+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8819 | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | GluA2 bound to antagonist ZK and GSG1L in digitonin, state 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | GluA2 bound to antagonist ZK and GSG1L in digitonin, state 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Ion channel / TRANSPORT PROTEIN | ||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of short-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / spine synapse / dendritic spine neck / dendritic spine cytoplasm / cellular response to amine stimulus / dendritic spine head / regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor internalization / perisynaptic space / Activation of AMPA receptors / ligand-gated monoatomic cation channel activity ...regulation of short-term neuronal synaptic plasticity / spine synapse / dendritic spine neck / dendritic spine cytoplasm / cellular response to amine stimulus / dendritic spine head / regulation of postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor internalization / perisynaptic space / Activation of AMPA receptors / ligand-gated monoatomic cation channel activity / AMPA glutamate receptor activity / Trafficking of GluR2-containing AMPA receptors / response to lithium ion / transmission of nerve impulse / AMPA glutamate receptor clustering / cellular response to glycine / kainate selective glutamate receptor activity / AMPA glutamate receptor complex / immunoglobulin binding / asymmetric synapse / regulation of receptor recycling / extracellularly glutamate-gated ion channel activity / ionotropic glutamate receptor complex / conditioned place preference / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / glutamate receptor binding / positive regulation of synaptic transmission / regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / response to fungicide / cytoskeletal protein binding / extracellular ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity / glutamate-gated receptor activity / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / regulation of long-term synaptic depression / somatodendritic compartment / glutamate-gated calcium ion channel activity / presynaptic active zone membrane / dendrite membrane / excitatory synapse / ionotropic glutamate receptor binding / ionotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway / dendrite cytoplasm / ligand-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of presynaptic membrane potential / synaptic membrane / positive regulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / dendritic shaft / SNARE binding / PDZ domain binding / synaptic transmission, glutamatergic / protein tetramerization / establishment of protein localization / transmitter-gated monoatomic ion channel activity involved in regulation of postsynaptic membrane potential / synapse organization / cerebral cortex development / postsynaptic density membrane / receptor internalization / modulation of chemical synaptic transmission / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / terminal bouton / synaptic vesicle / long-term synaptic potentiation / synaptic vesicle membrane / signaling receptor activity / amyloid-beta binding / presynapse / growth cone / presynaptic membrane / scaffold protein binding / dendritic spine / chemical synaptic transmission / perikaryon / postsynaptic membrane / neuron projection / postsynaptic density / axon / external side of plasma membrane / neuronal cell body / synapse / dendrite / protein kinase binding / protein-containing complex binding / glutamatergic synapse / cell surface / endoplasmic reticulum / protein-containing complex / identical protein binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.6 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Twomey EC / Yelshanskaya MV | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 5 items United States, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2017 Journal: Nature / Year: 2017Title: Channel opening and gating mechanism in AMPA-subtype glutamate receptors. Authors: Edward C Twomey / Maria V Yelshanskaya / Robert A Grassucci / Joachim Frank / Alexander I Sobolevsky /  Abstract: AMPA (α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid)-subtype ionotropic glutamate receptors mediate fast excitatory neurotransmission throughout the central nervous system. Gated by the ...AMPA (α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid)-subtype ionotropic glutamate receptors mediate fast excitatory neurotransmission throughout the central nervous system. Gated by the neurotransmitter glutamate, AMPA receptors are critical for synaptic strength, and dysregulation of AMPA receptor-mediated signalling is linked to numerous neurological diseases. Here we use cryo-electron microscopy to solve the structures of AMPA receptor-auxiliary subunit complexes in the apo, antagonist- and agonist-bound states and determine the iris-like mechanism of ion channel opening. The ion channel selectivity filter is formed by the extended portions of the re-entrant M2 loops, while the helical portions of M2 contribute to extensive hydrophobic interfaces between AMPA receptor subunits in the ion channel. We show how the permeation pathway changes upon channel opening and identify conformational changes throughout the entire AMPA receptor that accompany activation and desensitization. Our findings provide a framework for understanding gating across the family of ionotropic glutamate receptors and the role of AMPA receptors in excitatory neurotransmission. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8819.map.gz emd_8819.map.gz | 12 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8819-v30.xml emd-8819-v30.xml emd-8819.xml emd-8819.xml | 13.6 KB 13.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_8819.png emd_8819.png | 58.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-8819.cif.gz emd-8819.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8819 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8819 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8819 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8819 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5wekMC  8820C  8821C  8822C  8823C  5welC  5wemC  5wenC  5weoC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8819.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8819.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | GluA2 bound to antagonist ZK and GSG1L in digitonin, state 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.98 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
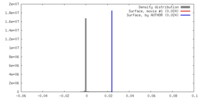
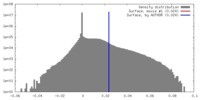
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : GluA2 bound to antagonist ZK and GSG1L in digitonin, state 1
| Entire | Name: GluA2 bound to antagonist ZK and GSG1L in digitonin, state 1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: GluA2 bound to antagonist ZK and GSG1L in digitonin, state 1
| Supramolecule | Name: GluA2 bound to antagonist ZK and GSG1L in digitonin, state 1 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Chimera of Glutamate receptor 2,Germ cell-specific gene 1-like protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Chimera of Glutamate receptor 2,Germ cell-specific gene 1-like protein type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 117.471211 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: NSIQIGGLFP RGADQEYSAF RVGMVQFSTS EFRLTPHIDN LEVANSFAVT NAFCSQFSRG VYAIFGFYDK KSVNTITSFC GTLHVSFIT PSFPTDGTHP FVIQMRPDLK GALLSLIEYY QWDKFAYLYD SDRGLSTLQA VLDSAAEKKW QVTAINVGNI N NDKKDETY ...String: NSIQIGGLFP RGADQEYSAF RVGMVQFSTS EFRLTPHIDN LEVANSFAVT NAFCSQFSRG VYAIFGFYDK KSVNTITSFC GTLHVSFIT PSFPTDGTHP FVIQMRPDLK GALLSLIEYY QWDKFAYLYD SDRGLSTLQA VLDSAAEKKW QVTAINVGNI N NDKKDETY RSLFQDLELK KERRVILDCE RDKVNDIVDQ VITIGKHVKG YHYIIANLGF TDGDLLKIQF GGAEVSGFQI VD YDDSLVS KFIERWSTLE EKEYPGAHTA TIKYTSALTY DAVQVMTEAF RNLRKQRIEI SRRGNAGDCL ANPAVPWGQG VEI ERALKQ VQVEGLSGNI KFDQNGKRIN YTINIMELKT NGPRKIGYWS EVDKMVLTED DTSGLEQKTV VVTTILESPY VMMK KNHEM LEGNERYEGY CVDLAAEIAK HCGFKYKLTI VGDGKYGARD ADTKIWNGMV GELVYGKADI AIAPLTITLV REEVI DFSK PFMSLGISIM IKKPQKSKPG VFSFLDPLAY EIWMCIVFAY IGVSVVLFLV SRFSPYEWHT EEFEDGRETQ SSESTN EFG IFNSLWFSLG AFMQQGCDIS PRSLSGRIVG GVWWFFTLII ISSYTANLAA FLTVERMVSP IESAEDLSKQ TEIAYGT LD SGSTKEFFRR SKIAVFDKMW TYMRSAEPSV FVRTTAEGVA RVRKSKGKYA YLLESTMNEY IEQRKPCDTM KVGGNLDS K GYGIATPKGS SLGTPVNLAV LKLSEQGVLD KLKNKWWYDK GECGAKDSGS KEKTSALSLS NVAGVFYILV GGLGLAMLV ALIEFCYKSR AEAKRMKGTG KTSRRGRALL AVALNLLALL FATTAFLTTY WCQGTQRVPK PGCGQGGGAN CPNSGANATA NSTAAPVAA SPAGAPYSWE AGDERFQLRR FHTGIWYSCE EELGGPGEKC RSFIDLAPAS EKGVLWLSVV SEVLYILLLV V GFSLMCLE LLHSSSVIDG LKLNAFAAVF TVLSGLLGMV AHMMYTQVFQ VTVSLGPEDW RPHSWDYGWS FCLAWGSFTC CM AASVTTL NSYTKTVIEF UniProtKB: Glutamate receptor 2, Germ cell-specific gene 1-like protein |
-Macromolecule #2: {[7-morpholin-4-yl-2,3-dioxo-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydroquino...
| Macromolecule | Name: {[7-morpholin-4-yl-2,3-dioxo-6-(trifluoromethyl)-3,4-dihydroquinoxalin-1(2H)-yl]methyl}phosphonic acid type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ZK1 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 409.254 Da |
| Chemical component information | 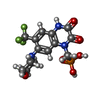 ChemComp-ZK1: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
| Grid | Model: C-flat-1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 200 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE Details: Gold-gold grids, hydrogen and oxygen glow discharge (20s, 10 watts, 6.4 sccm H2, 27.5 sccm O2) |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
| Details | GluA2 bound to antagonist ZK and GSG1L in digitonin, state 1 |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 67.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER / Details: GluA2-2xGSG1L ZK DDM map |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C2 (2 fold cyclic) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.6 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 26971 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: RANDOM ASSIGNMENT |
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-5wek: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)