn ilsefqrdln efvlwleead niasiplepg keqqlkekle qvkllveelp lrqgilkqln etggpvlvsa pispeeqdkl enklkqtnlq wikvsralpe kqgeieaqik dlgqlekkle dleeqlnhll lwlspirnql eiynqpnqeg pfdvqeteia vqakqpdvee ilskgqhlyk ekpatqpvkr kledlssewk avnrllqel |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name: SOLEIL SWING  / City: Saint-Aubin / 国: France / City: Saint-Aubin / 国: France  / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.1 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 1.82 mm / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Wavelength: 0.1 Å / Dist. spec. to detc.: 1.82 mm | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: AVIEX / Type: CCD | ||||||||||||||||||
| Scan |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Result |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller