+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7tap | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of archazolid A bound to yeast VO V-ATPase | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / inhibitor / complex / proton pump / ATPase | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcell wall mannoprotein biosynthetic process / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / cellular response to alkaline pH / protein localization to vacuolar membrane / Insulin receptor recycling / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / polyphosphate metabolic process / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Golgi lumen acidification ...cell wall mannoprotein biosynthetic process / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / cellular response to alkaline pH / protein localization to vacuolar membrane / Insulin receptor recycling / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / polyphosphate metabolic process / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / Golgi lumen acidification / P-type proton-exporting transporter activity / vacuolar transport / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / endosomal lumen acidification / vacuole organization / protein targeting to vacuole / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / fungal-type vacuole / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / cellular hyperosmotic response / vacuolar acidification / fungal-type vacuole membrane / phosphatidylinositol-3,5-bisphosphate binding / proton transmembrane transporter activity / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / intracellular copper ion homeostasis / Neutrophil degranulation / RNA endonuclease activity / proton transmembrane transport / cell periphery / transmembrane transport / endocytosis / ATPase binding / protein-containing complex assembly / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / membrane raft / Golgi membrane / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.8 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Keon, K.A. / Rubinstein, J.L. / Benlekbir, S. / Kirsch, S.H. / Muller, R. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Canada, 1items Canada, 1items
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: ACS Chem Biol / Year: 2022 Journal: ACS Chem Biol / Year: 2022Title: Cryo-EM of the Yeast V Complex Reveals Distinct Binding Sites for Macrolide V-ATPase Inhibitors. Authors: Kristine A Keon / Samir Benlekbir / Susanne H Kirsch / Rolf Müller / John L Rubinstein /   Abstract: Vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases) are proton pumps found in almost all eukaryotic cells. These enzymes consist of a soluble catalytic V region that hydrolyzes ATP and a membrane- ...Vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases) are proton pumps found in almost all eukaryotic cells. These enzymes consist of a soluble catalytic V region that hydrolyzes ATP and a membrane-embedded V region responsible for proton translocation. V-ATPase activity leads to acidification of endosomes, phagosomes, lysosomes, secretory vesicles, and the trans-Golgi network, with extracellular acidification occurring in some specialized cells. Small-molecule inhibitors of V-ATPase have played a crucial role in elucidating numerous aspects of cell biology by blocking acidification of intracellular compartments, while therapeutic use of V-ATPase inhibitors has been proposed for the treatment of cancer, osteoporosis, and some infections. Here, we determine structures of the isolated V complex from bound to two well-known macrolide inhibitors: bafilomycin A1 and archazolid A. The structures reveal different binding sites for the inhibitors on the surface of the proton-carrying c ring, with only a small amount of overlap between the two sites. Binding of both inhibitors is mediated primarily through van der Waals interactions in shallow pockets and suggests that the inhibitors block rotation of the ring. Together, these structures indicate the existence of a large chemical space available for V-ATPase inhibitors that block acidification by binding the c ring. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7tap.cif.gz 7tap.cif.gz | 493.6 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7tap.ent.gz pdb7tap.ent.gz | 405.1 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7tap.json.gz 7tap.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7tap_validation.pdf.gz 7tap_validation.pdf.gz | 1.4 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7tap_full_validation.pdf.gz 7tap_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.5 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7tap_validation.xml.gz 7tap_validation.xml.gz | 93.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7tap_validation.cif.gz 7tap_validation.cif.gz | 134.6 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ta/7tap https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ta/7tap ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ta/7tap ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ta/7tap | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  25780MC  7taoC C: citing same article ( M: map data used to model this data |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-V-type proton ATPase subunit ... , 6 types, 13 molecules DCMEFGHIJKLBA
| #1: Protein | Mass: 17046.361 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #2: Protein | Mass: 22610.641 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  | ||||
| #4: Protein | Mass: 8387.065 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  | ||||
| #5: Protein | Mass: 16357.501 Da / Num. of mol.: 8 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #7: Protein | | Mass: 39822.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #8: Protein | | Mass: 95625.484 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Protein , 2 types, 2 molecules NO
| #3: Protein | Mass: 29694.885 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
|---|---|
| #6: Protein | Mass: 9369.934 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  |
-Non-polymers , 1 types, 8 molecules 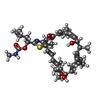
| #9: Chemical | ChemComp-KJL / |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | Y |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Cryo-EM structure of archazolid A bound to yeast VO V-ATPase Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#8 / Source: NATURAL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.4 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2550 nm / Nominal defocus min: 370 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 42 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Details: Prototype Falcon 4i camera |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.19_4092: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software | Name: PHENIX / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: NONE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.8 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 659182 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj












