+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8605 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
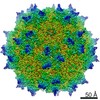
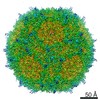
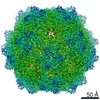
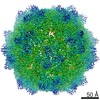
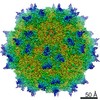
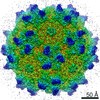
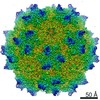
| Title | Human Bocavirus 4 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Human Bocavirus 4 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Human bocavirus 4 / Parvovirus / gastroenteritis / VIRUS LIKE PARTICLE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationphospholipase A2 activity => GO:0004623 / phospholipase A2 activity => GO:0004623 / phospholipase A2 activity / phospholipase A2 / T=1 icosahedral viral capsid / lipid catabolic process / host cell cytoplasm / host cell nucleus / structural molecule activity Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Human bocavirus 4 Human bocavirus 4 | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mietzsch M / Agbandje-McKenna M | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2017 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2017Title: Structural Insights into Human Bocaparvoviruses. Authors: Mario Mietzsch / Shweta Kailasan / Jamie Garrison / Maria Ilyas / Paul Chipman / Kalle Kantola / Mandy E Janssen / John Spear / Duncan Sousa / Robert McKenna / Kevin Brown / Maria Söderlund- ...Authors: Mario Mietzsch / Shweta Kailasan / Jamie Garrison / Maria Ilyas / Paul Chipman / Kalle Kantola / Mandy E Janssen / John Spear / Duncan Sousa / Robert McKenna / Kevin Brown / Maria Söderlund-Venermo / Timothy Baker / Mavis Agbandje-McKenna /    Abstract: Bocaparvoviruses are emerging pathogens of the family. Human bocavirus 1 (HBoV1) causes severe respiratory infections and HBoV2 to HBoV4 cause gastrointestinal infections in young children. Recent ...Bocaparvoviruses are emerging pathogens of the family. Human bocavirus 1 (HBoV1) causes severe respiratory infections and HBoV2 to HBoV4 cause gastrointestinal infections in young children. Recent reports of life-threatening cases, lack of direct treatment or vaccination, and a limited understanding of their disease mechanisms highlight the need to study these pathogens on a molecular and structural level for the development of therapeutics. Toward this end, the capsid structures of HBoV1, HBoV3, and HBoV4 were determined to a resolution of 2.8 to 3.0 Å by cryo-electron microscopy and three-dimensional image reconstruction. The bocaparvovirus capsids, which display different tissue tropisms, have features in common with other parvoviruses, such as depressions at the icosahedral 2-fold symmetry axis and surrounding the 5-fold symmetry axis, protrusions surrounding the 3-fold symmetry axis, and a channel at the 5-fold symmetry axis. However, unlike other parvoviruses, densities extending the 5-fold channel into the capsid interior are conserved among the bocaparvoviruses and are suggestive of a genus-specific function. Additionally, their major viral protein 3 contains loops with variable regions at their apexes conferring capsid surface topologies different from those of other parvoviruses. Structural comparisons at the strain (HBoV) and genus (bovine parvovirus and HBoV) levels identified differences in surface loops that are functionally important in host/tissue tropism, pathogenicity, and antigenicity in other parvoviruses and likely play similar roles in these viruses. This study thus provides a structural framework to characterize determinants of host/tissue tropism, pathogenicity, and antigenicity for the development of antiviral strategies to control human bocavirus infections. Human bocaviruses are one of only a few members of the family pathogenic to humans, especially young children and immunocompromised adults. There are currently no treatments or vaccines for these viruses or the related enteric bocaviruses. This study obtained the first high-resolution structures of three human bocaparvoviruses determined by cryo-reconstruction. HBoV1 infects the respiratory tract, and HBoV3 and HBoV4 infect the gastrointestinal tract, tissues that are likely targeted by the capsid. Comparison of these viruses provides information on conserved bocaparvovirus-specific features and variable regions resulting in unique surface topologies that can serve as guides to characterize HBoV determinants of tissue tropism and antigenicity in future experiments. Based on the comparison to other existing parvovirus capsid structures, this study suggests capsid regions that likely control successful infection, including determinants of receptor attachment, host cell trafficking, and antigenic reactivity. Overall, these observations could impact efforts to design antiviral strategies and vaccines for HBoVs. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8605.map.gz emd_8605.map.gz | 83.7 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8605-v30.xml emd-8605-v30.xml emd-8605.xml emd-8605.xml | 9.9 KB 9.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_8605.png emd_8605.png | 289.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-8605.cif.gz emd-8605.cif.gz | 5.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8605 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8605 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8605 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8605 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_8605_validation.pdf.gz emd_8605_validation.pdf.gz | 546.8 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_8605_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_8605_full_validation.pdf.gz | 546.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_8605_validation.xml.gz emd_8605_validation.xml.gz | 7.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_8605_validation.cif.gz emd_8605_validation.cif.gz | 8.7 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8605 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8605 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8605 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8605 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5us9MC 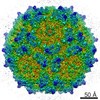 8598C 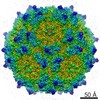 8604C  5urfC  5us7C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8605.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 242.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8605.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 242.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Human Bocavirus 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.95 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human bocavirus 4
| Entire | Name:  Human bocavirus 4 Human bocavirus 4 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human bocavirus 4
| Supramolecule | Name: Human bocavirus 4 / type: virus / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all / NCBI-ID: 645161 / Sci species name: Human bocavirus 4 / Virus type: VIRUS-LIKE PARTICLE / Virus isolate: SEROTYPE / Virus enveloped: No / Virus empty: Yes |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: Capsid protein VP2
| Macromolecule | Name: Capsid protein VP2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 60 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Human bocavirus 4 Human bocavirus 4 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 61.033809 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSENEIQDQQ PSDSMDGQRG GGGGATGSVG GGKGSGVGIS TGGWVGGSYF TDSYVITKNT RQFLVKIQNN HQYKTELISP STSQGKSQR CVSTPWSYFN FNQYSSHFSP QDWQRLTNEY KRFRPKGMHV KIYNLQIKQI LSNGADTTYN NDLTAGVHIF C DGEHAYPN ...String: MSENEIQDQQ PSDSMDGQRG GGGGATGSVG GGKGSGVGIS TGGWVGGSYF TDSYVITKNT RQFLVKIQNN HQYKTELISP STSQGKSQR CVSTPWSYFN FNQYSSHFSP QDWQRLTNEY KRFRPKGMHV KIYNLQIKQI LSNGADTTYN NDLTAGVHIF C DGEHAYPN ATHPWDEDVM PELPYQTWYL FQYGYIPVIH ELAEMEDSNA VEKAICLQIP FFMLENSDHE VLRTGESTEF TF NFDCEWI NNERAYIPPG LMFNPLVPTR RAQYIRRNNN PQTAESTSRI APYAKPTSWM TGPGLLSAQR VGPATSDTGA WMV AVKPEN ASIDTGMSGI GSGFDPPQGS LAPTNLEYKI QWYQTPQGTN NNGNIISNQP LSMLRDQALF RGNQTTYNLC SDVW MFPNQ IWDRYPITRE NPIWCKKPRS DKHTTIDPFD GSLAMDHPPG TIFIKMAKIP VPSNNNADSY LNIYCTGQVS CEIVW EVER YATKNWRPER RHTTFGLGIG GADNLNPTYH VDKNGTYIQP TTWDMCFPVK TNINKVL UniProtKB: Minor capsid protein VP1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: DIRECT ELECTRON DE-20 (5k x 3k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 13394 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: COMMON LINE |
| Final angle assignment | Type: NOT APPLICABLE |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller