[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-17396: Homomeric GluA1 in tandem with TARP gamma-3, desensitized conform... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Homomeric GluA1 in tandem with TARP gamma-3, desensitized conformation 3 | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | AMPAR / ion channels / neurotransmission / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationCargo concentration in the ER / axonal spine / positive regulation of locomotion involved in locomotory behavior / positive regulation of membrane potential / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / cellular response to ammonium ion / response to sucrose / neuron spine / myosin V binding / postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor diffusion trapping ...Cargo concentration in the ER / axonal spine / positive regulation of locomotion involved in locomotory behavior / positive regulation of membrane potential / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / cellular response to ammonium ion / response to sucrose / neuron spine / myosin V binding / postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor diffusion trapping / proximal dendrite / regulation of AMPA receptor activity / regulation of monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / Trafficking of AMPA receptors / channel regulator activity / LGI-ADAM interactions / response to arsenic-containing substance / cellular response to L-glutamate / cellular response to dsRNA / dendritic spine membrane / long-term synaptic depression / beta-2 adrenergic receptor binding / Synaptic adhesion-like molecules / cellular response to peptide hormone stimulus / response to morphine / neuronal cell body membrane / cellular response to amine stimulus / response to psychosocial stress / neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane / peptide hormone receptor binding / spinal cord development / Activation of AMPA receptors / perisynaptic space / protein kinase A binding / AMPA glutamate receptor activity / Trafficking of GluR2-containing AMPA receptors / transmission of nerve impulse / response to lithium ion / behavioral response to pain / AMPA glutamate receptor complex / adenylate cyclase binding / immunoglobulin binding / asymmetric synapse / ionotropic glutamate receptor complex / conditioned place preference / response to electrical stimulus / regulation of receptor recycling / excitatory synapse / G-protein alpha-subunit binding / glutamate receptor binding / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / positive regulation of synaptic transmission / long-term memory / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / postsynaptic density, intracellular component / neuronal action potential / protein targeting / response to fungicide / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / glutamate-gated receptor activity / synapse assembly / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / glutamate-gated calcium ion channel activity / presynaptic active zone membrane / somatodendritic compartment / ionotropic glutamate receptor binding / dendrite membrane / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / synaptic membrane / dendritic shaft / PDZ domain binding / response to cocaine / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / response to nutrient levels / neuromuscular junction / recycling endosome / postsynaptic density membrane / response to peptide hormone / cerebral cortex development / regulation of synaptic plasticity / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / receptor internalization / cellular response to growth factor stimulus / small GTPase binding / response to toxic substance / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / recycling endosome membrane / long-term synaptic potentiation / synaptic vesicle / cell-cell junction / synaptic vesicle membrane / intracellular protein localization / response to estradiol / G-protein beta-subunit binding / presynapse / amyloid-beta binding / presynaptic membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.53 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang D / Krieger JM / Yamashita K / Greger IH | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, European Union, 3 items United Kingdom, European Union, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Structural mobility tunes signalling of the GluA1 AMPA glutamate receptor. Authors: Danyang Zhang / Josip Ivica / James M Krieger / Hinze Ho / Keitaro Yamashita / Imogen Stockwell / Rozbeh Baradaran / Ondrej Cais / Ingo H Greger /   Abstract: AMPA glutamate receptors (AMPARs), the primary mediators of excitatory neurotransmission in the brain, are either GluA2 subunit-containing and thus Ca-impermeable, or GluA2-lacking and Ca-permeable. ...AMPA glutamate receptors (AMPARs), the primary mediators of excitatory neurotransmission in the brain, are either GluA2 subunit-containing and thus Ca-impermeable, or GluA2-lacking and Ca-permeable. Despite their prominent expression throughout interneurons and glia, their role in long-term potentiation and their involvement in a range of neuropathologies, structural information for GluA2-lacking receptors is currently absent. Here we determine and characterize cryo-electron microscopy structures of the GluA1 homotetramer, fully occupied with TARPγ3 auxiliary subunits (GluA1/γ3). The gating core of both resting and open-state GluA1/γ3 closely resembles GluA2-containing receptors. However, the sequence-diverse N-terminal domains (NTDs) give rise to a highly mobile assembly, enabling domain swapping and subunit re-alignments in the ligand-binding domain tier that are pronounced in desensitized states. These transitions underlie the unique kinetic properties of GluA1. A GluA2 mutant (F231A) increasing NTD dynamics phenocopies this behaviour, and exhibits reduced synaptic responses, reflecting the anchoring function of the AMPAR NTD at the synapse. Together, this work underscores how the subunit-diverse NTDs determine subunit arrangement, gating properties and ultimately synaptic signalling efficiency among AMPAR subtypes. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_17396.map.gz emd_17396.map.gz | 32.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-17396-v30.xml emd-17396-v30.xml emd-17396.xml emd-17396.xml | 15.8 KB 15.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_17396_fsc.xml emd_17396_fsc.xml | 9.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_17396.png emd_17396.png | 64.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-17396.cif.gz emd-17396.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_17396_half_map_1.map.gz emd_17396_half_map_1.map.gz emd_17396_half_map_2.map.gz emd_17396_half_map_2.map.gz | 59.5 MB 59.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17396 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17396 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17396 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-17396 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 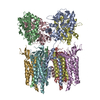 8p3vMC 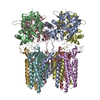 8c1pC  8c1qC  8c1rC  8c1sC  8c2hC  8c2iC  8p3qC  8p3sC  8p3tC  8p3uC  8p3wC  8p3xC  8p3yC  8p3zC  8pivC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_17396.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_17396.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.325 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_17396_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_17396_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Homomeric GluA1 AMPA receptor in tandem with TARP gamma 3 and 1mM...
