[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-6t7c: Structure of two copies of human Sox11 transcription factor in co... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 6t7c | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
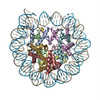
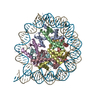
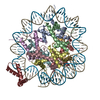
| Title | Structure of two copies of human Sox11 transcription factor in complex with a nucleosome | ||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | NUCLEAR PROTEIN / Nucleosome / DNA / histones / Sox11 / transcription factor / pioneer factor | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationclosure of optic fissure / positive regulation of lens epithelial cell proliferation / soft palate development / negative regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding / cornea development in camera-type eye / noradrenergic neuron differentiation / negative regulation of lymphocyte proliferation / regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / lens morphogenesis in camera-type eye / positive regulation of hippo signaling ...closure of optic fissure / positive regulation of lens epithelial cell proliferation / soft palate development / negative regulation of transcription regulatory region DNA binding / cornea development in camera-type eye / noradrenergic neuron differentiation / negative regulation of lymphocyte proliferation / regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway / lens morphogenesis in camera-type eye / positive regulation of hippo signaling / embryonic skeletal system morphogenesis / neuroepithelial cell differentiation / embryonic digestive tract morphogenesis / camera-type eye morphogenesis / sympathetic nervous system development / positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway / positive regulation of hormone secretion / hard palate development / oligodendrocyte development / positive regulation of ossification / positive regulation of neurogenesis / negative regulation of glial cell proliferation / ventricular septum morphogenesis / spinal cord development / positive regulation of stem cell proliferation / eyelid development in camera-type eye / lung morphogenesis / outflow tract morphogenesis / skeletal muscle cell differentiation / positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation / glial cell proliferation / negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / positive regulation of neuron differentiation / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / telomere organization / Interleukin-7 signaling / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / innate immune response in mucosa / Defective pyroptosis / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / kidney development / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / HDMs demethylate histones / brain development / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / RMTs methylate histone arginines / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / neuron differentiation / HCMV Early Events / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / structural constituent of chromatin / UCH proteinases / antibacterial humoral response / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / nervous system development / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||
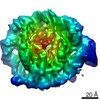
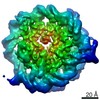
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Dodonova, S.O. / Zhu, F. / Dienemann, C. / Taipale, J. / Cramer, P. | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 3items Germany, 3items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Nucleosome-bound SOX2 and SOX11 structures elucidate pioneer factor function. Authors: Svetlana O Dodonova / Fangjie Zhu / Christian Dienemann / Jussi Taipale / Patrick Cramer /   Abstract: 'Pioneer' transcription factors are required for stem-cell pluripotency, cell differentiation and cell reprogramming. Pioneer factors can bind nucleosomal DNA to enable gene expression from regions ...'Pioneer' transcription factors are required for stem-cell pluripotency, cell differentiation and cell reprogramming. Pioneer factors can bind nucleosomal DNA to enable gene expression from regions of the genome with closed chromatin. SOX2 is a prominent pioneer factor that is essential for pluripotency and self-renewal of embryonic stem cells. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of the DNA-binding domains of SOX2 and its close homologue SOX11 bound to nucleosomes. The structures show that SOX factors can bind and locally distort DNA at superhelical location 2. The factors also facilitate detachment of terminal nucleosomal DNA from the histone octamer, which increases DNA accessibility. SOX-factor binding to the nucleosome can also lead to a repositioning of the N-terminal tail of histone H4 that includes residue lysine 16. We speculate that this repositioning is incompatible with higher-order nucleosome stacking, which involves contacts of the H4 tail with a neighbouring nucleosome. Our results indicate that pioneer transcription factors can use binding energy to initiate chromatin opening, and thereby facilitate nucleosome remodelling and subsequent transcription. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  6t7c.cif.gz 6t7c.cif.gz | 262.9 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb6t7c.ent.gz pdb6t7c.ent.gz | 193.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  6t7c.json.gz 6t7c.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t7/6t7c https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t7/6t7c ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t7/6t7c ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/t7/6t7c | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 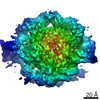 10393MC 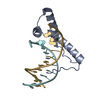 6t78C  6t79C 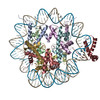 6t7aC  6t7bC  6t7dC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 5 types, 10 molecules AEBFCGDHKL
| #1: Protein | Mass: 15389.036 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST2H3A, HIST2H3C, H3F2, H3FM, HIST2H3D / Plasmid: pET22b / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST2H3A, HIST2H3C, H3F2, H3FM, HIST2H3D / Plasmid: pET22b / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 11394.426 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, ...Gene: HIST1H4A, H4/A, H4FA, HIST1H4B, H4/I, H4FI, HIST1H4C, H4/G, H4FG, HIST1H4D, H4/B, H4FB, HIST1H4E, H4/J, H4FJ, HIST1H4F, H4/C, H4FC, HIST1H4H, H4/H, H4FH, HIST1H4I, H4/M, H4FM, HIST1H4J, H4/E, H4FE, HIST1H4K, H4/D, H4FD, HIST1H4L, H4/K, H4FK, HIST2H4A, H4/N, H4F2, H4FN, HIST2H4, HIST2H4B, H4/O, H4FO, HIST4H4 Plasmid: pET3a / Production host:  #3: Protein | Mass: 16707.277 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2AB, H2AFM, HIST1H2AE, H2AFA / Plasmid: LIC-1B (MacroLabs) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2AB, H2AFM, HIST1H2AE, H2AFA / Plasmid: LIC-1B (MacroLabs) / Production host:  #4: Protein | Mass: 13921.213 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2BK, H2BFT, HIRIP1 / Plasmid: pET22b / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: HIST1H2BK, H2BFT, HIRIP1 / Plasmid: pET22b / Production host:  #7: Protein | Mass: 12856.941 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SOX11 / Plasmid: LIC-1B (MacroLabs) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: SOX11 / Plasmid: LIC-1B (MacroLabs) / Production host:  |
|---|
-DNA chain , 2 types, 2 molecules IJ
| #5: DNA chain | Mass: 45240.848 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
|---|---|
| #6: DNA chain | Mass: 45484.273 Da / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Source: (synth.) synthetic construct (others) |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.229 MDa / Experimental value: NO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (natural) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source (recombinant) |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | pH: 7.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer component |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.15 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: 0.39 mB, 25 mA / Grid material: COPPER / Grid mesh size: 300 divisions/in. / Grid type: Quantifoil R2/1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 289 K Details: The sample was applied onto glow-discharged Quantifoil holey carbon grids. The grids were blotted from both sides for 5-10 seconds at 16*C in a chamber at 100% humidity and plunge-frozen ...Details: The sample was applied onto glow-discharged Quantifoil holey carbon grids. The grids were blotted from both sides for 5-10 seconds at 16*C in a chamber at 100% humidity and plunge-frozen into liquid ethane using a manual plunger. |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS Details: At least 50% of the data were collected at 25* stage tilt in order to partially compensate for preferred orientation of particles on the grid, and to improve angular distribution. |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 130000 X / Nominal defocus max: 3500 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2.7 mm / C2 aperture diameter: 100 µm / Alignment procedure: COMA FREE |
| Specimen holder | Cryogen: NITROGEN / Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 1.125 e/Å2 / Detector mode: COUNTING / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Num. of grids imaged: 1 |
| EM imaging optics | Energyfilter name: GIF Bioquantum / Energyfilter slit width: 30 eV |
| Image scans | Movie frames/image: 40 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 4 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 109666 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EM volume selection | Details: 1733 vesicles and near-complete buds were picked from 61 tomograms. Subtomograms were extracted from the surface of the vesicles. Num. of tomograms: 54 / Num. of volumes extracted: 2547 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | B value: 130 / Protocol: OTHER / Space: REAL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | PDB-ID: 6FQ5 Accession code: 6FQ5 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





 PDBj
PDBj