+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7phl | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
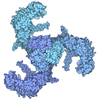
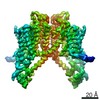
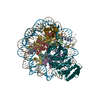
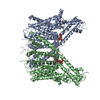
| Title | Human voltage-gated potassium channel Kv3.1 (with EDTA) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components | Potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN / Channel / potassium channel / tetramer / voltage-gated / membrane protein | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationresponse to nerve growth factor / globus pallidus development / response to fibroblast growth factor / response to potassium ion / corpus callosum development / response to auditory stimulus / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / Voltage gated Potassium channels / response to light intensity ...response to nerve growth factor / globus pallidus development / response to fibroblast growth factor / response to potassium ion / corpus callosum development / response to auditory stimulus / voltage-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / Voltage gated Potassium channels / response to light intensity / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / optic nerve development / response to amine / neuronal cell body membrane / action potential / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / axolemma / kinesin binding / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / dendrite membrane / axon terminus / cerebellum development / calyx of Held / protein tetramerization / potassium ion transport / protein homooligomerization / response to toxic substance / cellular response to xenobiotic stimulus / presynaptic membrane / transmembrane transporter binding / postsynaptic membrane / cell surface / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Chi, G. / Qian, P. / Castro-Hartmann, P. / Venkaya, S. / Singh, N.K. / McKinley, G. / Mukhopadhyay, S.M.M. / Fernandez-Cid, A. / Pike, A.C.W. / Marsden, B. ...Chi, G. / Qian, P. / Castro-Hartmann, P. / Venkaya, S. / Singh, N.K. / McKinley, G. / Mukhopadhyay, S.M.M. / Fernandez-Cid, A. / Pike, A.C.W. / Marsden, B. / MacLean, E.M. / Sader, K. / Burgess-Brown, N.A. / Duerr, K.L. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 1items United Kingdom, 1items
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2022Title: Cryo-EM structure of the human Kv3.1 channel reveals gating control by the cytoplasmic T1 domain. Authors: Gamma Chi / Qiansheng Liang / Akshay Sridhar / John B Cowgill / Kasim Sader / Mazdak Radjainia / Pu Qian / Pablo Castro-Hartmann / Shayla Venkaya / Nanki Kaur Singh / Gavin McKinley / ...Authors: Gamma Chi / Qiansheng Liang / Akshay Sridhar / John B Cowgill / Kasim Sader / Mazdak Radjainia / Pu Qian / Pablo Castro-Hartmann / Shayla Venkaya / Nanki Kaur Singh / Gavin McKinley / Alejandra Fernandez-Cid / Shubhashish M M Mukhopadhyay / Nicola A Burgess-Brown / Lucie Delemotte / Manuel Covarrubias / Katharina L Dürr /    Abstract: Kv3 channels have distinctive gating kinetics tailored for rapid repolarization in fast-spiking neurons. Malfunction of this process due to genetic variants in the KCNC1 gene causes severe epileptic ...Kv3 channels have distinctive gating kinetics tailored for rapid repolarization in fast-spiking neurons. Malfunction of this process due to genetic variants in the KCNC1 gene causes severe epileptic disorders, yet the structural determinants for the unusual gating properties remain elusive. Here, we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of the human Kv3.1a channel, revealing a unique arrangement of the cytoplasmic tetramerization domain T1 which facilitates interactions with C-terminal axonal targeting motif and key components of the gating machinery. Additional interactions between S1/S2 linker and turret domain strengthen the interface between voltage sensor and pore domain. Supported by molecular dynamics simulations, electrophysiological and mutational analyses, we identify several residues in the S4/S5 linker which influence the gating kinetics and an electrostatic interaction between acidic residues in α6 of T1 and R449 in the pore-flanking S6T helices. These findings provide insights into gating control and disease mechanisms and may guide strategies for the design of pharmaceutical drugs targeting Kv3 channels. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7phl.cif.gz 7phl.cif.gz | 292.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7phl.ent.gz pdb7phl.ent.gz | 232.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7phl.json.gz 7phl.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ph/7phl https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ph/7phl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ph/7phl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ph/7phl | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  13419MC  7phhC  7phiC  7phkC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 58850.078 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCNC1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCNC1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q3KNS8 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q3KNS8#2: Chemical | ChemComp-PCF / #3: Chemical | ChemComp-ZN / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-K / Has ligand of interest | N | Has protein modification | N | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Homotetrameric complex of human Kv3.1 / Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Experimental value: NO |
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 3 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 47.6 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| Software | Name: PHENIX / Version: 1.17.1_3660: / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C4 (4 fold cyclic) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 217788 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj