[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-8c1q: Resting state homomeric GluA1 AMPA receptor in complex with TARP ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 8c1q | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Resting state homomeric GluA1 AMPA receptor in complex with TARP gamma 3 | |||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / AMPAR / ion channels / neurotransmission | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationCargo concentration in the ER / axonal spine / positive regulation of locomotion involved in locomotory behavior / positive regulation of membrane potential / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / cellular response to ammonium ion / response to sucrose / neuron spine / myosin V binding / postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor diffusion trapping ...Cargo concentration in the ER / axonal spine / positive regulation of locomotion involved in locomotory behavior / positive regulation of membrane potential / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / cellular response to ammonium ion / response to sucrose / neuron spine / myosin V binding / postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor diffusion trapping / proximal dendrite / channel regulator activity / regulation of monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / LGI-ADAM interactions / regulation of AMPA receptor activity / Trafficking of AMPA receptors / response to arsenic-containing substance / cellular response to L-glutamate / cellular response to dsRNA / dendritic spine membrane / long-term synaptic depression / beta-2 adrenergic receptor binding / Synaptic adhesion-like molecules / cellular response to peptide hormone stimulus / response to morphine / neuronal cell body membrane / cellular response to amine stimulus / response to psychosocial stress / peptide hormone receptor binding / neurotransmitter receptor localization to postsynaptic specialization membrane / spinal cord development / perisynaptic space / protein kinase A binding / Activation of AMPA receptors / AMPA glutamate receptor activity / response to lithium ion / Trafficking of GluR2-containing AMPA receptors / behavioral response to pain / transmission of nerve impulse / adenylate cyclase binding / AMPA glutamate receptor complex / immunoglobulin binding / asymmetric synapse / ionotropic glutamate receptor complex / conditioned place preference / response to electrical stimulus / regulation of receptor recycling / excitatory synapse / G-protein alpha-subunit binding / glutamate receptor binding / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / positive regulation of synaptic transmission / long-term memory / positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / postsynaptic density, intracellular component / neuronal action potential / protein targeting / response to fungicide / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / synapse assembly / glutamate-gated receptor activity / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / glutamate-gated calcium ion channel activity / presynaptic active zone membrane / somatodendritic compartment / dendrite membrane / ionotropic glutamate receptor binding / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / synaptic membrane / dendritic shaft / PDZ domain binding / response to cocaine / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / response to nutrient levels / neuromuscular junction / recycling endosome / regulation of synaptic plasticity / response to peptide hormone / postsynaptic density membrane / cerebral cortex development / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / receptor internalization / cellular response to growth factor stimulus / small GTPase binding / response to toxic substance / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / recycling endosome membrane / long-term synaptic potentiation / synaptic vesicle / cell-cell junction / synaptic vesicle membrane / intracellular protein localization / response to estradiol / G-protein beta-subunit binding / presynapse / amyloid-beta binding / presynaptic membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.82 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhang, D. / Ivica, J. / Krieger, J.M. / Ho, H. / Yamashita, K. / Cais, O. / Greger, I. | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2items United Kingdom, 2items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2023 Journal: Nature / Year: 2023Title: Structural mobility tunes signalling of the GluA1 AMPA glutamate receptor. Authors: Danyang Zhang / Josip Ivica / James M Krieger / Hinze Ho / Keitaro Yamashita / Imogen Stockwell / Rozbeh Baradaran / Ondrej Cais / Ingo H Greger /   Abstract: AMPA glutamate receptors (AMPARs), the primary mediators of excitatory neurotransmission in the brain, are either GluA2 subunit-containing and thus Ca-impermeable, or GluA2-lacking and Ca-permeable. ...AMPA glutamate receptors (AMPARs), the primary mediators of excitatory neurotransmission in the brain, are either GluA2 subunit-containing and thus Ca-impermeable, or GluA2-lacking and Ca-permeable. Despite their prominent expression throughout interneurons and glia, their role in long-term potentiation and their involvement in a range of neuropathologies, structural information for GluA2-lacking receptors is currently absent. Here we determine and characterize cryo-electron microscopy structures of the GluA1 homotetramer, fully occupied with TARPγ3 auxiliary subunits (GluA1/γ3). The gating core of both resting and open-state GluA1/γ3 closely resembles GluA2-containing receptors. However, the sequence-diverse N-terminal domains (NTDs) give rise to a highly mobile assembly, enabling domain swapping and subunit re-alignments in the ligand-binding domain tier that are pronounced in desensitized states. These transitions underlie the unique kinetic properties of GluA1. A GluA2 mutant (F231A) increasing NTD dynamics phenocopies this behaviour, and exhibits reduced synaptic responses, reflecting the anchoring function of the AMPAR NTD at the synapse. Together, this work underscores how the subunit-diverse NTDs determine subunit arrangement, gating properties and ultimately synaptic signalling efficiency among AMPAR subtypes. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  8c1q.cif.gz 8c1q.cif.gz | 515.8 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb8c1q.ent.gz pdb8c1q.ent.gz | 391.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  8c1q.json.gz 8c1q.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c1/8c1q https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c1/8c1q ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c1/8c1q ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/c1/8c1q | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  16380MC  8c1pC  8c1rC  8c1sC  8c2hC  8c2iC  8p3qC  8p3sC  8p3tC  8p3uC  8p3vC  8p3wC  8p3xC  8p3yC  8p3zC  8pivC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 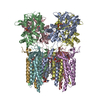
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
-Protein , 2 types, 8 molecules ABCDEFGH
| #1: Protein | Mass: 102661.930 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P19490 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P19490#2: Protein | Mass: 35435.332 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8VHX0 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: Q8VHX0 |
|---|
-Non-polymers , 5 types, 43 molecules 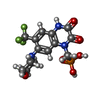
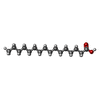
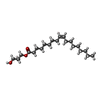






| #3: Chemical | ChemComp-ZK1 / {[ #4: Chemical | ChemComp-PLM / #5: Chemical | ChemComp-OLC / ( #6: Chemical | ChemComp-POV / ( #7: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Details
| Has ligand of interest | N |
|---|---|
| Has protein modification | Y |
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Homomeric GluA1 AMPA receptor in complex with TARP gamma 3 Type: COMPLEX / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: TFS KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2400 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1400 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 50 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software | Name: REFMAC / Category: model refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C1 (asymmetric) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 2.82 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 252544 / Symmetry type: POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Space: RECIPROCAL / Details: Servalcat | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | Resolution: 2.82→2.82 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.922 / SU B: 9.356 / SU ML: 0.174 / ESU R: 0.292 Stereochemistry target values: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD WITH PHASES Details: HYDROGENS HAVE BEEN USED IF PRESENT IN THE INPUT
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Solvent model: PARAMETERS FOR MASK CACLULATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 135.112 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: 1 / Total: 18462 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 PDBj
PDBj















