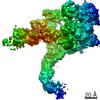
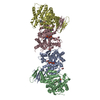
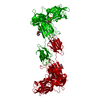
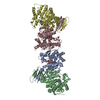
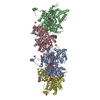
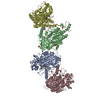
登録情報 データベース : PDB / ID : 7mobタイトル Cryo-EM structure of 2:2 c-MET/NK1 complex Hepatocyte growth factor Hepatocyte growth factor receptor キーワード / / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト)手法 / / / 解像度 : 5 Å データ登録者 Uchikawa, E. / Chen, Z.M. / Xiao, G.Y. / Zhang, X.W. / Bai, X.C. ジャーナル : Nat Commun / 年 : 2021タイトル : Structural basis of the activation of c-MET receptor.著者 : Emiko Uchikawa / Zhiming Chen / Guan-Yu Xiao / Xuewu Zhang / Xiao-Chen Bai / 要旨 : The c-MET receptor is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) that plays essential roles in normal cell development and motility. Aberrant activation of c-MET can lead to both tumors growth and metastatic ... The c-MET receptor is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) that plays essential roles in normal cell development and motility. Aberrant activation of c-MET can lead to both tumors growth and metastatic progression of cancer cells. C-MET can be activated by either hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), or its natural isoform NK1. Here, we report the cryo-EM structures of c-MET/HGF and c-MET/NK1 complexes in the active state. The c-MET/HGF complex structure reveals that, by utilizing two distinct interfaces, one HGF molecule is sufficient to induce a specific dimerization mode of c-MET for receptor activation. The binding of heparin as well as a second HGF to the 2:1 c-MET:HGF complex further stabilize this active conformation. Distinct to HGF, NK1 forms a stable dimer, and bridges two c-METs in a symmetrical manner for activation. Collectively, our studies provide structural insights into the activation mechanisms of c-MET, and reveal how two isoforms of the same ligand use dramatically different mechanisms to activate the receptor. 履歴 登録 2021年5月1日 登録サイト / 処理サイト 改定 1.0 2021年6月9日 Provider / タイプ 改定 1.1 2021年7月28日 Group / カテゴリ / citation_authorItem _citation.country / _citation.journal_abbrev ... _citation.country / _citation.journal_abbrev / _citation.journal_id_CSD / _citation.journal_id_ISSN / _citation.journal_volume / _citation.page_first / _citation.page_last / _citation.pdbx_database_id_DOI / _citation.pdbx_database_id_PubMed / _citation.title / _citation.year / _citation_author.identifier_ORCID / _citation_author.name 改定 1.2 2024年11月13日 Group / Database references / Structure summaryカテゴリ chem_comp_atom / chem_comp_bond ... chem_comp_atom / chem_comp_bond / database_2 / em_admin / pdbx_entry_details / pdbx_modification_feature Item / _database_2.pdbx_database_accession / _em_admin.last_update
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報 要素
要素 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) データ登録者
データ登録者 引用
引用 ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2021
ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2021

 構造の表示
構造の表示 ムービービューア
ムービービューア Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク ダウンロード
ダウンロード 7mob.cif.gz
7mob.cif.gz PDBx/mmCIF形式
PDBx/mmCIF形式 pdb7mob.ent.gz
pdb7mob.ent.gz PDB形式
PDB形式 7mob.json.gz
7mob.json.gz PDBx/mmJSON形式
PDBx/mmJSON形式 その他のダウンロード
その他のダウンロード 7mob_validation.pdf.gz
7mob_validation.pdf.gz wwPDB検証レポート
wwPDB検証レポート 7mob_full_validation.pdf.gz
7mob_full_validation.pdf.gz 7mob_validation.xml.gz
7mob_validation.xml.gz 7mob_validation.cif.gz
7mob_validation.cif.gz https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mo/7mob
https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mo/7mob ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mo/7mob
ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/mo/7mob リンク
リンク 集合体
集合体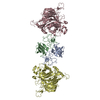
 要素
要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: HGF, HPTA / 発現宿主:
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: HGF, HPTA / 発現宿主:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P14210
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P14210 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: MET / 発現宿主:
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 遺伝子: MET / 発現宿主:  Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P08581, receptor protein-tyrosine kinase
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 参照: UniProt: P08581, receptor protein-tyrosine kinase 試料調製
試料調製 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) 電子顕微鏡撮影
電子顕微鏡撮影
 FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM
FIELD EMISSION GUN / 加速電圧: 300 kV / 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM 解析
解析 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー



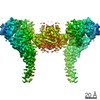
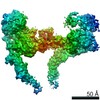
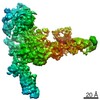




 PDBj
PDBj












