+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 9g8m | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
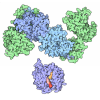
| Title | human 80S ribosome bound by a SKI2-exosome complex | ||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | RIBOSOME / RNase / Helicase / RNA-binding / mRNA-degradation / cytoplasm | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDNA deamination / nucleolar exosome (RNase complex) / exoribonuclease II activity / exoribonuclease II / Dom34-Hbs1 complex / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, no-go decay / CUT catabolic process / U1 snRNA 3'-end processing / Ski complex / U5 snRNA 3'-end processing ...DNA deamination / nucleolar exosome (RNase complex) / exoribonuclease II activity / exoribonuclease II / Dom34-Hbs1 complex / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, no-go decay / CUT catabolic process / U1 snRNA 3'-end processing / Ski complex / U5 snRNA 3'-end processing / TRAMP-dependent tRNA surveillance pathway / exosome (RNase complex) / mRNA decay by 3' to 5' exoribonuclease / cytoplasmic exosome (RNase complex) / U4 snRNA 3'-end processing / nuclear polyadenylation-dependent rRNA catabolic process / poly(A)-dependent snoRNA 3'-end processing / nuclear-transcribed mRNA catabolic process, 3'-5' exonucleolytic nonsense-mediated decay / nuclear exosome (RNase complex) / exonucleolytic trimming to generate mature 3'-end of 5.8S rRNA from tricistronic rRNA transcript (SSU-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA, LSU-rRNA) / Tristetraprolin (TTP, ZFP36) binds and destabilizes mRNA / ATF4 activates genes in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress / Butyrate Response Factor 1 (BRF1) binds and destabilizes mRNA / 3'-5' RNA helicase activity / positive regulation of isotype switching / histone mRNA catabolic process / nuclear mRNA surveillance / rRNA catabolic process / 7S RNA binding / translation at presynapse / mRNA 3'-UTR AU-rich region binding / exit from mitosis / isotype switching / optic nerve development / response to insecticide / eukaryotic 80S initiation complex / negative regulation of protein neddylation / regulation of translation involved in cellular response to UV / axial mesoderm development / negative regulation of formation of translation preinitiation complex / regulation of G1 to G0 transition / retinal ganglion cell axon guidance / oxidized pyrimidine DNA binding / response to TNF agonist / negative regulation of endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response / positive regulation of base-excision repair / ribosomal protein import into nucleus / protein-DNA complex disassembly / positive regulation of respiratory burst involved in inflammatory response / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage by p53 class mediator / ribosome disassembly / positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage / positive regulation of gastrulation / 90S preribosome assembly / protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor activity / RNA catabolic process / positive regulation of endodeoxyribonuclease activity / nucleolus organization / IRE1-RACK1-PP2A complex / positive regulation of Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport / TNFR1-mediated ceramide production / alpha-beta T cell differentiation / negative regulation of DNA repair / negative regulation of RNA splicing / GAIT complex / positive regulation of DNA damage response, signal transduction by p53 class mediator / TORC2 complex binding / G1 to G0 transition / supercoiled DNA binding / KSRP (KHSRP) binds and destabilizes mRNA / NF-kappaB complex / neural crest cell differentiation / oxidized purine DNA binding / cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process / middle ear morphogenesis / positive regulation of ubiquitin-protein transferase activity / maturation of 5.8S rRNA / negative regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to hydrogen peroxide / negative regulation of bicellular tight junction assembly / regulation of establishment of cell polarity / ubiquitin-like protein conjugating enzyme binding / rRNA modification in the nucleus and cytosol / negative regulation of phagocytosis / erythrocyte homeostasis / Formation of the ternary complex, and subsequently, the 43S complex / nuclear chromosome / cytoplasmic side of rough endoplasmic reticulum membrane / negative regulation of ubiquitin protein ligase activity / protein kinase A binding / laminin receptor activity / homeostatic process / ion channel inhibitor activity / Ribosomal scanning and start codon recognition / pigmentation / Association of TriC/CCT with target proteins during biosynthesis / Translation initiation complex formation / mRNA catabolic process / positive regulation of mitochondrial depolarization / macrophage chemotaxis / lung morphogenesis Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) Cricket paralysis virus Cricket paralysis virus | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Koegel, A. / Keidel, A. / Loukeri, M.J. / Kuhn, C.C. / Langer, L.M. / Schaefer, I.B. / Conti, E. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, European Union, Germany, European Union,  Denmark, 5items Denmark, 5items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: Structural basis of mRNA decay by the human exosome-ribosome supercomplex. Authors: Alexander Kögel / Achim Keidel / Matina-Jasemi Loukeri / Christopher C Kuhn / Lukas M Langer / Ingmar B Schäfer / Elena Conti /  Abstract: The interplay between translation and mRNA decay is widespread in human cells. In quality-control pathways, exonucleolytic degradation of mRNA associated with translating ribosomes is mediated ...The interplay between translation and mRNA decay is widespread in human cells. In quality-control pathways, exonucleolytic degradation of mRNA associated with translating ribosomes is mediated largely by the cytoplasmic exosome, which includes the exoribonuclease complex EXO10 and the helicase complex SKI238 (refs. ). The helicase can extract mRNA from the ribosome and is expected to transfer it to the exoribonuclease core through a bridging factor, HBS1L3 (also known as SKI7), but the mechanisms of this molecular handover remain unclear. Here we reveal how human EXO10 is recruited by HBS1L3 (SKI7) to an active ribosome-bound SKI238 complex. We show that rather than a sequential handover, a direct physical coupling mechanism takes place, which culminates in the formation of a cytoplasmic exosome-ribosome supercomplex. Capturing the structure during active decay reveals a continuous path in which an RNA substrate threads from the 80S ribosome through the SKI2 helicase into the exoribonuclease active site of the cytoplasmic exosome complex. The SKI3 subunit of the complex directly binds to HBS1L3 (SKI7) and also engages a surface of the 40S subunit, establishing a recognition platform in collided disomes. Exosome and ribosome thus work together as a single structural and functional unit in co-translational mRNA decay, coordinating their activities in a transient supercomplex. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  9g8m.cif.gz 9g8m.cif.gz | 6.2 MB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb9g8m.ent.gz pdb9g8m.ent.gz | Display |  PDB format PDB format | |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  9g8m.json.gz 9g8m.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g8/9g8m https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g8/9g8m ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g8/9g8m ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/g8/9g8m | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  51132MC  9g8nC  9g8oC  9g8pC  9g8qC  9g8rC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 7 types, 7 molecules AEMSfSgLILm
| #1: Protein | Mass: 137913.688 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SKIV2L, DDX13, SKI2W, SKIV2, W / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SKIV2L, DDX13, SKI2W, SKIV2, W / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q15477, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
|---|---|
| #11: Protein | Mass: 30196.131 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HBS1L, HBS1, KIAA1038 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HBS1L, HBS1, KIAA1038 / Production host:  References: UniProt: Q9Y450, Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement |
| #12: Protein | Mass: 125229.984 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DIS3L, DIS3L1, KIAA1955 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: DIS3L, DIS3L1, KIAA1955 / Production host:  |
| #35: Protein | Mass: 18004.041 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62979 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62979 |
| #36: Protein | Mass: 35115.652 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P63244 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P63244 |
| #59: Protein | Mass: 24570.949 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q96L21 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q96L21 |
| #88: Protein | Mass: 14758.394 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62987 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P62987 |
-Exosome complex component ... , 9 types, 9 molecules LNOFGHIJK
| #2: Protein | Mass: 26416.996 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC4, RRP41, SKI6 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC4, RRP41, SKI6 / Production host:  |
|---|---|
| #3: Protein | Mass: 30429.893 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC8, OIP2, RRP43 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC8, OIP2, RRP43 / Production host:  |
| #4: Protein | Mass: 25636.312 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC5, CML28, RRP46 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC5, CML28, RRP46 / Production host:  |
| #5: Protein | Mass: 32216.762 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC7, KIAA0116, RRP42 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC7, KIAA0116, RRP42 / Production host:  |
| #6: Protein | Mass: 28267.127 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC6, MTR3 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC6, MTR3 / Production host:  |
| #7: Protein | Mass: 39512.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC3, RRP40, CGI-102, EXOSC6, MTR3 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC3, RRP40, CGI-102, EXOSC6, MTR3 / Production host:  |
| #8: Protein | Mass: 33190.355 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC2, RRP4 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC2, RRP4 / Production host:  |
| #9: Protein | Mass: 21835.100 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC1, CSL4, CGI-108 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC1, CSL4, CGI-108 / Production host:  |
| #10: Protein | Mass: 49370.312 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC9, PMSCL1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: EXOSC9, PMSCL1 / Production host:  |
-RNA chain , 5 types, 5 molecules XS2L5L7L8
| #13: RNA chain | Mass: 78988.750 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.)  Cricket paralysis virus Cricket paralysis virus |
|---|---|
| #14: RNA chain | Mass: 602752.875 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| #48: RNA chain | Mass: 1638937.000 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| #49: RNA chain | Mass: 38998.078 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: GenBank: 23898 Homo sapiens (human) / References: GenBank: 23898 |
| #50: RNA chain | Mass: 50449.812 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: GenBank: 555853 Homo sapiens (human) / References: GenBank: 555853 |
+40S ribosomal protein ... , 31 types, 31 molecules SASBSDSESFSHSISKSLSPSQSRSSSTSUSVSXSaScSdSCSGSJSMSNSOSWSYSZSbSe
+60S ribosomal protein ... , 38 types, 38 molecules LALBLCLDLGLHLJLLLMLNLOLPLQLRLSLTLULVLWLXLYLZLaLbLcLdLeLfLgLh...
-Large ribosomal subunit protein ... , 2 types, 2 molecules LELF
| #55: Protein | Mass: 32810.176 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q02878 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q02878 |
|---|---|
| #56: Protein | Mass: 29290.973 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P18124 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P18124 |
-Non-polymers , 2 types, 238 molecules 


| #93: Chemical | ChemComp-MG / #94: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: human 80S ribosome bound by a SKI2-exosome complex / Type: RIBOSOME / Entity ID: #1-#92 / Source: MULTIPLE SOURCES |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Specimen support | Grid mesh size: 200 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2400 nm / Nominal defocus min: 600 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 64.2 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Num. of real images: 48004 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.20.1_4487: / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 79353 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Cross valid method: NONE Stereochemistry target values: GeoStd + Monomer Library + CDL v1.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 172.8 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 PDBj
PDBj