| Entire | Name: Homomeric GluA1 AMPA receptor in tandem with TARP gamma 3 and 1mM quisqualate |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Homomeric GluA1 AMPA receptor in tandem with TARP gamma 3 and 1mM...
| Supramolecule | Name: Homomeric GluA1 AMPA receptor in tandem with TARP gamma 3 and 1mM quisqualate type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Glutamate receptor 1 flip isoform
| Macromolecule | Name: Glutamate receptor 1 flip isoform / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 102.66193 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MPYIFAFFCT GFLGAVVGAD YKDDDDKNFP NNIQIGGLFP NQQSQEHAAF RFALSQLTEP PKLLPQIDIV NISDSFEMTY RFCSQFSKG VYAIFGFYER RTVNMLTSFC GALHVCFITP SFPVDTSNQF VLQLRPELQE ALISIIDHYK WQTFVYIYDA D RGLSVLQR ...String: MPYIFAFFCT GFLGAVVGAD YKDDDDKNFP NNIQIGGLFP NQQSQEHAAF RFALSQLTEP PKLLPQIDIV NISDSFEMTY RFCSQFSKG VYAIFGFYER RTVNMLTSFC GALHVCFITP SFPVDTSNQF VLQLRPELQE ALISIIDHYK WQTFVYIYDA D RGLSVLQR VLDTAAEKNW QVTAVNILTT TEEGYRMLFQ DLEKKKERLV VVDCESERLN AILGQIVKLE KNGIGYHYIL AN LGFMDID LNKFKESGAN VTGFQLVNYT DTIPARIMQQ WRTSDSRDHT RVDWKRPKYT SALTYDGVKV MAEAFQSLRR QRI DISRRG NAGDCLANPA VPWGQGIDIQ RALQQVRFEG LTGNVQFNEK GRRTNYTLHV IEMKHDGIRK IGYWNEDDKF VPAA TDAQA GGDNSSVQNR TYIVTTILED PYVMLKKNAN QFEGNDRYEG YCVELAAEIA KHVGYSYRLE IVSDGKYGAR DPDTK AWNG MVGELVYGRA DVAVAPLTIT LVREEVIDFS KPFMSLGISI MIKKPQKSKP GVFSFLDPLA YEIWMCIVFA YIGVSV VLF LVSRFSPYEW HSEEFEEGRD QTTSDQSNEF GIFNSLWFSL GAFMQQGCDI SPRSLSGRIV GGVWWFFTLI IISSYTA NL AAFLTVERMV SPIESAEDLA KQTEIAYGTL EAGSTKEFFR RSKIAVFEKM WTYMKSAEPS VFVRTTEEGM IRVRKSKG K YAYLLESTMN EYIEQRKPCD TMKVGGNLDS KGYGIATPKG SALRGPVNLA VLKLSEQGVL DKLKSKWWYD KGECGSKDS GSKDKTSALS LSNVAGVFYI LIGGLGLAML VALIEFCYKS RSESKRMKGF CLIPQQSINE AIRTSTLPRN SGAGASGGGG SGENGRVVS QDFPKSMQSI PCMSHSSGMP LGATGL UniProtKB: Glutamate receptor 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Voltage-dependent calcium channel gamma-3 subunit
| Macromolecule | Name: Voltage-dependent calcium channel gamma-3 subunit / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 35.435332 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: RMCDRGIQML ITTVGAFAAF SLMTIAVGTD YWLYSRGVCR TKSTSDNETS RKNEEVMTHS GLWRTCCLEG AFRGVCKKID HFPEDADYE QDTAEYLLRA VRASSVFPIL SVTLLFFGGL CVAASEFHRS RHSVILSAGI FFVSAGLSNI IGIIVYISAN A GDPGQRDS ...String: RMCDRGIQML ITTVGAFAAF SLMTIAVGTD YWLYSRGVCR TKSTSDNETS RKNEEVMTHS GLWRTCCLEG AFRGVCKKID HFPEDADYE QDTAEYLLRA VRASSVFPIL SVTLLFFGGL CVAASEFHRS RHSVILSAGI FFVSAGLSNI IGIIVYISAN A GDPGQRDS KKSYSYGWSF YFGAFSFIIA EIVGVVAVHI YIEKHQQLRA RSHSELLKKS TFARLPPYRY RFRRRSSSRS TE PRSRDLS PISKGFHTIP STDISMFTLS RDPSKLTMGT LLNSDRDHAF LQFHNSTPKE FKESLHNNPA NRRTTPV UniProtKB: Voltage-dependent calcium channel gamma-3 subunit |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)