+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6wlw | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
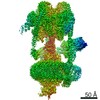
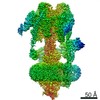
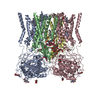
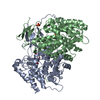
| Title | The Vo region of human V-ATPase in state 1 (focused refinement) | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / V-ATPase / proton pump | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationproton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex / Ion channel transport / intracellular pH reduction / eye pigmentation / central nervous system maturation / transporter activator activity / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / rostrocaudal neural tube patterning / cellular response to increased oxygen levels / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta1 production ...proton-transporting two-sector ATPase complex / Ion channel transport / intracellular pH reduction / eye pigmentation / central nervous system maturation / transporter activator activity / ATPase-coupled ion transmembrane transporter activity / rostrocaudal neural tube patterning / cellular response to increased oxygen levels / positive regulation of transforming growth factor beta1 production / synaptic vesicle lumen acidification / endosome to plasma membrane protein transport / Golgi lumen acidification / proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / Transferrin endocytosis and recycling / plasma membrane proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / lysosomal lumen acidification / clathrin-coated vesicle membrane / endosomal lumen acidification / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase, V0 domain / vacuolar transport / XBP1(S) activates chaperone genes / Amino acids regulate mTORC1 / proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / head morphogenesis / ROS and RNS production in phagocytes / vacuolar proton-transporting V-type ATPase complex / dendritic spine membrane / regulation of cellular pH / vacuolar acidification / osteoclast development / azurophil granule membrane / autophagosome membrane / regulation of MAPK cascade / tertiary granule membrane / ATPase activator activity / ficolin-1-rich granule membrane / positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway / cilium assembly / RHOA GTPase cycle / transmembrane transporter complex / regulation of macroautophagy / angiotensin maturation / Metabolism of Angiotensinogen to Angiotensins / axon terminus / proton transmembrane transport / Insulin receptor recycling / RNA endonuclease activity / proton-transporting ATPase activity, rotational mechanism / endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / receptor-mediated endocytosis / secretory granule membrane / transmembrane transport / synaptic vesicle membrane / small GTPase binding / phagocytic vesicle membrane / melanosome / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / signaling receptor activity / ATPase binding / postsynaptic membrane / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / receptor-mediated endocytosis of virus by host cell / Hydrolases; Acting on ester bonds / lysosome / early endosome / endosome membrane / nuclear speck / apical plasma membrane / lysosomal membrane / external side of plasma membrane / axon / Golgi membrane / intracellular membrane-bounded organelle / focal adhesion / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / Neutrophil degranulation / protein-containing complex binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / perinuclear region of cytoplasm / Golgi apparatus / extracellular exosome / membrane / plasma membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Wang, L. / Wu, H. / Fu, T.-M. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2020 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2020Title: Structures of a Complete Human V-ATPase Reveal Mechanisms of Its Assembly. Authors: Longfei Wang / Di Wu / Carol V Robinson / Hao Wu / Tian-Min Fu /   Abstract: Vesicular- or vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases) are ATP-driven proton pumps comprised of a cytoplasmic V complex for ATP hydrolysis and a membrane-embedded V complex for proton ...Vesicular- or vacuolar-type adenosine triphosphatases (V-ATPases) are ATP-driven proton pumps comprised of a cytoplasmic V complex for ATP hydrolysis and a membrane-embedded V complex for proton transfer. They play important roles in acidification of intracellular vesicles, organelles, and the extracellular milieu in eukaryotes. Here, we report cryoelectron microscopy structures of human V-ATPase in three rotational states at up to 2.9-Å resolution. Aided by mass spectrometry, we build all known protein subunits with associated N-linked glycans and identify glycolipids and phospholipids in the V complex. We define ATP6AP1 as a structural hub for V complex assembly because it connects to multiple V subunits and phospholipids in the c-ring. The glycolipids and the glycosylated V subunits form a luminal glycan coat critical for V-ATPase folding, localization, and stability. This study identifies mechanisms of V-ATPase assembly and biogenesis that rely on the integrated roles of ATP6AP1, glycans, and lipids. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6wlw.cif.gz 6wlw.cif.gz | 503.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6wlw.ent.gz pdb6wlw.ent.gz | 420.7 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6wlw.json.gz 6wlw.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  6wlw_validation.pdf.gz 6wlw_validation.pdf.gz | 2.2 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  6wlw_full_validation.pdf.gz 6wlw_full_validation.pdf.gz | 2.3 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  6wlw_validation.xml.gz 6wlw_validation.xml.gz | 85.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  6wlw_validation.cif.gz 6wlw_validation.cif.gz | 120.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/6wlw https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/6wlw ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/6wlw ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/wl/6wlw | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  21844MC  6wlzC  6wm2C  6wm3C  6wm4C M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-11132 (Title: Cryo-EM structures of human V-ATPase / Data size: 8.4 TB EMPIAR-11132 (Title: Cryo-EM structures of human V-ATPase / Data size: 8.4 TBData #1: Unaligned multi frame micrographs of human V-ATPase in complex with SidK [micrographs - multiframe]) |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller Assembly
Assembly



 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera



 PDBj
PDBj
















