+検索条件
-Structure paper
| タイトル | Antibody escape by polyomavirus capsid mutation facilitates neurovirulence. |
|---|---|
| ジャーナル・号・ページ | Elife, Vol. 9, Year 2020 |
| 掲載日 | 2020年9月17日 |
 著者 著者 | Matthew D Lauver / Daniel J Goetschius / Colleen S Netherby-Winslow / Katelyn N Ayers / Ge Jin / Daniel G Haas / Elizabeth L Frost / Sung Hyun Cho / Carol M Bator / Stephanie M Bywaters / Neil D Christensen / Susan L Hafenstein / Aron E Lukacher /  |
| PubMed 要旨 | JCPyV polyomavirus, a member of the human virome, causes progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), an oft-fatal demyelinating brain disease in individuals receiving immunomodulatory therapies. ...JCPyV polyomavirus, a member of the human virome, causes progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML), an oft-fatal demyelinating brain disease in individuals receiving immunomodulatory therapies. Mutations in the major viral capsid protein, VP1, are common in JCPyV from PML patients (JCPyV-PML) but whether they confer neurovirulence or escape from virus-neutralizing antibody (nAb) in vivo is unknown. A mouse polyomavirus (MuPyV) with a sequence-equivalent JCPyV-PML VP1 mutation replicated poorly in the kidney, a major reservoir for JCPyV persistence, but retained the CNS infectivity, cell tropism, and neuropathology of the parental virus. This mutation rendered MuPyV resistant to a monoclonal Ab (mAb), whose specificity overlapped the endogenous anti-VP1 response. Using cryo-EM and a custom sub-particle refinement approach, we resolved an MuPyV:Fab complex map to 3.2 Å resolution. The structure revealed the mechanism of mAb evasion. Our findings demonstrate convergence between nAb evasion and CNS neurovirulence in vivo by a frequent JCPyV-PML VP1 mutation. |
 リンク リンク |  Elife / Elife /  PubMed:32940605 / PubMed:32940605 /  PubMed Central PubMed Central |
| 手法 | EM (単粒子) |
| 解像度 | 2.9 - 4.2 Å |
| 構造データ | EMDB-22640, PDB-7k22: EMDB-22641, PDB-7k23: EMDB-22642, PDB-7k24: EMDB-22643, PDB-7k25: 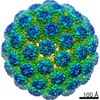 EMDB-22645:  EMDB-22646: |
| 由来 |
|
 キーワード キーワード | VIRAL PROTEIN / polyomavirus / capsomer / VP1 / Fab |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー 構造ビューア
構造ビューア 万見文献について
万見文献について



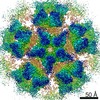
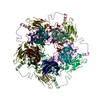
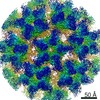


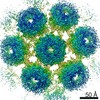


 Murine polyomavirus strain A2 (ウイルス)
Murine polyomavirus strain A2 (ウイルス)